Abstract
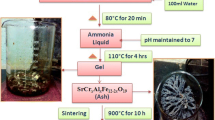
The strontium–aluminium–hexaferrite was substituted with the divalent ions (Mg/Cu) with the chemical formula of Sr1–xMxAl2Fe10O19 (M = Mg, Cu; x = 0.1, 0.2), and all the samples were synthesized via sol–gel auto combustion method. The thermal studies disclosed endothermic and exothermic peaks and showed magnetic phase transition behaviour in the range of 350–450 °C. The particles are shaped in a hexagonal structure with space group P63/mmc and the crystallize size ranges between 44 and 53 nm. The field-emission scanning microscopy revealed the platelet-like morphology of the particles. The magnetic studies disclosed the fine range of magnetic saturation (40.87–49.76 emu/g) and coercivity values (4619–7647 Oe). The particles own single-domain arrangement and decent energy product value (0.32–0.38 MGOe), implying their potential application in permanent magnets. The lower dielectric constant values at high-frequency range suggest their potential employment in microwave applications.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
M.A. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, H. Güngüneş, A.D. Korkmaz, T. Zubar, S. Trukhanov, A. Trukhanov, A. Manikandan, F. Alahmari, A. Baykal, Influence of Dy3+ions on the microstructures and magnetic, electrical, and microwave properties of [Ni0.4Cu0.2Zn0.4](Fe2–xDyx)O4(0.00 ≤ x ≤ 0.04) Spinel Ferrites. ACS Omega 6, 10266–10280 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c00611
M.A. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, A.V. Trukhanov, A. Baykal, H. Gungunes, E.L. Trukhanova, S.V. Trukhanov, V.G. Kostishin, Strong correlation between Dy3+ concentration, structure, magnetic and microwave properties of the [Ni0.5Co0.5](DyxFe2–x)O4 nanosized ferrites. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 90, 251–259 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2020.07.020
R.C. Pullar, Hexagonal ferrites: a review of the synthesis, properties and applications of hexaferrite ceramics. Prog. Mater. Sci. 57, 1191–1334 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2012.04.001
Z. Saeed, B. Azhdar, Influence of high temperature on the crystal structure of SrFe12O19 nanoparticle. J. Nanomater.Nanomater. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5467020
E. Kiani, A.S.H. Rozatian, M.H. Yousefi, Synthesis and characterization of SrFe12O19 nanoparticles produced by a low-temperature solid-state reaction method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24, 2485–2492 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1122-5
K. Kamishima, T. Mashiko, K. Kakizaki, M. Sakai, K. Watanabe, H. Abe, Synthesis and magnetic characterization of Sr-based Ni2X-type hexaferrite. AIP Adv. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4934792
S.P. Dalawai, T.J. Shinde, A.B. Gadkari, N.L. Tarwal, J.H. Jang, P.N. Vasambekar, Influence of Sn4+ on structural and DC electrical resistivity of Ni-Zn ferrite thick films. J. Electron. Mater. 46, 1427–1438 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-5167-0
A.R. Makhdoom, F. Ahmed, U.R. Ghori, Q.A. Ranjha, K.A. Rao, A. Javed, M.E. Mazhar, M. Bukhari, A. Maqsood, S.U. Asif, M.W. Khan, Tuning magnetic properties in the Ce–Al Co-substituted M-type BaSr (6:4) hexaferrites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 33, 7266–7274 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07915-5
K.S. Jithendra Kumara, G. Krishnamurthy, N. Sunil-Kumar, N. Naik, T.M. Praveen, Sustainable synthesis of magnetically separable SiO2/Co@Fe2O4 nanocomposite and its catalytic applications for the benzimidazole synthesis. J. Magn. Magn. Mater.Magn. Magn. Mater. 451, 808–821 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.10.125
M.A. Malana, R.B. Qureshi, M.N. Ashiq, M.F. Ehsan, Synthesis, structural, magnetic and dielectric characterizations of molybdenum doped calcium strontium M-type hexaferrites. Ceram. Int. 42, 2686–2692 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.10.144
