Abstract
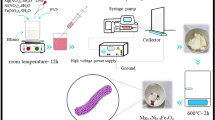
1D CuFe2O4 (CFO) nanostructures were synthesized by sol–gel electrospinning technique, followed by calcination at 600 and 800 °C. The influence of morphology directing templates such as polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) on the structural, optical, magnetic and electrochemical properties was investigated. XRD pattern of the samples confirmed formation of tetragonal CuFe2O4 with extra phases of CuO and Fe2O3. The spinel phase of PVP/CFO was boosted by increasing calcination temperature, contrary to the behavior of PVA/CFO sample which is associated with an increase in impurity phase. The FESEM images revealed that PVP/CFO fibers have a lower average diameter compared to PVA/CFO. Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy indicated that PVA/CFO-800 °C sample has the lowest band gap value. VSM analyses declared that PVP/CFO-800 °C nanofibers have superior saturation magnetization and anisotropy constant. The CV, EIS and GCD measurements of coated nanofibers on Ni foam revealed that PVA/CFO-600 °C has the highest specific capacitance (Cs = 435.5 F g−1 at current density of 1 A g−1) and minimum value of charge transfer resistance (Rct = 13.43 Ω) belongs to the PVP/CFO-800 °C.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.V. Patil, S.S. Mali, A.S. Kamble, Ch.K. Hong, J.H. Kim, P.S. Patil, Electrospinning: A versatile technique for making of 1D growth of nanostructured nanofibers and its applications: an experimental approach. Appl. Surf. Sci. 423, 641–674 (2017)
Z. Bazhan, F. E. Ghodsi, J. Mazloom, Surface morphology, optical, and electrochromic properties of nanostructured nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4) prepared by sol–gel method: effects of Ni/Fe molar ratios, Appl. Phys. A 122 (2016)
B. G. Manju, P. Raji, Biological synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of nickel-doped copper ferrite nanoparticles, Appl. Phys.s A 125 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2619-4
W. Ponhan, S. Maensiri, Fabrication and magnetic properties of electrospun copper ferrite (CuFe2O4) nanofibers. Solid State Sci. 11, 479–484 (2009)
Kh. Roumaih, R.A. Manapov, E.K. Sadykov, A.V. Pyataev, Mssbauer studies of Cu1-xNixFeMnO4 spinel ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 288, 267–275 (2005)
K. Zaharieva, V. Rives, M. Tsvetkov, ZCh. Zhelev, B. Kunev, R. Trujillano, I. Mitov, M. Milanova, Preparation, characterization and application of nanosized copper ferrite photocatalysts for dye degradation under UV irradiation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 160, 271–278 (2015)
Th. Dippong, E.A. Levei, O. Cadar, Recent advances in synthesis and applications of MFe2O4 (M = Co, Cu, Mn, Ni, Zn) nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 11, 1560 (2021)
Y. Liu, H. Zhang, W. Fu, Z. Yang, Z. Li, Characterization of temperature sensitivity of V-modified CuFe2O4 ceramics for NTC thermistors. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 18797–18806 (2018)
M. Talaei, S.A. Hassanzadeh, A.S. Teluri, Synthesis of mesoporous CuFe2O4@SiO2 core-shell nanocomposites for simultaneous drug release and hyperthermia applications, Ceramic Int. 47, 30287–30297 (2021)
Y. Guo, Y. Chen, X. Hu, Y. Yao, Zh. Li, Tween modified CuFe2O4 nanoparticles with enhanced supercapacitor performance, Colloids Surface A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 631 (2021) 127676
Th. Dippong, I. G. Deac, O. Cadar, E. A. Levei, I. Petean, Impact of Cu2+ substitution by Co2+ on the structural and magnetic properties of CuFe2O4 synthesized by sol-gel route, Mater. Characterization 163 (2020) 110248
A. I. Ayesh, M. A. Haij, A. Shaheen, F. Banat, Spinel ferrite nanoparticles for H2S gas sensor, Appl. Phys. A 123 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1305-7
