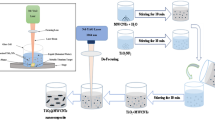
Abstract
Pulsed laser ablation in liquid technique (PLAL) had started getting attention in late 1990, particularly for the production of the nanomaterials due to its easy handling and room-temperature synthesis process. Soon after the initial demonstration of nanomaterials generation from the PLAL technique, PLAL gradually becomes a green, facile and inexpensive method for the generation of ultrapure carbon nanomaterials (CNMs). In the past two decades, different allotropic forms of CNMs have been fabricated by using PLAL techniques such as graphene/graphene oxide nanosheet, carbon nanotubes, graphene oxide quantum dots, nanodiamonds, carbogenic nanoparticles, polyynes and carbon-encapsulated metal-based nanoparticles. In this review article, we offer a comprehensive discussion on the progress achieved in the design and development of the PLAL method for the production of CNMs only (the year 1998–2020). Firstly, we have introduced the different types of PLAL methods widely used for CNMs fabrication. Secondly, the different types of factors affecting the physicochemical (structural, morphological, optical) properties of CNMs and the efficiency of CNMs production from PLAL method have been summarized in detail. The laser parameters and experimental conditions of the PLAL method, that affecting the physicochemical properties and efficiency of CNMs production are laser wavelengths, pulse duration and repetition rate, ablation duration, per-pulse energy density (fluence), PLAL setup design and nature of solvents. The results from different spectroscopic techniques for each kind of CNMs have been discussed thoroughly, to unambiguously differentiate the structural integrity of the CNMs from one another. Finally, the uses of CNMs for different applications in the present time, existing challenges in the PLAL methods and the future outlook of laser-assisted synthesized CNMs for novel applications were also discussed.


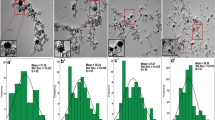
source and d ultrasonication bath treatment




Reproduced with permission from Elsevier, License No. 5026361316347) [115]

Reproduced with permission from Elsevier, License No. 5026370382265) [114]

Reproduced with permission from Elsevier, License No. 5026370731138) [117]



Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Georgakilas, J.A. Perman, J. Tucek, R. Zboril, Broad family of carbon nanoallotropes: Classification, chemistry, and applications of fullerenes, carbon dots, nanotubes, graphene, nanodiamonds, and combined superstructures. Chem. Rev. 115, 4744–4822 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500304f
I.V. Grigorieva, A.A. Firsov, K.S. Novoselov, A.K. Geim, S.V. Morozov, D. Jiang, Y. Zhang, S.V. Dubonos, Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Nat. Mater. 306, 666–669 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1102896
S. Lijima, Helical microtubles of graphitic carbon. Nature 354, 56–58 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1038/354056a0
S. Iijima, T. Ichihashi, Single-shell carbon nanotubes of 1-nm diameter. Nature 363, 603–605 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/363603a0
R.F. Curl, R.E. Smalley, H.W. Kroto, J.R. Heath, S.C. O’Brien, C60: Buckminsterfullerene. Nature 318, 162–163 (1985)
W. Krätschmer, L.D. Lamb, K. Fostiropoulos, D.R. Huffman, Solid C60: a new form of carbon. Nature 347, 354–358 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1038/347354a0
X. Xu, R. Ray, Y. Gu, H.J. Ploehn, L. Gearheart, K. Raker, W.A. Scrivens, Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 12736–12737 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja040082h
C. Doñate-Buendía, M. Fernández-Alonso, Pulsed laser ablation in liquids for the production of gold nanoparticles and carbon quantum dots : From plasmonic to fluorescence and cell labelling Pulsed laser ablation in liquids for the production of gold nanoparticles and carbon quantum dots : from. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1537, 012013–012018 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1537/1/012013
D. Zhang, C. Zhang, J. Liu, Q. Chen, X. Zhu, C. Liang, Carbon-encapsulated metal/metal carbide/metal oxide core-shell nanostructures generated by laser ablation of metals in organic solvents. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2, 28–39 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.8b01541
R.L. Calabro, D.S. Yang, D.Y. Kim, Liquid-phase laser ablation synthesis of graphene quantum dots from carbon nano-onions: Comparison with chemical oxidation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 527, 132–140 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.04.113
E.A. Ganash, G.A. Al-Jabarti, R.M. Altuwirqi, The synthesis of carbon-based nanomaterials by pulsed laser ablation in water. Mater. Res. Express. 7, 015002–015012 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab572b
A. Reina, X. Jia, J. Ho, D. Nezich, H. Son, V. Bulovic, M.S. Dresselhaus, J. Kong, Large Area, few-layer graphene films on arbitrary substrates by chemical vapor deposition. Nano Lett. 9, 30–35 (2008)
R.B. Kaner, L.M. Viculis, J.J. Mack, A chemical route to carbon nanoscrolls. Science 299, 1361 (2003)
Y. Ando, X. Zhao, Synthesis of carbon nanotubes by arc-discharge method. New Diam. Front. Carbon Technol. 16, 123–137 (2006)
J. Prasek, J. Drbohlavova, J. Chomoucka, J. Hubalek, O. Jasek, V. Adam, R. Kizek, Methods for carbon nanotubes synthesis: Review. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 15872–15884 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/c1jm12254a
A.M. Cassell, J.A. Raymakers, J. Kong, H. Dai, Large scale CVD synthesis of single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. B. 103, 6484–6492 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp990957s
M. Escobar, M.S. Moreno, R.J. Candal, M.C. Marchi, A. Caso, P.I. Polosecki, G.H. Rubiolo, S. Goyanes, Synthesis of carbon nanotubes by CVD: Effect of acetylene pressure on nanotubes characteristics. Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 251–256 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.07.044
