Abstract
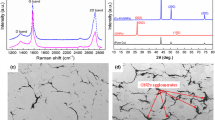
Copper (Cu)-based nanocomposites were produced by mechanical alloying process using various volume percentages of graphene up to 8 vol.%. Subsequently, nanocomposites powders were milled for 20 h, cold-pressed and subjected to different sintering temperatures up to 850 °C for 1 h in argon atmosphere. Furthermore, X-ray diffraction technique along with transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was employed to examine the milled powders. The microstructure, physical, mechanical, electrical properties and wear behavior of the sintered nanocomposites samples were determined also. The obtained TEM micrographs showed homogenous distribution of graphene in Cu matrix and noticed grains refinement. Additionally, it was responsible for measurable decreases in the densification and the electrical conductivity of the sintered bodies. Furthermore, the mechanical properties, on the contrary to work-hardening capacity, of the sintered samples were improved by the increasing in graphene contents and sintering temperatures. The weight loss and wear rate of nanocomposites reduced with both of graphene content and sintering temperature, while increased with increasing in the applied load. Taking all these results into consideration, we can conclude that Cu-graphene nanocomposites are promising candidates for industrial applications.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.M. Sadouna, A. Fathy, Experimental study on tribological properties of Cu–Al2O3 nanocomposite hybridized by graphene nanoplatelets. Ceram. Int. 45, 24784–24792 (2019)
M.A. Taha, M.F. Zawrah, Effect of nano ZrO2 on strengthening and electrical properties of Cu-matrix nanocomposits prepared by mechanical alloying. Ceram. Int. 43(15), 12698–12704 (2017)
P.H. Manrique, X.G. Lei, R. Xu, M. Zhou, I.A. Kinloch, R.J. Young, Copper/graphene composites: a review. J. Mater. Sci. 54, 12236–12289 (2019)
L. Zhang, Z. Duan, H. Zhu, K. Yin, Advances in synthesizing copper/graphene composite material. Mater. Manuf. Process. 32, 475–479 (2017)
M.F. Zawrah, H.A. Zayed, R.A. Essawy, A.H. Nassar, M.A. Taha, Preparation by mechanical alloying, characterization and sintering of Cu-20 wt.% Al2O3 nanocomposites. Mater. Des. 46, 485–490 (2013)
H.R. Akramifard, M. Shamanian, M. Sabbaghian, M. Esmailzadeh, Microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu/SiC metal matrix composite fabricated via friction stir processing. Mater. Des. 54, 838–844 (2014)
I. Altinsoy, F.G.C. Efe, D. Aytaş, M. Kılıç, I. Ozbek, C. Bindal, Some properties of Cu-B4C composites manufactured by powder metallurgy, period. Eng. Nat. Sci. 1(10), 34–38 (2013)
Y. Huang, P. Bazarnik, D. Wan, D. Luo, P. Henrique, R. Pereira, M. Lewandowska, J. Yao, B.E. Hayden, T.G. Langdon, The fabrication of graphene-reinforced Al-based nanocomposites using high-pressure torsion. Acta. Mater. 164, 499–511 (2019)
M.F. Zawrah, M.A. Taha, H. Abo Mostafa, In-situ formation of Al2O3/Al core-shell from waste material: production of porous composite improved by graphene. Ceram. Int. 44, 10693–10699 (2018)
A. Abu-Oqail, A. Samir, A.R.S. Essa, A. Wagih, A. Fathy, Effect of GNPs coated Ag on microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu-Fe dual-matrix nanocomposite. Alloys Compds. 781, 64–74 (2019)
K. Chu, J. Wang, Y.P. Liu, Y.B. Li, C.C. Jia, H. Zhang, Creating defects on grapheme basal-plane toward interface optimization of graphene/CuCr composites. Carbon 143, 85–96 (2019)
A. Saboori, M. Pavese, C. Badini, P. Fino, A Novel approach to enhance the mechanical strength and electrical and thermal conductivity of Cu-GNP nanocomposites. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 49, 333–345 (2018)
A. Saboori, S.K. Moheimani, M. Dadkhah, M. Pavese, C. Badini, P. Fino, An overview of key challenges in the fabrication of metal matrix nanocomposites reinforced by graphene nanoplatelets. Metals 8, 1–25 (2018)