J.M. Liu, Y.H. Lu, Z.F. Xu, R.X. Wang, H.C. Yan, X. Li, Effect of citric acid-to-nitrate ratio on combustion synthesis of CuFe2O4 for sodium-ion storage. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 94–101 (2021)
Y. Sohail, A. Liaquat, A. ul Haq, M. F. Zafar, N. Ul-Haq, Impedance spectroscopy and investigation of conduction mechanism in reduced graphene/CuFe2O4 nanocomposites, Appl. Phys. A 127 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04563-0
Th. Dippong, E.A. Levei, I.G. Deac, E. Neag, O. Cadar, Influence of Cu2+, Ni2+, and Zn2+ Ions Doping on the Structure, Morphology, and Magnetic Properties of Co-Ferrite Embedded in SiO2 Matrix Obtained by an Innovative Sol-Gel Route. Nanomaterials 10, 580 (2020)
Th. Dippong, E. Andrea Levei, O. Cadar, I. G. Deac, M. Lazar, Gh. Borodi, I. Petean, Effect of amorphous SiO2 matrix on structural and magnetic properties of Cu0.6Co0.4Fe2O4/SiO2 nanocomposites, J. Alloys Compounds 849 (2020) 156695
B. G. Manju, P. Raji, Green synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of lime-juice mediated copper–nickel mixed ferrite nanoparticles, Appl. Phys. A 126 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-3313-2
H. Brooks, N. Tucker, Electrospinning predictions using artificial neural networks. Polymer 58, 22–29 (2015)
Y.W. Ju, J.H. Park, H. R. Jung, S. June Cho, W. J. Lee, Electrospun MnFe2O4 nanofibers: Preparation and morphology, Composites Sci. Technol. 68 (2008) 1704–1709
S. Agarwal, J.H. Wendorff, A. Greiner, Use of electrospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer 49, 5603–5621 (2008)
Y. Hong, Electrospun fibrous polyurethane scaffolds in tissue engineering, Adv. Polyurethane Biomater.(2016) 543–559
A. R. Pedrazzo, C. Cecone, S. Morandi, M. Manzoli, P. Bracco, M. Zanetti, Nanosized SnO2 Prepared by Electrospinning: Influence of the Polymer on Both Morphology and Microstructure, Polymers 13, 977 (2021)
K.M. Koczkur, S. Mourdikoudis, L. Polavarapu, S.E. Skrabalak, Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) in nanoparticle synthesis. Dalton Trans 44, 17883–17905 (2015)
J. Wang, L. Ye, Structure and properties of polyvinyl alcohol/polyurethane blends, Composites: Part B 69, 389–396 (2015)
N.V. Hoang, Ch.M. Hung, N.D. Hoa, N.V. Duy, N.V. Hieu, Facile on-chip electrospinning of ZnFe2O4 nanofiber sensors with excellent sensing performance to H2S down ppb level. J. Hazard. Mater. 360, 6–16 (2018)
K.H. Na, W.T. Kim, DCh. Park, H.G. Shin, S.H. Lee, J. Park, T.H. Song, W.Y. Choi, Fabrication and characterization of the magnetic ferrite nanofibers by electrospinning process. Thin Solid Films 660, 358–364 (2018)
A.B. Salunkhe, V.M. Khot, N.D. Thorat, M.R. Phadatare, C.I. Sathish, D.S. Dhawale, S.H. Pawar, Polyvinyl alcohol functionalized cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 264, 598–604 (2013)
M. Rahimi, P. Kameli, M. Ranjbar, H. Salamati, The effect of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) coating on structural, magnetic properties and spin dynamics of Ni0.3Zn0.7Fe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles, J. Magnet. Magnetic Mater. 347, 139–145 (2013)
S. Shafiu, R. Topkaya, A. Baykal, M.S. Toprak, Facile synthesis of PVA–MnFe2O4 nanocomposite: Its magnetic Investigation. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 4066–4071 (2013)
Th. Dippong, E. A. Levei, Ch. L. Lengauer, A. Daniel, D. Toloman, O. Cadar, Investigation of thermal, structural, morphological and photocatalytic properties of CuxCo1-xFe2O4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) nanoparticles embedded in SiO2 matrix, Mater. Characterization 163, 110268 (2020
L. Luo, R. Cui, H. Qiao, K. Chen, Y. Fei, D. Li, Z. Pang, K. Liu, Q, Wei, High lithium electroactivity of electrospun CuFe2O4 nanofibers as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 144, 85–91 (2014)