J. Chrzanowska, J. Hoffman, A. Małolepszy, M. Mazurkiewicz, T.A. Kowalewski, Z. Szymanski, L. Stobinski, Synthesis of carbon nanotubes by the laser ablation method: Effect of laser wavelength. Phys. Status Solidi. 252, 1860–1867 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.201451614
R.A. Ismail, M.H. Mohsin, A.K. Ali, K.I. Hassoon, S. Erten-Ela, Preparation and characterization of carbon nanotubes by pulsed laser ablation in water for optoelectronic application. Phys. E Low-Dimensional Syst. Nanostructures. 119, 113997–114004 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2020.113997
D.P. Yu, X.S. Sun, C.S. Lee, I. Bello, S.T. Lee, H.D. Gu, K.M. Leung, G.W. Zhou, Z.F. Dong, Z. Zhang, Synthesis of boron nitride nanotubes by means of excimer laser ablation at high temperature. Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 1966–1968 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.121236
D. Amans, A.C. Chenus, G. Ledoux, C. Dujardin, C. Reynaud, O. Sublemontier, K. Masenelli-Varlot, O. Guillois, Nanodiamond synthesis by pulsed laser ablation in liquids. Diam. Relat. Mater. 18, 177–180 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2008.10.035
E.A. Ekimov, K.M. Kondrina, N.E. Mordvinova, O.I. Lebedev, D.G. Pasternak, I.I. Vlasov, High-pressure, high-temperature synthesis of nanodiamond from adamantane. Inorg. Mater. 55, 437–442 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168519050042
S. Gottlieb, N. Wöhrl, S. Schulz, V. Buck, Simultaneous synthesis of nanodiamonds and graphene via plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (MW PE-CVD) on copper. Springerplus 5, 568–584 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-2201-x
B.P. Tolochko, V.M. Titov, A.P. Chernyshev, K.A. Ten, E.R. Pruuel, I.L. Zhogin, P.I. Zubkov, N.Z. Lyakhov, L.A. Lukyanchikov, M.A. Sheromov, Physical-chemical model of processes at detonation synthesis of nanodiamonds. Diam. Relat. Mater. 16, 2014–2017 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2007.09.002
G.N. Churilov, Synthesis of fullerenes and other nanomaterials in arc discharge. Fullerenes Nanotub. Carbon Nanostructures. 16, 395–403 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1080/15363830802281641
J. Guo, X. Wang, Y. Yao, X. Yang, X. Liu, B. Xu, Structure of nanocarbons prepared by arc discharge in water. Mater. Chem. Phys. 105, 175–178 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2007.04.022
G.K. Yogesh, E.P. Shuaib, P. Roopmani, M.B. Gumpu, U.M. Krishnan, D. Sastikumar, Synthesis, characterization and bioimaging application of laser-ablated graphene-oxide nanoparticles (nGOs). Diam. Relat. Mater. 104, 107733–107746 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2020.107733
P. Russo, R. Liang, E. Jabari, E. Marzbanrad, E. Toyserkani, Y.N. Zhou, Single-step synthesis of graphene quantum dots by femtosecond laser ablation of graphene oxide dispersions. Nanoscale 8, 8863–8877 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6nr01148a
S.Z. Mortazavi, P. Parvin, A. Reyhani, Fabrication of graphene based on Q-switched Nd:YAG laser ablation of graphite target in liquid nitrogen. Laser Phys. Lett. 9, 547–552 (2012). https://doi.org/10.7452/lapl.201210033
A. Al-Hamaoy, E. Chikarakara, H. Jawad, K. Gupta, D. Kumar, M.S.R. Rao, S. Krishnamurthy, M. Morshed, E. Fox, D. Brougham, X. He, M. Vázquez, D. Brabazon, Liquid phase - pulsed laser ablation: A route to fabricate different carbon nanostructures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 302, 141–144 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.09.102
J. Sun, S.L. Hu, X.W. Du, Y.W. Lei, L. Jiang, Ultrafine diamond synthesized by long-pulse-width laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 1–4 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2385210
J.R. Heath, Q. Zhang, S.C. O’brien, R.F. Curl, H.W. Kroto, R.E. Smalley, The formation of long carbon chain molecules during laser vaporization of graphite. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 109, 359–363 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00236a012
M. Tsuji, S. Kuboyama, T. Matsuzaki, T. Tsuji, Formation of hydrogen-capped polyynes by laser ablation of C60 particles suspended in solution. Carbon N. Y. 41, 2141–2148 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(03)00241-0
S.B. Ogale, P.P. Patil, D.M. Phase, Y.V. Bhandarkar, S.K. Kulkarni, S. Kulkarni, S.V. Ghaisas, S.M. Kanetkar, V.G. Bhide, S. Guha, Synthesis of metastable phases via pulsed-laser-induced reactive quenching at liquid-solid interfaces. Phys. Rev. B. 36, 8237–8250 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.36.8237
S.B.O.P.P. Patil, D.M. Phase, S.A. Kulkarni, S.V. Ghaisas, S.K. Kulkarni, S.M. Kanetkar, Pulsed-laser-induced reactive quenching at a liquid-solid interface: Aqueous oxidation of iron. Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 237–241 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.58.238
A. Fojtik, A. Henglein, Laser ablation of films and suspended particles in a solvent: Formation of cluster and colloid solutions. Berichte Der Bunsen-Gesellschaft. 97, 252–254 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2013.2259225
Y. Guo-Wei, W. Jin-Bin, L. Qui-Xiang, Preparation of nano-crystalline diamonds using pulsed laser induced reactive quenching. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 10, 7923–7927 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/10/35/024
D. Amans, W. Cai, S. Barcikowski, Status and demand of research to bring laser generation of nanoparticles in liquids to maturity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 488, 445–454 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.05.117
D. Amans, M. Diouf, J. Lam, G. Ledoux, C. Dujardin, Origin of the nano-carbon allotropes in pulsed laser ablation in liquids synthesis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 489, 114–125 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.08.017