A. Morel, J.M. Le Breton, J. Kreisel, G. Wiesinger, F. Kools, P. Tenaud, Sublattice occupation in Sr1-xLaxFe12-xCoxO19 hexagonal ferrite analyzed by Mössbauer spectrometry and Raman spectroscopy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 242–245, 1405–1407 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(01)00962-3
Z.F. Zi, Y.P. Sun, X.B. Zhu, Z.R. Yang, J.M. Dai, W.H. Song, Structural and magnetic properties of SrFe12O19 hexaferrite synthesized by a modified chemical co-precipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 2746–2751 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2008.06.009
M. Naeem, M. Javed, I. Hussain, Structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of Zr–Cd substituted strontium hexaferrite (SrFe12O19) nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 487, 341–345 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.07.140
M. Fu, Z. Zhu, Y. Zhou, W. Xu, W. Chen, Q. Liu, X. Zhu, Multifunctional pompon flower-like nickel ferrites as novel pseudocapacitive electrode materials and advanced absorbing materials. Ceram. Int. 46, 850–856 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.09.042
M.W. Pieper, A. Morel, F. Kools, NMR analysis of La + Co doped M-type ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 242–245, 1408–1410 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(01)00963-5
K. Tanwar, D.S. Gyan, P. Gupta, S. Pandey, D. Kumar, Investigation of crystal structure, microstructure and low temperature magnetic behavior of Ce4+ and Zn2+ co-doped barium hexaferrites (BaFe12O19). RSC Adv. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra02455c
M.A. Almessiere, B. Unal, A. Baykal, I. Ercan, Electrical properties of cerium and yttrium co-substituted strontium nanohexaferrites. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 29, 402–415 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-1010-9
J. Lakshmikantha, G. Krishnamurthy, R. Hanumantha-Nayak, M. Pari, N. Ranjitha, N. Naik, Synthesis, structure, thermal, magnetic, dielectric properties of Ce3+ doped M-type SrFe12O19 and electrochemical determination of L-cysteine. Inorg. Chem. Commun.. Chem. Commun. 146, 110175 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2022.110175
G. Asghar, M. Anis-Ur-Rehman, Structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of Cr-Zn doped strontium hexa-ferrites for high frequency applications. J. Alloys Compd. 526, 85–90 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.02.086
S.M. El-Sayed, T.M. Meaz, M.A. Amer, H.A. El Shersaby, Magnetic behavior and dielectric properties of aluminum substituted M-type barium hexaferrite. Physica B Condens Matter. 426, 137–143 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2013.06.026
A. Lohmaah, K. Chokprasombat, S. Pinitsoontorn, C. Sirisathitkul, Magnetic properties and morphology copper-substituted barium hexaferrites from sol-gel auto-combustion synthesis. Materials 14, 1–8 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195873
S. Asiri, S. Güner, A. Demir, A. Yildiz, A. Manikandan, A. Baykal, Synthesis and magnetic characterization of Cu substituted barium hexaferrites. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 28, 1065–1071 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-017-0735-1
M.A. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, H.S. El Sayed, A. Baykal, Ca2+ and Mg2+ incorporated barium hexaferrites: structural and magnetic properties. J. Solgel. Sci. Technol. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-018-4853-1
A. Davoodi, B. Hashemi, Magnetic properties of Sn-Mg substituted strontium hexaferrite nanoparticles synthesized via coprecipitation method. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 5893–5896 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.03.002
L.A. Trusov, E.A. Gorbachev, V.A. Lebedev, A.E. Sleptsova, I.V. Roslyakov, E.S. Kozlyakova, A.V. Vasiliev, R.E. Dinnebier, M. Jansen, P.E. Kazin, Ca-Al double-substituted strontium hexaferrites with giant coercivity. Chem. Commun. 54, 479–482 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cc08675j