J. Wang, Ch. Gao, Y. Zhang, Y. Wan, Preparation and in vitro characterization of BC/PVA hydrogel composite for its potential use as artificial cornea biomaterial. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 30, 214–218 (2010)
S. N. Hosseini, M. H. Enayati, F. Karimzad eh, N. M. Sammes, Synthesizing CuFe2O4 Spinel Powders by a Combustion-Like Process for Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Interconnect Coatings, Int. J. Chem. Molecular Nuclear Mater. Metal. Eng. 9, 857–860 (2015)
A. H. Cahyana, A. R. Liandi, Y. Yulizar, Y. Romdoni, T. P. Wendari, Green synthesis of CuFe2O4 nanoparticles mediated by Morus alba L. leaf extract: Crystal structure, grain morphology, particle size, magnetic and catalytic properties in Mannich reaction, Ceramics Int. 47, 21373–21380 (2021)
AKh. Zak, W.H.A. Majid, M.E. Abrishami, R. Yousefi, X-ray analysis of ZnO nanoparticles by Williamsone-Hall and size-strain plot methods. Solid State Sci. 13, 251–256 (2011)
S. Deshpande, S. Patil, S. VNT. Kuchibhatla, S. Seal, Size dependency variation in lattice parameter and valency states in nanocrystalline cerium oxide, Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 133113 (2005)
V. Rathod, A.V. Anupama, R.V. Kumar, V.M. Jali, B. Sahoo, Correlated vibrations of the tetrahedral and octahedral complexes and splitting of the absorption bands in FTIR spectra of Li-Zn ferrites. Vib. Spectrosc. 92, 267–272 (2017)
K. Kombaiah, J.J. Vijaya, L.J. Kennedy, M. Bououdina, B. Al-Najar, Conventional and microwave combustion synthesis of optomagnetic CuFe2O4 nanoparticles for hyperthermia studies. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 115, 162–171 (2018)
S. Phoka, P. Laokul, E. Swatsitang, V. Promarak, S. Seraphin, S. Maensiri, Synthesis, structural and optical properties of CeO2 nanoparticles synthesized by a simple polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) solution route. Mater. Chem. Phys. 115, 423–428 (2009)
J. Zhao, Y. Cheng, X. Yan, D. Sun, F. Zhub, Q. Xue, Magnetic and electrochemical properties of CuFe2O4 hollow fibers fabricated by simple electrospinning and direct annealing. CrystEngComm 14, 5879–5885 (2012)
A.M. EL-Rafeia, A. S. El-Kallinyb, T. A. Gad-Allahb, Electrospun magnetically separable calcium ferrite nanofibers for photocatalytic water purification, J. Magnet. Magnetic Mater. 428, 92–98 (2017)
A.C. Nawle, A.V. Humbe, M.K. Babrekar, S.S. Deshmukh, K.M. Jadhav, Deposition, characterization, magnetic and optical properties of Zn doped CuFe2O4 thin films. J. Alloy. Compd. 695, 1573–1582 (2017)
Z. Bazhan, F.E. Ghodsi, J. Mazloom, Modified voltammetric, impedimetric and optical behavior of polymer-assisted sol-gel MgFe2O4 nanostructured thin films. Electrochim. Acta 250, 143–151 (2017)
K. Ramachandran, S. Chidambaram, B. Baskaran, A. Muthukumarasamy, G.M. Kumar, One pot polyol synthesis of CuO-CuFe2O4 nanocomposites and their structural, optical and electrical property studies. Mater. Lett. 175, 106–109 (2016)
S.S. Selimaa, M. Khairya, M.A. Mousa, Comparative studies on the impact of synthesis methods on structural, optical, magnetic and catalytic properties of CuFe2O4. Ceram. Int. 45, 6535–6540 (2019)
X.G. Zhang, D.L. Guan, C.G. Niu, Zh. Cao, Ch. Liang, N. Tang, L. Zhang, X.J. Wen, G.M. Zeng, Constructing magnetic and high-efficiency AgI/CuFe2O4 photocatalysts for inactivation of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus under visible light: Inactivation performance and mechanism analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 668, 730–742 (2019)
J.C. Tauc, Optical Properties of Solids (North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1972)
A. Manohar, C. Krishnamoorthi, Photocatalytic study and superparamagnetic nature of Zn-doped MgFe2O4 colloidal size nanocrystals prepared by solvothermal reflux method, J. Photochem. Photobiol. B: Biol. 173, 456–465 (2017)