C. Liang, Y. Shimizu, T. Sasaki, N. Koshizaki, Synthesis, characterization, and phase stability of ultrafine TiO2 nanoparticles by pulsed laser ablation in liquid media. J. Mater. Res. 19, 1551–1557 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2004.0208
V. Amendola, M. Meneghetti, What controls the composition and the structure of nanomaterials generated by laser ablation in liquid solution? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, 3027–3046 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cp42895d
V. Amendola, P. Riello, M. Meneghetti, Magnetic nanoparticles of iron carbide, iron oxide, iron@iron oxide, and metal iron synthesized by laser ablation in organic solvents. J. Phys. Chem. C. 115, 5140–5146 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp109371m
V. Amendola, I.D. Amans, Y. Ishikawa, N. Koshizaki, S. Scirè, G. Compagnini, S. Reichenberger, Room-temperature laser synthesis in liquid of oxide, metal-oxide core-shells and doped oxide nanoparticles. Chemistry 26, 9206–9242 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.202000686
S. Kang, K.H. Jung, S. Mhin, Y. Son, K. Lee, W.R. Kim, H. Choi, J.H. Ryu, H. Han, K.M. Kim, Fundamental understanding of the formation mechanism for graphene quantum dots fabricated by pulsed laser fragmentation in liquid: Experimental and theoretical insight. Small 16, 1–9 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202003538
S.C. Ray, A. Saha, N.R. Jana, R. Sarkar, Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and bioimaging application. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 18546–18551 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp905912n
L. Han, D. Ghosh, W. Chen, S. Pradhan, X. Chang, S. Chen, Nanosized carbon particles from natural gas soot. Chem. Mater. 21, 2803–2809 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm900709w
Z.-A. Qiao, Y. Wang, Y. Gao, H. Li, T. Dai, Y. Liu, Commercially activated carbon as the source for producing multicolor photoluminescent carbon dots by chemical oxidation. Chem. Commun. 46, 8812–8814 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cc02724c
Y. Dong, N. Zhou, X. Lin, J. Lin, Y. Chi, G. Chen, Extraction of electrochemiluminescent oxidized carbon quantum dots from activated carbon. Chem. Mater. 22, 5895–5899 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm1018844
H. Peng, J. Travas-Sejdic, Simple aqueous solution route to luminescent carbogenic dots from carbohydrates. Chem. Mater. 21, 5563–5565 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm901593y
L. Shen, L. Zhang, M. Chen, X. Chen, J. Wang, The production of pH-sensitive photoluminescent carbon nanoparticles by the carbonization of polyethylenimine and their use for bioimaging. Carbon N. Y. 55, 343–349 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2012.12.074
M. Qian, Y.S. Zhou, Y. Gao, J.B. Park, T. Feng, S.M. Huang, Z. Sun, L. Jiang, Y.F. Lu, Formation of graphene sheets through laser exfoliation of highly ordered pyrolytic graphite. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 173108–173011 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3584021
T. Guo, P. Nikolaev, A. Thess, D.T. Colbert, R.E. Smalley, Catalytic growth of single-walled manotubes by laser vaporization. Chem. Phys. Lett. 243, 49–54 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2614(95)00825-O
J. Zhou, C. Booker, R. Li, X. Zhou, T.K. Sham, X. Sun, Z. Ding, An electrochemical avenue to blue luminescent nanocrystals from multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 744–745 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0669070
D.B. Shinde, V.K. Pillai, Electrochemical preparation of luminescent graphene quantum dots from multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Chem. A Eur. J. 18, 12522–12528 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201201043
L. Bao, Z.L. Zhang, Z.Q. Tian, L. Zhang, C. Liu, Y. Lin, B. Qi, D.W. Pang, Electrochemical tuning of luminescent carbon nanodots: From preparation to luminescence mechanism. Adv. Mater. 23, 5801–5806 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201102866
S. Chandra, P. Das, S. Bag, D. Laha, P. Pramanik, Synthesis, functionalization and bioimaging applications of highly fluorescent carbon nanoparticles. Nanoscale 3, 1533–1540 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/c0nr00735h
T.N.J.I. Edison, R. Atchudan, M.G. Sethuraman, J.J. Shim, Y.R. Lee, Microwave assisted green synthesis of fluorescent N-doped carbon dots: Cytotoxicity and bio-imaging applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 161, 154–161 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.05.017
H. Zhu, X. Wang, Y. Li, Z. Wang, F. Yang, X. Yang, Microwave synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanoparticles with electrochemiluminescence properties. Chem. Commun. 34, 5118–5120 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1039/b907612c
L. Zhu, Y. Yin, C.F. Wang, S. Chen, Plant leaf-derived fluorescent carbon dots for sensing, patterning and coding. J. Mater. Chem. C. 1, 4925–4932 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tc30701h
R. Atchudan, T.N.J.I. Edison, M.G. Sethuraman, Y.R. Lee, Efficient synthesis of highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots for cell imaging using unripe fruit extract of Prunus mume. Appl. Surf. Sci. 384, 432–441 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.05.054
W. Lu, X. Qin, S. Liu, G. Chang, Y. Zhang, Y. Luo, A.M. Asiri, A.O. Al-Youbi, X. Sun, Economical, green synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanoparticles and their use as probes for sensitive and selective detection of mercury(II) ions. Anal. Chem. 84, 5351–5357 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/ac3007939
N. Papaioannou, A. Marinovic, N. Yoshizawa, A.E. Goode, M. Fay, A. Khlobystov, M.M. Titirici, A. Sapelkin, Structure and solvents effects on the optical properties of sugar-derived carbon nanodots. Sci. Rep. 8, 1–10 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-25012-8