S.N. Rout, M.K. Manglam, J. Mallick, S. Datta, M. Kar, Magnetic anisotropy and (BH)max studies in microwave sintered Al-substituted strontium hexaferrite. Physica B Condens Matter. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2023.415134
H. Luo, B.K. Rai, S.R. Mishra, V.V. Nguyen, J.P. Liu, Physical and magnetic properties of highly aluminum doped strontium ferrite nanoparticles prepared by auto-combustion route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 2602–2608 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.02.106
P. Kumar, A. Gaur, R.K. Kotnala, Magneto-electric response in Pb substituted M-type barium-hexaferrite. Ceram. Int. 43, 1180–1185 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.10.060
M. Ishaque, M.A. Khan, I. Ali, M. Athair, H.M. Khan, M. Asif Iqbal, M.U. Islam, M.F. Warsi, Synthesis of nickel-zinc-yttrium ferrites: Structural elucidation and dielectric behavior evaluation. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process.Semicond. Process. 41, 508–512 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2015.10.028
A. Gupta, P.K. Roy, Effect of Zn2+ ion substitution in Al3+-substituted rare-earth free Sr-hexaferrite for different permanent magnet applications. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 155, 111114 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2023.111114
G. Abbas, L. Zhang, W. Abbas, G. Murtaza, Magnetic and optical properties of Gd-Tl substituted M-type barium hexaferrites synthesized by co-precipitation technique. Curr. Appl. Phys. 19, 506–515 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2019.02.005
V.E. Zhivulin, E.A. Trofimov, O.V. Zaitseva, D.P. Sherstyuk, N.A. Cherkasova, S.V. Taskaev, D.A. Vinnik, Y.A. Alekhina, N.S. Perov, D.I. Tishkevich, T.I. Zubar, A.V. Trukhanov, S.V. Trukhanov, Effect of configurational entropy on phase formation, structure, and magnetic properties of deeply substituted strontium hexaferrites. Ceram. Int. 49, 1069–1084 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.09.082
F.M.M. Pereira, M.R.P. Santos, R.S.T.M. Sohn, J.S. Almeida, A.M.L. Medeiros, M.M. Costa, A.S.B. Sombra, Magnetic and dielectric properties of the M-type barium strontium hexaferrite (Ba xSr1-xFe12O19) in the RF and microwave (MW) frequency range. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 20, 408–417 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-008-9744-8
G.A. Al-garalleh, S.H. Mahmood, I. Bsoul, R. Loloee, Structural and magnetic properties of RE-Al substituted nanocrystalline hexaferrites Structural and magnetic properties of RE-Al substituted nanocrystalline hexaferrites ( Sr 1 − x RE x Al 2 Fe 10 O 19 ), 19 (n.d.) 0–12.
R.D. Shannon, Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. A 32, 751–767 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0567739476001551
G. Sriramulu, N. Maramu, B.R. Reddy, A. Kandasami, S. Katlakunta, Structural, magnetic and electromagnetic properties of microwave-hydrothermally synthesized Sr(Zr-Mn)2xFe12-2xO19 hexaferrites. Mater. Res. Bull. 149, 111732 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2022.111732
G. Lal, K. Punia, H. Bhoi, S.N. Dolia, B.L. Choudhary, P.A. Alvi, S. Dalela, S.K. Barbar, S. Kumar, Exploring the structural, elastic, optical, dielectric and magnetic characteristics of Ca2+ incorporated superparamagnetic Zn0.5−xCa0.1Co0.4+xFe2O4 (x = 0.0, 0.05 & 0.1) nanoferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 886, 161190 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.161190
T. Yener, İ Araz, A. Kırsoy, O. Yalçın, M. Okutan, P. Haring Bolivar, Electromagnetic properties in the structure of Cerium-Copper substituted barium hexaferrite. J. Mol. Struct. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.133752
R.S. Sundari, S. Harish, V. Vijay, M. Shimomura, S. Ponnusamy, J. Archana, M. Navaneethan, Suppression of intrinsic thermal conductivity in Sr1−xGdxTiO3 ceramics via phonon-point defect scattering for enhanced thermoelectric application. RSC Adv. 13, 665–673 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ra04829a
