Abstract.
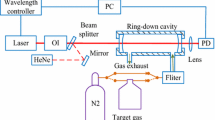
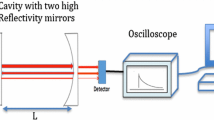
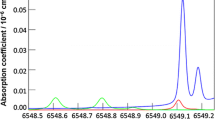
We report the spectroscopic detection of formaldehyde in ambient air using cavity leak-out spectroscopy, a cw variant of cavity ring-down spectroscopy. This technique proved to be suitable for a real-time quantitative analysis of polluted air without any preprocessing of the air sample. Using a tunable CO-overtone sideband laser for the λ=3 μm spectral region and a ring-down cell with R=99.95% mirrors, we achieved a detection limit of 2 parts per billion formaldehyde in ambient air, corresponding to a minimum detectable absorption coefficient of 7×10-9/cm (sampling time: 2 s). Calibration problems arising from the polarity of the molecule and due to HITRAN database uncertainties are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 28 March 2002 / Revised version: 7 June 2002 / Published online: 21 August 2002
RID="*"
ID="*"Corresponding author. Fax: +49-211/811-3121, E-mail: muertz@uni-duesseldorf.de
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dahnke, H., von Basum, G., Kleinermanns, K. et al. Rapid formaldehyde monitoring in ambient air by means of mid-infrared cavity leak-out spectroscopy. Appl Phys B 75, 311–316 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-002-0986-5
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-002-0986-5