J. Yu, N. Song, Y.K. Zhang, S.X. Zhong, A.J. Wang, J. Chen, Green preparation of carbon dots by Jinhua bergamot for sensitive and selective fluorescent detection of Hg2+ and Fe3+. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 214, 29–35 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.03.006
X. Zheng, H. Wang, Q. Gong, L. Zhang, G. Cui, Q. Li, L. Chen, F. Wu, S. Wang, Highly luminescent carbon nanoparticles as yellow emission conversion phosphors. Mater. Lett. 143, 290–293 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.12.138
H. Li, X. He, Y. Liu, H. Huang, S. Lian, S.T. Lee, Z. Kang, One-step ultrasonic synthesis of water-soluble carbon nanoparticles with excellent photoluminescent properties. Carbon N. Y. 49, 605–609 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2010.10.004
Z. Ma, H. Ming, H. Huang, Y. Liu, Z. Kang, One-step ultrasonic synthesis of fluorescent N-doped carbon dots from glucose and their visible-light sensitive photocatalytic ability. New J. Chem. 36, 861–864 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2nj20942j
E. Fazio, B. Gökce, A. De Giacomo, M. Meneghetti, G. Compagnini, M. Tommasini, F. Waag, A. Lucotti, C.G. Zanchi, P.M. Ossi, M. Dell’aglio, L. D’urso, M. Condorelli, V. Scardaci, F. Biscaglia, L. Litti, M. Gobbo, G. Gallo, M. Santoro, S. Trusso, F. Neri, Nanoparticles engineering by pulsed laser ablation in liquids: Concepts and applications. Nanomaterials 10, 1–50 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112317
J. Xiao, P. Liu, C.X. Wang, G.W. Yang, External field-assisted laser ablation in liquid: An efficient strategy for nanocrystal synthesis and nanostructure assembly. Prog. Mater. Sci. 87, 140–220 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2017.02.004
D. Zhang, B. Gökce, S. Barcikowski, Laser synthesis and processing of colloids: Fundamentals and applications. Chem. Rev. 117, 3990–4103 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00468
D. Zhang, Z. Li, K. Sugioka, Laser ablation in liquids for nanomaterial synthesis: diversities of targets and liquids. J. Phys. Photonics. 3, 042002–104072 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/2515-7647/ac0bfd
Z. Yan, D.B. Chrisey, Pulsed laser ablation in liquid for micro-/nanostructure generation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 13, 204–223 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2012.04.004
R.C. Forsythe, C.P. Cox, M.K. Wilsey, A.M. Müller, Pulsed laser in liquids made nanomaterials for catalysis. Chem. Rev. 121, 7568–7637 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c01069
H. Zeng, X.W. Du, S.C. Singh, S.A. Kulinich, S. Yang, J. He, W. Cai, Nanomaterials via laser ablation/irradiation in liquid: A review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 22, 1333–1353 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201102295
G.W. Yang, Laser ablation in liquids : Applications in the synthesis of nanocrystals. Prog. Matter. Sci. 52, 648–698 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2006.10.016
A. Pyatenko, H. Wang, N. Koshizaki, T. Tsuji, Mechanism of pulse laser interaction with colloidal nanoparticles. Laser Photon. Rev. 7, 596–604 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/lpor.201300013
V. Amendola, D. Amans, Y. Ishikawa, N. Koshizaki, S. Scirè, G. Compagnini, S. Reichenberger, S. Barcikowski, Room-temperature laser synthesis in liquid of oxide, metal-oxide core-shells and doped oxide nanoparticles. Chem. A Eur. J. 26, 9206–9242 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.202000686
S.R.J. Pearce, S.J. Henley, F. Claeyssens, P.W. May, K.R. Hallam, J.A. Smith, K.N. Rosser, Production of nanocrystalline diamond by laser ablation at the solid/liquid interface. Diam. Relat. Mater. 13, 661–665 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2003.08.027
L. Yang, P.W. May, L. Yin, J.A. Smith, K.N. Rosser, Growth of diamond nanocrystals by pulsed laser ablation of graphite in liquid. Diam. Relat. Mater. 16, 725–729 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2006.11.010
Y.P. Sun, B. Zhou, Y. Lin, W. Wang, K.A.S. Fernando, P. Pathak, M.J. Meziani, B.A. Harruff, X. Wang, H. Wang, P.G. Luo, H. Yang, M.E. Kose, B. Chen, L.M. Veca, S.Y. Xie, Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 7756–7757 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja062677d
I.M. Masaharu Tsuji, T. Tsuji, S. Kuboyama, S.-H. Yoon, Y. Korai, T. Tsujimoto, K. Kubo, A. Mori, Formation of hydrogen-capped polyynes by laser ablation of graphite particles suspended in solution. Chem. Phys. Lett. 355, 101–108 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(03)00241-0
A. Małolepszy, S. Błonski, J. Chrzanowska-Giżyńska, M. Wojasiński, T. Płocinski, L. Stobinski, Z. Szymanski, Fluorescent carbon and graphene oxide nanoparticles synthesized by the laser ablation in liquid. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 124, 1–7 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1711-5
J. Zhang, Z. Gan, G. Hu, Y. Tang, L. Zhou, Q. Jiang, Y. Cui, The luminescent carbon nanoparticles with controllable oxygen-related functional groups prepared by pulsed laser ablation in water. Mod. Phys. Lett. B. 30, 3–6 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217984916503206
C. Doñate-Buendia, R. Torres-Mendieta, A. Pyatenko, E. Falomir, M. Fernández-Alonso, G. Mínguez-Vega, Fabrication by laser irradiation in a continuous flow jet of carbon quantum dots for fluorescence imaging. ACS Omega 3, 2735–2742 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.7b02082
L. Franzel, M.F. Bertino, Z.J. Huba, E.E. Carpenter, Synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles by pulsed laser ablation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 261, 332–336 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.08.010