G.A. Alna’washi, A.M. Alsmadi, I. Bsoul, B. Salameh, G.M. Alzoubi, M. Shatnawi, S.M. Hamasha, S.H. Mahmood, Investigation on X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, structural and low temperature magnetic properties of Ni-Ti co-substituted M-type strontium hexaferrites prepared by ball milling technique. Results Phys. 28, 104574 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2021.104574
L.L. Rusevich, E.A. Kotomin, G. Zvejnieks, M.M. Kržmanc, S. Gupta, N. Daneu, J.C.S. Wu, Y.G. Lee, W.Y. Yu, Effects of Al doping on hydrogen production efficiency upon photostimulated water splitting on SrTiO3 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 126, 21223–21233 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.2c05993
T. Xie, C. Liu, L. Xu, J. Yang, W. Zhou, Novel heterojunction Bi2O3/SrFe12O19 magnetic photocatalyst with highly enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 24601–24610 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp408627e
V.K. Mittal, S. Bera, R. Nithya, M.P. Srinivasan, S. Velmurugan, S.V. Narasimhan, Solid state synthesis of Mg-Ni ferrite and characterization by XRD and XPS. J. Nucl. Mater. 335, 302–310 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2004.05.010
Z. Jin, C. Liu, K. Qi, X. Cui, Photo-reduced Cu/CuO nanoclusters on TiO2 nanotube arrays as highly efficient and reusable catalyst. Sci. Rep. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep39695
P.N. Anantharamaiah, H.M. Shashanka, S. Saha, K. Haritha, C.V. Ramana, Aluminum doping and nanostructuring enabled designing of magnetically recoverable hexaferrite catalysts. ACS Omega 7, 6549–6559 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c05548
H. Joshi, A.R. Kumar, Scrutiny and correlations of structural, magnetic, and dielectric properties of M-type strontium hexaferrite (SrFe12O19) for permanent magnet applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 4331–4346 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-05176-8
S. Tiwari, G. Lal, H. Bhoi, K. Punia, S. Singh Meena, S. Kumar, Coexistence of superparamagnetism and superspin glass in non-stoichiometric Zn0.5Ca0.5Fe2O4 nanoferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater.Magn. Magn. Mater. 570, 170466 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2023.170466
G. Lal, K. Punia, S.N. Dolia, P.A. Alvi, S. Dalela, S. Kumar, Rietveld refinement, Raman, optical, dielectric, Mössbauer and magnetic characterization of superparamagnetic fcc-CaFe2O4 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 45, 5837–5847 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.12.050
M.N. Ashiq, R.B. Qureshi, M.A. Malana, M.F. Ehsan, Fabrication, structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of tantalum and potassium doped M-type strontium calcium hexaferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 651, 266–272 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.05.181
C. Sudakar, G.N. Subbanna, T.R.N. Kutty, Wet chemical synthesis of multicomponent hexaferrites by gel-to-crystallite conversion and their magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 263, 253–268 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(02)01572-X
J.M.D. Coey, Permanent magnet applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 248, 441–456 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(02)00335-9
C. de Julián Fernández, C. Sangregorio, J. de la Figuera, B. Belec, D. Makovec, A. Quesada, Progress and prospects of hard hexaferrites for permanent magnet applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/abd272
M.A. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, S.G.J. Van Leusen, A.B.P. Kögerler, Effect of Nb3+ ion substitution on the magnetic properties of SrFe12O19 hexaferrites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 11181–11192 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01464-0
M. Naeem, R. Beenish, M. Aslam, M. Fahad, Fabrication, structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of tantalum and potassium doped M-type strontium calcium hexaferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 651, 266–272 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.05.181