M. Dadkhah, A. Saboori, P. Fino, An Overview of the recent developments in metal matrix nanocomposites reinforced by graphene. Materials 12, 1–38 (2019)
L.Y. Chen, H. Konishi, A. Fehrenbacher, C. Ma, J.Q. Xu, H. Choi, H.F. Xu, F.E. Pfefferkorn, X.C. Li, Novel nanoprocessing route for bulk graphene nanoplatelets reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites. Scr. Mater. 67, 29–33 (2012)
W.G. Chen, L.L. Dong, J.J. Wang, Y. Zuo, S.X. Ren, Y.Q. Fu, Synergistic enhancing effect for mechanical and electrical properties of tungsten copper composites using spark plasma infiltrating sintering of copper coated graphene. Sci. Rep. 7, 17836–17845 (2017)
A. Saboori, M. Pavese, C. Badini, P. Fino, A novel Cu–GNPs nanocomposite with improved thermal and mechanical properties. Acta Metall. Sin. 31, 148–152 (2018)
A. Saboori, S.K. Moheimani, M. Pavese, C. Badini, P. Fino, New nanocomposite materials with improved mechanical strength and tailored coefficient of thermal expansion for electro-packaging applications. Metals 7, 1–14 (2017)
F. Nazeer, Z. Ma, L.H. Gao, F.C. Wang, M.A. Khan, A. Malik, Thermal and mechanical properties of copper-graphite and copper-reduced graphene oxide composites. Compos. Part B 163, 77–85 (2019)
R.A. Youness, M.A. Taha, M. Ibrahim, In vitro bioactivity, molecular structure and mechanical properties of zirconia-carbonated hydroxyapatite nanobiocomposites sintered at different temperatures. Mater. Chem. Phys. 239, 122011 (2020)
M.A. Taha, R.A. Youness, M.F. Zawrah, Review on nanocomposites fabricated by mechanical alloying. Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 26(9), 1047–1058 (2019)
R.A. Youness, M.A. Taha, M.A. Ibrahim, Effect of sintering temperatures on the in vitro bioactivity, molecular structure and mechanical properties of titanium/carbonated hydroxyapatite nanobiocomposites. Mol. Struct. 1150, 188–195 (2017)
R.P. Bustamante, D.B. Morales, J.B. Martínez, I.E. Guel, R.M. Sánchez, Microstructural and hardness behavior of graphene-nanoplatelets/aluminum composites synthesized by mechanical alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 615, 578–582 (2014)
M. Karadag, G. Acikbas, Investigation of electrical and mechanical properties of Cu Matrix TiC reinforced composites. Sch. J. Eng. Technol. 6(2), 58–63 (2018)
A. Abu-Oqail, A. Wagih, A. Fathy, O. Elkady, A.M. Kabee, Effect of high energy ball milling on strengthening of Cu-ZrO2 nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. 45(5), 5866–5875 (2019)
N. Khobragade, K. Sikdar, B. Kumar, S. Bera, D. Roy, Mechanical and electrical properties of copper-graphene nanocomposite fabricated by high pressure torsion. Alloys Compd. 776, 123–132 (2019)
R.A. Youness, M.A. Taha, H. Elhaes, M. Ibrahim, Molecular modeling, FTIR spectral characterization and mechanical properties of carbonated hydroxyapatite prepared by mechanochemical synthesis. Mater. Chem. Phys. 190, 209–218 (2017)
R.A. Youness, M.A. Taha, H. Elhaes, M. Ibrahim, Preparation, FTIR characterization and mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite nanopowders. J. Theor. Nanosci. 14, 2409–2415 (2017)
A. Prosviryakov, A. Bazlov, A. Pozdniakov, N. Emelina, Low-cost mechanically alloyed copper-based composite reinforced with silicate glass particles for thermal applications. JOM 71(3), 995–1001 (2019)
R.A. Youness, M.A. Taha, A.A. El-Kheshen, N. El-Faramawy, M. Ibrahim, In vitro bioactivity evaluation, antimicrobial behavior and mechanical properties of cerium-containing phosphate glasses. Mater. Res. Express 6, 075212 (2019)
M.A. Ouis, M.A. Taha, G.T. El-bassyouni, M.A. Azooz, Thermal, mechanical and electrical properties of lithium phosphate glasses doped with copper oxide. Bull. Mater. Sci. 42, 246–255 (2019)