T.N. Lin, K.H. Chih, C.T. Yuan, J.L. Shen, C.A.J. Lin, W.R. Liu, Laser-ablation production of graphene oxide nanostructures: From ribbons to quantum dots. Nanoscale 7, 2708–2715 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr05737f
S.L. Hu, K.Y. Niu, J. Sun, J. Yang, N.Q. Zhao, X.W. Du, One-step synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanoparticles by laser irradiation. J. Mater. Chem. 19, 484–488 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1039/b812943f
H. Yu, X. Li, X. Zeng, Y. Lu, Preparation of carbon dots by non-focusing pulsed laser irradiation in toluene. Chem. Commun. 52, 819–822 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cc08384b
C. Doñate-Buendía, M. Fernández-Alonso, J. Lancis, G. Mínguez-Vega, Overcoming the barrier of nanoparticle production by femtosecond laser ablation in liquids using simultaneous spatial and temporal focusing. Photonics Res. 7, 1249 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1364/prj.7.001249
J.S. Hoppius, S. Maragkaki, A. Kanitz, P. Gregorčič, E.L. Gurevich, Optimization of femtosecond laser processing in liquids. Appl. Surf. Sci. 467–468, 255–260 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.10.121
A. Menéndez-Manjón, P. Wagener, S. Barcikowski, Transfer-matrix method for efficient ablation by pulsed laser ablation and nanoparticle generation in liquids. J. Phys. Chem. C. 115, 5108–5114 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp109370q
C.D.-B. Tim Hupfeld, A. Sommereyns, F. Riahi, B. Gokce, S.B. Stan Gann, Michael schmidt, analysis of the nanoparticle dispersion and its E ect on the crystalline microstructure in carbon-additivated PA12 feedstock material for laser powder bed fusion. Materials (Basel) 13, 3312–3329 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153312
S.Z. Mortazavi, P. Parvin, A. Reyhani, S. Mirershadi, R. Sadighi-Bonabi, Generation of various carbon nanostructures in water using IR/UV laser ablation. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 46, 165303–165311 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/46/16/165303
P. Russo, A. Hu, G. Compagnini, W.W. Duley, N.Y. Zhou, Femtosecond laser ablation of highly oriented pyrolytic graphite: A green route for large-scale production of porous graphene and graphene quantum dots. Nanoscale 6, 2381–2389 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nr05572h
E. Perevedentseva, D. Peer, V. Uvarov, B. Zousman, O. Levinson, Nanodiamonds of laser synthesis for biomedical applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 15, 1045–1052 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2015.9747
D. Reyes-Contreras, M. Camacho-López, M.A. Camacho-López, S. Camacho-López, R.I. Rodríguez-Beltrán, M. Mayorga-Rojas, Influence of the per pulse laser fluence on the optical properties of carbon nanoparticles synthesized by laser ablation of solids in liquids. Opt. Laser Technol. 74, 48–52 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2015.05.010
N. Tarasenka, A. Stupak, N. Tarasenko, S. Chakrabarti, D. Mariotti, Structure and optical properties of carbon nanoparticles generated by laser treatment of graphite in liquids. ChemPhysChem 18, 1074–1083 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.201601182
A.K. Narasimhan, S.B. Lakshmi, T.S. Santra, M.S.R. Rao, G. Krishnamurthi, Oxygenated graphene quantum dots (GQDs) synthesized using laser ablation for long-term real-time tracking and imaging. RSC Adv. 7, 53822–53829 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra10702a
L. Escobar-Alarcón, M.E. Espinosa-Pesqueira, D.A. Solis-Casados, J. Gonzalo, J. Solis, M. Martinez-Orts, E. Haro-Poniatowski, Two-dimensional carbon nanostructures obtained by laser ablation in liquid: effect of an ultrasonic field. Appl. Phys. A. 124, 141–148 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1559-8
G.R. Kiran, B. Chandu, S.G. Acharyya, S.V. Rao, V.V.S.S. Srikanth, One-step synthesis of bulk quantities of graphene from graphite by femtosecond laser ablation under ambient conditions. Philos. Mag. Lett. 97, 229–234 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/09500839.2017.1320437
L. Basso, F. Gorrini, N. Bazzanella, M. Cazzanelli, C. Dorigoni, A. Bifone, A. Miotello, The modeling and synthesis of nanodiamonds by laser ablation of graphite and diamond-like carbon in liquid-confined ambient. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 124, 72–78 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1491-3
E. Perevedentseva, Y. Lin, C. Song, Z. Lin, C. Chang, C. Cheng, E. Perevedentseva, A. Karmenyan, Y. Lin, C. Song, Z. Lin, C. Chang, S. Norina, V. Bessalova, N. Perov, O. Levinson, B. Zousman, Multifunctional biomedical applications of magnetic nanodiamond. J. Biomed. Opt. 23, 091404–091413 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.jbo.23.9.091404
L. Basso, N. Bazzanella, M. Cazzanelli, A. Miotello, On the route towards a facile fluorescent nanodiamonds laser-synthesis. Carbon N. Y. 153, 148–155 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.07.025
L. Basso, M. Sacco, N. Bazzanella, M. Cazzanelli, A. Barge, M. Orlandi, A. Bifone, A. Miotello, Laser-synthesis of NV-centers-enriched nanodiamonds: Effect of different nitrogen sources. Micromachines 11, 1–13 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/MI11060579
S. Hu, F. Tian, P. Bai, S. Cao, J. Sun, J. Yang, Synthesis and luminescence of nanodiamonds from carbon black. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 157, 11–14 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2008.12.001
D. Tan, S. Zhou, B. Xu, P. Chen, Y. Shimotsuma, K. Miura, J. Qiu, Simple synthesis of ultra-small nanodiamonds with tunable size and photoluminescence. Carbon N. Y. 62, 374–381 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.06.019
C.H. Nee, S.L. Yap, T.Y. Tou, H.C. Chang, S.S. Yap, Direct synthesis of nanodiamonds by femtosecond laser irradiation of ethanol. Sci. Rep. 6, 1–8 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep33966
