Abstract
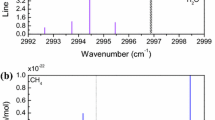
We have developed a compact instrument for sensitive, rapid and continuous measurement of trace gases in air, with results presented here for methane (CH4), nitric oxide (NO), nitrous oxide (N2O) and ammonia (NH3). This instrument takes advantage of recent technology in quantum cascade (QC) lasers and infrared detectors, which allows high sensitivity without cryogenic liquids, e.g., 0.2 ppb (0.2×10-9) of NH3 in air in 1 s. One may substitute a QC laser operating at a different wavelength to measure other gases. The instrument operates continuously, requiring little operator attention, and web-based remote access is provided for instrument control, calibration and data retrieval. The instrument design includes a thermoelectrically (TE) cooled pulsed distributed feedback (DFB) QC laser, a low volume (0.5 l) multipass cell offering 76 m absorption path length and a TE cooled detector. Integrated software for laser control and data analysis using direct absorption provides quantitative trace gas measurements without calibration gases. The instrument may be applied to field measurements of gases of environmental concern.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F.K. Tittel, D. Richter, A. Fried, Top. Appl. Phys. 89, 445 (2003)
J. Faist, F. Capasso, D.L. Sivco, C. Sirtori, A.L. Hutchinson, A.Y. Cho, Science 264, 508 (1994)
J. Faist, A. Tredicucci, F. Capasso, C. Sirtori, D.L. Sivco, J.N. Baillargeon, A.L. Hutchinson, A.Y. Cho, IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-34, 336 (1998)
C. Gmachl, F. Capasso, J. Faist, A.L. Hutchinson, A. Tredicucci, D.L. Sivco, J.N. Baillargeon, S.N.G. Chu, A.Y. Cho, Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 1430 (1998)
D.D. Nelson, J.B. McManus, S. Urbanski, S.C. Herndon, M.S. Zahniser, Spectrochim. Acta A 60, 3325 (2004)
J.B. McManus, D.D. Nelson, S.C. Herndon, J.H. Shorter, M.S. Zahniser, S. Blaser, L. Hvozdara, A. Müller, M. Giovannini, J. Faist, Appl. Phys. B 85, 235 (2006)
D.D. Nelson, J.B. McManus, S.C. Herndon, J. Shorter, M.S. Zahniser, S. Blaser, L. Hvozdara, A. Müller, M. Giovannini, J. Faist, Opt. Lett. 31, 2012 (2006)
J.B. McManus, P.L. Kebabian, M.S. Zahniser, Appl. Opt. 34, 3336 (1995)
J.B. McManus, Appl. Opt. 46, 472 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
PACS
07.57.Ty; 42.62.Fi; 92.70.Cp
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McManus, J., Shorter, J., Nelson, D. et al. Pulsed quantum cascade laser instrument with compact design for rapid, high sensitivity measurements of trace gases in air. Appl. Phys. B 92, 387–392 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-008-3129-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-008-3129-9