S.V. Trukhanov, T.I. Zubar, V.A. Turchenko, A.V. Trukhanov, T. Kmječ, J. Kohout, L. Matzui, O. Yakovenko, D.A. Vinnik, A.Y. Starikov, V.E. Zhivulin, A.S.B. Sombra, D. Zhou, R.B. Jotania, C. Singh, A.V. Trukhanov, Exploration of crystal structure, magnetic and dielectric properties of titanium-barium hexaferrites. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2021.115345
V.A. Turchenko, S.V. Trukhanov, V.G. evich Kostishin, F. Damay, F. Porcher, D.S. Klygach, M.G. evich Vakhitov, L.Y. evna Matzui, O.S. Yakovenko, B. Bozzo, I. Fina, M.A. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, A. Baykal, D. Zhou, A.V. Trukhanov, Impact of In3+ cations on structure and electromagnetic state of M−type hexaferrites. J. Energy Chem. 69, 667–676 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2021.12.027
M. Lakshmi, K.V. Kumar, K. Thyagarajan, Study of the dielectric behaviour of Cr-doped zinc nano ferrites synthesized by sol-gel method. Adv. Mater. Phys. Chem. 06, 141–148 (2016). https://doi.org/10.4236/ampc.2016.66015
Z. Hu, G.B.G. Stenning, V. Koval, J. Wu, B. Yang, A. Leavesley, R. Wylde, M.J. Reece, C. Jia, H. Yan, Terahertz faraday rotation of SrFe12O19 hexaferrites enhanced by Nb doping. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14, 46738–46747 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c13088
K.M. Batoo, R. Verma, A. Chauhan, R. Kumar, M. Hadi, O.M. Aldossary, Y. Al Douri, Improved room temperature dielectric properties of Gd3+ and Nb5+ co-doped Barium Titanate ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 883, 160836 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.160836
F. Bibi, S. Iqbal, H. Sabeeh, T. Saleem, B. Ahmad, M. Nadeem, I. Shakir, M. Aadil, A. Kalsoom, Evaluation of structural, dielectric, magnetic and photocatalytic properties of Nd and Cu co-doped barium hexaferrite. Ceram. Int. 47, 30911–30921 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.07.274
B. Ahmad, S. Mumtaz, M.F. Ehsan, M. Najam-ul-Haq, A. Shah, M.N. Ashiq, Magnetic and dielectric properties of Nd–Mn substituted Co2Y-hexaferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 460, 171–176 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.04.002
M.M. Costa, G.F.M. Pires Júnior, A.S.B. Sombra, Dielectric and impedance properties’ studies of the of lead doped (PbO)-Co2Y type hexaferrite (Ba2Co2Fe12O22 (Co2Y)). Mater. Chem. Phys. 123, 35–39 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.03.026
T.A. Alrebdi, I. Khalil Yahaya, J. Mohammed, Y.S. Wudil, A. Paray, T. Tchouank Tekoucarol, H.Y. Hafeez, A.K. Srivastava, Phase structure refinement, electric modulus spectroscopy, urbach energy analysis, and magnetic properties of Ce3+–Ni2+-substituted Y-type barium hexaferrites. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 280, 115682 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2022.115682
H. Shakeel, H.M. Khan, I. Ali, K. Ali, M.A. Iqbal, I. Sadiq, G. Murtaza, M.U. Islam, M.N. Ashiq, M. Nadeem, Structural, magnetic and electrical study of rare earth doped Y-type hexaferrites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 6708–6717 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00982-1
K. Lily, K. Kumari, R.N.P. Prasad, Choudhary, impedance spectroscopy of (Na0.5Bi0.5)(Zr0.25Ti0.75)O3 lead-free ceramic. J. Alloys Compd. 453, 325–331 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2006.11.081
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge VIT management for the facilities provided for this work. The authors also would like to convey their gratefulness to all the lab members.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis and investigation, writing—original draft preparation: HJ; writing—review and editing, supervision: ARK.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interest to disclose. The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Joshi, H., Ruban Kumar, A. Magnesium- and copper-substituted strontium–aluminium–hexaferrite (SrAl2Fe10O19): synthesis and scrutiny. Appl. Phys. A 130, 24 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-07170-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-07170-3