V. Nguyen, J. Si, L. Yan, X. Hou, Direct demonstration of photoluminescence originated from surface functional groups in carbon nanodots. Carbon N. Y. 108, 268–273 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.07.019
G.K. Yogesh, E.P. Shuaib, A. Kalai Priya, P. Rohini, S.V. Anandhan, U.M. Krishnan, V. Kalyanavalli, S. Shukla, D. Sastikumar, Synthesis of water-soluble fluorescent carbon nanoparticles (CNPs) from nanosecond pulsed laser ablation in ethanol. Opt. Laser Technol. 135, 106717–106726 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106717
A. Thomas, M.S. Parvathy, K.B. Jinesh, Synthesis of nanodiamonds using liquid-phase laser ablataion of graphene and its application in resistive random access memory. Carbon Trends. 3, 100023–110029 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cartre.2020.100023
X.D. Ren, R. Liu, L.M. Zheng, Y.P. Ren, Z.Z. Hu, H. He, Morphology selective preparation and formation mechanism of graphene nanoribbons from graphite by liquid-phase pulsed laser ablation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 108(2016), 071904–071907 (1908). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4941801
M. Barberio, P. Antici, Laser-plasma driven synthesis of carbon-based nanomaterials. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–8 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12243-4
H. Sadeghi, E. Solati, D. Dorranian, Producing graphene nanosheets by pulsed laser ablation: Effects of liquid environment. J. Laser Appl. 31, 042003–0420013 (2019). https://doi.org/10.2351/1.5109424
E. Ghavidel, A.H. Sari, D. Dorranian, Experimental investigation of the effects of different liquid environments on the graphene oxide produced by laser ablation method. Opt. Laser Technol. 103, 155–162 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2018.01.034
E. Vaghri, D. Dorranian, M. Ghoranneviss, Effects of CTAB concentration on the quality of graphene oxide nanosheets produced by green laser ablation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 203, 235–242 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.10.010
E. Vaghri, Z. Khalaj, D. Dorranian, Investigating the effects of different liquid environments on the characteristics of multilayer graphene and graphene oxide nanosheets synthesized by green laser ablation method. Diam. Relat. Mater. 103, 107697–107710 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2020.107697
E. Solati, E. Vaghri, D. Dorranian, Effects of wavelength and fluence on the graphene nanosheets produced by pulsed laser ablation. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 124, 1–9 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2176-2
R. Hameed, K.S. Khashan, G.M. Sulaiman, Preparation and characterization of graphene sheet prepared by laser ablation in liquid. Mater. Today Proc. 20, 535–539 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.09.185
A. Pramanik, S. Karmakar, P. Kumbhakar, S. Biswas, R. Sarkar, P. Kumbhakar, Synthesis of bilayer graphene nanosheets by pulsed laser ablation in liquid and observation of its tunable nonlinearity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 499, 143902–143910 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.143902
P.M. Bota, D. Dorobantu, I. Boerasu, D. Bojin, M. Enachescu, Synthesis of single-wall carbon nanotubes by excimer laser ablation. Surf. Eng. Appl. Electrochem. 50, 294–299 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3103/S106837551404005X
K. Habiba, V.I. Makarov, J. Avalos, M.J.F. Guinel, B.R. Weiner, G. Morell, Luminescent graphene quantum dots fabricated by pulsed laser synthesis. Carbon N. Y. 64, 341–350 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.07.084
S. Kang, J.H. Ryu, B. Lee, K.H. Jung, K.B. Shim, H. Han, K.M. Kim, Laser wavelength modulated pulsed laser ablation for selective and efficient production of graphene quantum dots. RSC Adv. 9, 13658–13663 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra02087j
I.C. Novoa-De León, J. Johny, S. Vázquez-Rodríguez, N. García-Gómez, S. Carranza-Bernal, I. Mendivil, S. Shaji, S. Sepúlveda-Guzmán, Tuning the luminescence of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots synthesized by pulsed laser ablation in liquid and their use as a selective photoluminescence on-off-on probe for ascorbic acid detection. Carbon N. Y. 150, 455–464 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.05.057
G.K. Yogesh, M.B. Gumpu, D. Sastikumar, Laser-induced transformation of graphene into graphene oxide nanospheres (GONs). Mater. Res. Bull. 115, 227–234 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2019.03.030
B.I. Kharisov, O.V. Kharissova, L. Chávez-Guerrero, Synthesis techniques, properties, and applications of nanodiamonds. Synth. React. Inorganic Met. Nano-Metal Chem. 40, 84–101 (2010). https://doi.org/10.3109/10799890903555665
J. Wells, O. Kazakova, O. Posth, U. Steinhoff, S. Petronis, L.K. Bogart, P. Southern, Q. Pankhurst, C. Johansson, Standardisation of magnetic nanoparticles in liquid suspension. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 50, 383003–383027 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/aa7fa5
J.B. Wang, C.Y. Zhang, X.L. Zhong, G.W. Yang, Cubic and hexagonal structures of diamond nanocrystals formed upon pulsed laser induced liquid-solid interfacial reaction. Chem. Phys. Lett. 361, 86–90 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2614(02)00871-0
J. Xiao, G. Ouyang, P. Liu, C.X. Wang, G.W. Yang, Reversible nanodiamond-carbon onion phase transformations. Nano Lett. 14, 3645–3652 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl5014234
B. Zousman, O. Levinson, Pure nanodiamonds produced by laser-assisted technique. RSC Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 112–127 (2014)
P. Nemeth, L.A.J. Garvie, T. Aoki, N. Dubrovinskaia, L. Dubrovinsky, P.R. Buseck, Lonsdaleite is faulted and twinned cubic diamond and does not exist as a discrete material. Nat. Commun. 5, 1–5 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6447