R.A. Youness, M.A. Taha, A.A. El-Kheshen, M. Ibrahim, Influence of the addition of carbonated hydroxyapatite and selenium dioxide on mechanical properties and in vitro bioactivity of borosilicate inert glass. Ceram. Int. 44, 20677–20685 (2018)
R.A. Youness, M.A. Taha, M. Ibrahim, In vitro bioactivity, physical and mechanical properties of carbonated fluoroapatite during mechanochemical synthesis. Ceram. Int. 44, 21323–21329 (2018)
A. Alizadeh, M. Maleki, A. Abdollahi, Preparation of super-high strength nanostructured B4C reinforced Al-2Cu aluminum alloy matrix composites by mechanical milling and hot press method: microstructural, mechanical and tribological. Adv. Powder Technol. 28, 3274–3287 (2017)
N. Afrin, D. Chen, X. Cao, M. Jahazi, Strain hardening behavior of a friction stir welded magnesium alloy. Scr. Material. 57, 1004–1007 (2007)
J. Stein, B. Lenczowski, N. Fréty, E. Anglaret, Mechanical reinforcement of a high-performance aluminium alloy AA5083 with homogeneously dispersed multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 50, 2264–2272 (2012)
K. Chu, C. Jia, Enhanced strength in bulk graphene-copper composites. Phys. Status Solidi A 211(1), 184–190 (2014)
Y. Chen, X. Zhang, E. Liu, C. He, C. Shi, J. Li, P. Nash, N. Zhao, Fabrication of in-situ grown graphene reinforced Cu matrix composites. Sci. Rep. 8, 1–9 (2016)
M.A. Taha, A.H. Nassar, M.F. Zawrah, Effect of milling parameters on sinterability, mechanical and electrical properties of Cu-4 wt% ZrO2 nanocomposite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 181, 26–32 (2016)
I. Mobasherpour, A.A. Tofigh, M. Ebrahimi, Effect of nano-size Al2O3 reinforcement on the mechanical behavior of synthesis 7075 aluminum alloy composites by mechanical alloying. Mater. Chem. Phys. 138, 535–541 (2013)
A. Fathy, A. Wagih, A. Abu-Oqail, Effect of ZrO2 content on properties of Cu-ZrO2 nanocomposites synthesized by optimized high energy ball milling. Ceram. Int. 45(1), 2319–2329 (2019)
A.S. Prosviryakov, SiC content effect on the properties of Cu–SiC composites produced by mechanical alloying. Alloys Compd. 632, 707–710 (2015)
M.J. Sabl, V.K. Tripathi, Fabrication and study of optimum properties of copper alumina metal matrix nanocomposites for high temperature applications. Ind. Eng. Technol. 3(2), 143–154 (2011)
Y.A. Sorkhe, H. Aghajani, A.T. Tabrizi, Mechanical alloying and sintering of nanostructured TiO2 reinforced copper nanocomposite and its characterization. Mater. Des. 58, 168–174 (2014)
S. Islak, D. Kır, S. Buytoz, Effect of sintering temperature on electrical and microstructure properties of hot pressed Cu-TiC composites. Sci. Sinter. 46, 15–21 (2014)
M.A. Taha, A.H. Nassar, M.F. Zawrah, Improvement of wettability, sinterability, mechanical and electrical properties of Al2O3-Ni nanocomposites prepared by mechanical alloying. Ceram. Inter. 43, 3576–3582 (2017)
M.A. Taha, G.M. Elkomy, H. Abo-Mostafa, E. Gouda, Effect of ZrO2 contents and ageing times on mechanical and electrical properties of Al-4.5 wt% Cu nanocomposites prepared by mechanical alloying. Mater. Chem. Phys. 206, 116–123 (2018)
A. Saboori, C. Novara, M. Pavese, C. Badini, F. Giorgis, P. Fino, An Investigation on the sinterability and the compaction behavior of aluminum/graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) prepared by powder metallurgy. JMEPEG 26, 993–999 (2017)
S. Islak, H. Çelik, Effect of sintering temperature and boron carbide content on the wear behavior of hot pressed diamond cutting segments. Sci. Sinter. 47, 131–143 (2015)
Z. Zhang, D.L. Chen, Consideration of Orowan strengthening effect in particulate-reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites: a model for predicting their yield strength. Scr. Mater. 54(7), 1321–1326 (2006)
F. Chen, J. Ying, Y. Wang, S. Du, Z. Liu, Q. Huang, Effects of graphene content on the microstructure and properties of copper matrix composites. Carbon 96, 836–842 (2016)