P. Laokul, V. Amornkitbamrung, S. Seraphin, S. Maensiri, Characterization and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline CuFe2O4, NiFe2O4, ZnFe2O4 powders prepared by the Aloe vera extract solution. Curr. Appl. Phys. 11, 101–108 (2011)
G.F. Goya, H.R. Rechenberg, J.Z. Jiang, Structural and magnetic properties of ball milled copper ferrite. J. Appl. Phys. 84, 1101–1108 (1998)
L. Frolova, O, Khmelenko, Investigation of the magnetic properties of ferrites in the CoO-NiO-ZnO using simplex-lattice design, J. Nanomater. Article ID 5686741, 8 pages (2018)
T.G. Altincekic, I. Boza, A. Baykal, S. Kazan, R. Topkaya, M.S. Toprak, Synthesis and characterization of CuFe2O4 nanorods synthesized by polyol route. J. Alloy. Compd. 493, 493–498 (2010)
B. J. Rani, B. Saravanakumar, G. Ravi1, V. Ganesh, S. Ravichandran, R. Yuvakkumar, Structural, optical and magnetic properties of CuFe2O4 Nanoparticles, J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 1975–1984 (2018)
R.S. Yadav, I. Kuritka, J. Vilcakova, J. Havlica, J. Masilko, L. Kalina, J. Tkacz, M. Hajduchova, V. Enev, Structural, dielectric, electrical and magnetic properties of CuFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by honey mediated sol–gel combustion method and annealing effect. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 6245–6261 (2017)
M. Bałanda, R. Pełka, Magnetism (Chapter 1). In: B. Sieklucka, D. Pinkowicz (editors) Molecular Magnetic Materials: Concepts and Applications. Wiley‐VCH, New York, pp 1–28 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527694228.ch1
M.M. Rashad, R.M. Mohamed, M.A. Ibrahim, L.F.M. Ismail, E.A. Abdel-Aal, Magnetic and catalytic properties of cubic copper ferrite nanopowders synthesized from secondary resources. Adv. Powder Technol. 23, 315–323 (2012)
M.A. Gabal, Structural and magnetic properties of nano-sized Cu–Cr ferrites prepared through a simple method using egg white. Mater. Lett. 64, 1887–1890 (2010)
M. Abdullah Dar, J. Shah, W. A. Siddiqui, R. K. Kotnala, Study of structure and magnetic properties of Ni–Zn ferrite nano-particles synthesized via co-precipitation and reverse micro-emulsion technique, Appl Nanosci. 4, 675–682 (2014)
J. Xiang, Y. Chu, X. Shen, G. Zhou, Y. Guo, Electrospinning preparation, characterization and magnetic properties of cobalt–nickel ferrite (Co1-xNixFe2O4) nanofibers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 376, 57–61 (2012)
H. Gao, J. Xiang, Y. Cao, Hierarchically porous CoFe2O4 nanosheets supported on Ni foam with excellent electrochemical properties for asymmetric supercapacitors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 413, 351–359 (2017)
S. Nilmoung, T. Sinprachim, I. Kotutha, P. Kidkhunthod, R. Yimnirun, S. Rujirawat, S. Maensiri, Electrospun carbon/CuFe2O4 composite nanofibers with improved electrochemical energy storage performance. J. Alloy. Compd. 688, 1131–1140 (2016)
B. Saravanakumar, S.P. Ramacahndran, G. Ravi, V. Ganesh, Ramesh K. Guduru, R. Yuvakkumar, Electrochemical performances of monodispersed spherical CuFe2O4 nanoparticles for pseudocapacitive applications, Vacuum 168, 108798 (2019)
D. Hama, J. Chang, S.H. Pathan, W.Y. Kim, R.S. Mane, B.N. Pawar, OSh. Joo, H. Chung, M.Y. Yoon, S.H. Han, Electrochemical capacitive properties of spray-pyrolyzed copper-ferrite thin films. Curr. Appl. Phys. 9, 98–100 (2009)
B. Bhujun, M.T. Tan, A.S. Shanmugam, Study of mixed ternary transition metal ferrites as potential electrodes for supercapacitor applications. Results in Physics 7, 345–353 (2017)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the University of Guilan Research Council for the support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Safartoobi, A., Mazloom, J. & Ghodsi, F.E. Electrochemical and optical properties of magnetic CuFe2O4 nanofibers grown by PVP and PVA-assisted sol–gel electrospinning. Appl. Phys. A 128, 13 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05162-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05162-9