S.N. Baker, G.A. Baker, Luminescent carbon nanodots: Emergent nanolights. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 49, 6726–6744 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200906623
X. Wen, P. Yu, Y.R. Toh, Y.C. Lee, A.C. Hsu, J. Tang, Near-infrared enhanced carbon nanodots by thermally assisted growth. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 1–5 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4760275
X. Guo, C.F. Wang, Z.Y. Yu, L. Chen, S. Chen, Facile access to versatile fluorescent carbon dots toward light-emitting diodes. Chem. Commun. 48, 2692–2694 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cc17769b
M.J. Krysmann, A. Kelarakis, E.P. Giannelis, Photoluminescent carbogenic nanoparticles directly derived from crude biomass. Green Chem. 14, 3141–3145 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2gc35907c
M.J. Krysmann, A. Kelarakis, P. Dallas, E.P. Giannelis, Formation mechanism of carbogenic nanoparticles with dual photoluminescence emission. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 747–750 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja204661r
A.B. Bourlinos, A. Stassinopoulos, D. Anglos, R. Zboril, V. Georgakilas, E.P. Giannelis, Photoluminescent carbogenic dots. Chem. Mater. 20, 4539–4541 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm800506r
X. Li, H. Wang, Y. Shimizu, A. Pyatenko, K. Kawaguchi, N. Koshizaki, Preparation of carbon quantum dots with tunable photoluminescence by rapid laser passivation in ordinary organic solvents. Chem. Commun. 47, 932–934 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cc03552a
V. Nguyen, J. Si, L. Yan, X. Hou, Electron-hole recombination dynamics in carbon nanodots. Carbon N. Y. 95, 659–663 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2015.08.066
G.X. Chen, M.H. Hong, T.C. Chong, H.I. Elim, G.H. Ma, W. Ji, Preparation of carbon nanoparticles with strong optical limiting properties by laser ablation in water. J. Appl. Phys. 95, 1455–1459 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1637933
S.I. Kitazawa, H. Abe, S. Yamamoto, Formation of nanostructured solid-state carbon particles by laser ablation of graphite in isopropyl alcohol. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 66, 555–559 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2004.06.031
Y.-P. Sun, X. Wang, F. Lu, L. Cao, M.J. Meziani, P.G. Luo, L. Gu, L.M. Veca, Doped Carbon Nanoparticles as a New Platform for Highly Photoluminescent Dots. J. Phys. Chem. C. Nanomater. Interfaces. 112, 18295–18298 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp8076485
S. Hu, Y. Dong, J. Yang, J. Liu, S. Cao, Simultaneous synthesis of luminescent carbon nanoparticles and carbon nanocages by laser ablation of carbon black suspension and their optical limiting properties. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 1957–1961 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c1jm14510j
V. Thongpool, P. Asanithi, P. Limsuwan, Synthesis of carbon particles using laser ablation in ethanol. Procedia Eng. 32, 1054–1060 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2012.02.054
V. Thongpool, A. Phunpueok, V. Piriyawong, S. Limsuwan, P. Limsuwan, Pulsed laser ablation of graphite target in dimethyformamide. Energy Procedia. 34, 610–616 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2013.06.792
K. Bagga, R. McCann, M. Wang, A. Stalcup, M. Vázquez, D. Brabazon, Laser assisted synthesis of carbon nanoparticles with controlled viscosities for printing applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 447, 263–268 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.10.046
D. Reyes, M. Camacho, M. Camacho, M. Mayorga, D. Weathers, G. Salamo, Z. Wang, A. Neogi, Laser ablated carbon nanodots for light emission. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 11, 424–434 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1638-8
G.K. Yogesh, E.P. Shuaib, D. Sastikumar, Photoluminescence properties of carbon nanoparticles synthesized from activated carbon powder (4% ash) by laser ablation in solution. Mater. Res. Bull. 91, 220–226 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.02.038
E.P. Shuaib, P.M. Shafi, G.K. Yogesh, A. Chandra Bose, D. Sastikumar, Carbon nanoparticles synthesized by laser ablation of coconut shell charcoal in liquids for glucose sensing applications. Mater. Res. Express 6, 115610–115619 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab49d1
G.K. Yogesh, E.P. Shuaib, P. Roopmani, M.B. Gumpu, U.M. Krishnan, D. Sastikumar, Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles from laser-ablated Bougainvillea alba flower extract for bioimaging applications. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 125, 379–389 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2673-y
A. Hu, J. Sanderson, A.A. Zaidi, C. Wang, T. Zhang, Y. Zhou, W.W. Duley, Direct synthesis of polyyne molecules in acetone by dissociation using femtosecond laser irradiation. Carbon N. Y. 46, 1823–1825 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2008.07.036
G. Compagnini, V. Mita, R.S. Cataliotti, L. D’Urso, O. Puglisi, Short polyyne chains produced by pulsed laser ablation of graphite in water. Carbon N. Y. 45, 2456–2458 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2007.07.002
H. Tabata, M. Fujii, S. Hayashi, Laser ablation of diamond nanoparticles suspended in solvent: Synthesis of polyynes. Chem. Phys. Lett. 395, 138–142 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2004.07.063
K.S. Khashan, Synthesis of polyynes by laser ablation of graphite in ethanol. Iraqi J. Phys. 11, 37–47 (2013). https://doi.org/10.30723/ijp.v11i21.365
R. Matsutani, T. Kakimoto, H. Tanaka, K. Kojima, Preparation of polyynes by liquid-phase laser ablation using different irradiation target materials and solvents. Carbon N. Y. 49, 77–81 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2010.08.044