J.N. Wei, Z.B. Li, F.S. Han, Thermal mismatch dislocations in macroscopic graphite particle-reinforced metal matrix composites studied by internal friction. Phys. Status Solidi A 191(1), 125–136 (2002)
R. Yilmaz, M.R. Ekici, Microstructural and hardness characterisation of sintered low alloyed steel. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 31(1), 23–28 (2008)
M.A. Taha, M.F. Zawrah, Mechanical alloying and sintering of a Ni/10wt.%Al2O3 nanocomposite and its characterization. Silicon. 10(4), 1351–1359 (2018)
M.F. Zawrah, H.A. Mostafa, M.A. Taha, Effect of SiC content on microstructure, mechanical and electrical properties of sintered Al-20Si-xSiC nanocomposites fabricated by mechanical alloying. Mater. Res. Express. 6, 125014 (2019)
J. Linn, Y. Huang, H. Zhang, Y. Yang, Y. Wu, Spark plasma sintering of ZrO2 fiber toughened ZrB2-based ultra-high temperature ceramics Jia Linn. Ceram. Int. 41, 10336–10340 (2015)
M. Shabania, M.H. Paydara, R. Zamirib, M. Goodarzic, M.M. Moshksar, Microstructural and sliding wear behavior of SiC-particle reinforced copper matrix composites fabricated by sintering and sinter-forging processes. Mater. Res. Technol. 5(1), 5–12 (2016)
A. Baradeswaran, S.C. Vettivel, A. Elaya-Perumal, N. Selvakumar, R. Franklin Issac, Experimental investigation on mechanical behaviour, modeling and optimization of wear parameters of B4C and graphite reinforced aluminium hybrid composites. Mater. Des. 63, 620–632 (2014)
M.T. Khorshid, E. Omrani, P.L. Menezes, P.K. Rohatgi, Tribological performance of self-lubricating aluminum matrix nanocomposites: role of graphene nanoplatelets. Eng. Sci. Technol. 19, 463–469 (2016)
M.Z. Hussain, U. Khan, R. Jangid, S. Khan, Hardness and wear analysis of Cu/Al2O3 composite for application in EDM electrode. Mater. Sci. Eng. 310, 1–9 (2018)
P. Lakshmanan, S. Dharmaselvan, S. Paramasivam, L. Kirubanandan, R. Vignesh, Tribological properties of B4C nano particulates reinforced copper matrix nanocomposites, mater. Today Proc. 16(2), 584–591 (2019)
A.T. Alpas, J. Zhang, Effect of microstructure (particle size and volume fraction) and counterface material on the sliding wear resistance of particulate-reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 25, 969–983 (1994)
C.S. Ramesh, M. Safiulla, Wear behavior of hot extruded Al6061 based composites. Wear 263, 629–635 (2007)
T. Kannana, B. Anandavel, Experimental study on the effect of sic and graphite particles on weight loss of al 6061 hybrid composite materials. JOTSE 2, 49–68 (2011)
N. Nemati, M. Emamy, A.R. Emami, M. Mashhoodi, Hardness and wear properties of Al4.5% Cu/Al3Mg2 nanocomposite prepared by mechanical alloying. Mater. Trans. 53(7), 1310–1317 (2012)
F.E. Kennedy, A.C. Balbahadur, D.S. Lashmore, The friction and wear of Cu-based silicon carbide particulate metal matrix composites for brake applications. Wear 203(204), 715–721 (1997)
J.P. Tu, W. Rong, S.Y. Guo, Y.Z. Yang, Dry sliding wear behavior of in situ Cu–TiB2 nanocomposites against medium carbon steel. Wear 255, 832–835 (2003)
B. Wei, D. Qu, C. Hu, F. Li, T. Zhou, R. Xie, Z. Zhou, Synthesis and physical properties of graphene nanosheets reinforced copper composites. Adv. Mater. Res. 833, 310–314 (2014)
W.D. Calister, Materials Science and Engineering an Introduction, vol. 563, 5th edn. (Wiley, New York, 1999)
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR), King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, under grant No. (D-186-135-1441). The authors therefore gratefully acknowledge technical and financial support from DSR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moustafa, E.B., Taha, M.A. Preparation of high strength graphene reinforced Cu-based nanocomposites via mechanical alloying method: microstructural, mechanical and electrical properties. Appl. Phys. A 126, 220 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-3412-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-3412-0