T. Milenov, A. Nikolov, G. Avdeev, I. Avramova, S. Russev, D. Karashanova, I. Konstadinov, B. Georgieva, J. Mladenoff, I. Balchev, N. Stankova, S. Kolev, E. Valcheva, Synthesis of graphene-like phases in a water colloid by laser ablation of graphite. Mater. Sci Eng. B Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 247, 114379–114185 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2019.114379
S. Kamali, E. Solati, D. Dorranian, Effect of laser fluence on the characteristics of graphene nanosheets produced by pulsed laser ablation in water. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 86, 238–243 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-019-00806-4
G.W. Yang, J.B. Wang, Pulsed-laser-induced transformation path of graphite to diamond via an intermediate rhombohedral graphite. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 72, 475–479 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390000537
J. Hao, L. Pan, S. Gao, H. Fan, B. Gao, Production of fluorescent nano-diamonds through femtosecond pulsed laser ablation. Opt. Mater. Express. 9, 4734–4741 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1364/ome.9.004734
F.D. Lipsa, E.L. Ursu, C. Ursu, E. Ulea, A. Cazacu, Evaluation of the antifungal activity of gold-chitosan and carbon nanoparticles on fusarium oxysporum. Agronomy 10, 1–11 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10081143
R. Kaimal, G.K. Yogesh, D. Sastikumar, J.J. Wu, S. Anandan, M. Ashokkumar, Laser-assisted decoration of carbon nanotubes with palladium nanoparticles for application in electrochemical methanol oxidation. Bull. Mater. Sci. 44, 125–135 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-021-02428-z
Q. Zou, M.Z. Wang, Y.G. Li, Analysis of the nanodiamond particle fabricated by detonation. J. Exp. Nanosci. 5, 319–328 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1080/17458080903531021
S. Sahu, B. Behera, T.K. Maiti, S. Mohapatra, Simple one-step synthesis of highly luminescent carbon dots from orange juice: Application as excellent bio-imaging agents. Chem. Commun. 48, 8835–8837 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cc33796g
C. Liu, Z. Zhao, R. Zhang, L. Yang, Z. Wang, J. Yang, H. Jiang, M.Y. Han, B. Liu, Z. Zhang, Strong infrared laser ablation produces white-light-emitting materials via the formation of silicon and carbon dots in silica nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 119, 8266–8272 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp512918h
V.I. Korepanov, H.O. Hamaguchi, E. Osawa, V. Ermolenkov, I.K. Lednev, B.J.M. Etzold, O. Levinson, B. Zousman, C.P. Epperla, H.C. Chang, Carbon structure in nanodiamonds elucidated from Raman spectroscopy. Carbon N. Y. 121, 322–329 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.06.012
A. Ganguly, S. Sharma, P. Papakonstantinou, J. Hamilton, Probing the thermal deoxygenation of graphene oxide using. J. Phys. Chem. 115, 17009–17019 (2011)
F. Tian, J. Sun, S.L. Hu, X.W. Du, Growth dynamics of nanodiamonds synthesized by pulsed-laser ablation. J. Appl. Phys. 104, 132–135 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2978213
G. Eda, Y.Y. Lin, C. Mattevi, H. Yamaguchi, H.A. Chen, I.S. Chen, C.W. Chen, M. Chhowalla, Blue photoluminescence from chemically derived graphene oxide. Adv. Mater. 22, 505–509 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200901996
P. Cherukuri, S.M. Bachilo, S.H. Litovsky, R.B. Weisman, Near-infrared fluorescence microscopy of single-walled carbon nanotubes in phagocytic cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 15638–15639 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0466311
Z. Gan, H. Xu, Y. Hao, Mechanism for excitation-dependent photoluminescence from graphene quantum dots and other graphene oxide derivates: Consensus, debates and challenges. Nanoscale 8, 7794–7807 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6nr00605a
G. Eda, Y.-Y. Lin, C. Mattevi, H. Yamaguchi, H. Chen, I. Chen, C. Chen, M. Chhowalla, B.G. Eda, Y.-Y. Lin, C. Mattevi, H. Yamaguchi, H. Chen, I. Chen, C. Chen, M. Chhowalla, Blue photoluminescence from chemically derived graphene oxide. Adv. Mater. 22, 1–5 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200901996
S. Zhu, Y. Song, X. Zhao, J. Shao, J. Zhang, B. Yang, The photoluminescence mechanism in carbon dots (graphene quantum dots, carbon nanodots, and polymer dots): Current state and future perspective. Nano Res. 8, 355–381 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0644-3
A. Sommereyns, T. Hupfeld, S. Gann, T. Wang, C. Wu, E. Zhuravlev, A. Lüddecke, S. Baumann, J. Rudloff, M. Lang, B. Gökce, S. Barcikowski, M. Schmidt, Influence of sub-monolayer quantities of carbon nanoparticles on the melting and crystallization behavior of polyamide 12 powders for additive manufacturing. Mater. Des. 201, 109487–109504 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2021.109487
M.S. Jabir, F.A. Abdulameer, K.S. Khashan, Carbon nanoparticles decorated with cupric oxide nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation in liquid as an antibacterial therapeutic agent. Mater. Res. Express 5, 035003–035019 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aab0ed
P. Russo, L. D’Urso, A. Hu, N. Zhou, G. Compagnini, In liquid laser treated graphene oxide for dye removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 348, 85–91 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.12.014
A. Gimeno-Furió, R. Martínez-Cuenca, R. Mondragón, A.F.V. Gasulla, C. Doñate-Buendía, G. Mínguez-Vega, L. Hernández, Optical characterisation and photothermal conversion efficiency of a water-based carbon nanofluid for direct solar absorption applications. Energy (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.118763
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest among the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yogesh, G.K., Shukla, S., Sastikumar, D. et al. Progress in pulsed laser ablation in liquid (PLAL) technique for the synthesis of carbon nanomaterials: a review. Appl. Phys. A 127, 810 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04951-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04951-6