Abstract
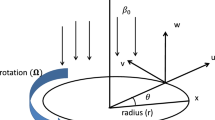
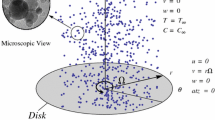
Entropy generation analysis for three-dimensional (3D) magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) flow of viscous fluid through a rotating disk is addressed in this article. Entropy generation is explored as a function of temperature and velocity. The modeling of the considered problem is performed through Buongiorno model. Conservation of energy comprises dissipation, convective heat transport and Joule heating. Flow under consideration is because of nonlinear stretching velocity of disk. Transformations used lead to the reduction of partial differential equations into ordinary differential equations. Total entropy generation rate is scrutinized. Non-linear computations have been carried out. Domain of convergence for the obtained solutions is identified. Radial, axial and tangential velocities are interpreted. Entropy equation is studied in the presence of dissipation, Brownian diffusion and thermophoresis effects. Velocity and temperature gradients are discussed graphically. Meaningful results are summed up in the concluding section.



























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the article, the data are made by the authors themselves and do not involve references of others.
Abbreviations
- u, V, w :
-
Velocity components
- \(r,\vartheta ,z\) :
-
Space coordinates
- T :
-
Fluid temperature
- T ∞ :
-
Ambient temperature
- T f :
-
Convective fluid temperature
- C:
-
Fluid concentration
- C ∞ :
-
Ambient concentration
- u :
-
Stretching velocity in r direction
- B 0 :
-
Strength of magnetic field
- ρ :
-
Fluid density
- c p :
-
Specific heat
- qr:
-
Radiative heat flux
- ℎ:
-
Convective heat transfer coefficient
- D :
-
Brownian diffusion coefficient
- D :
-
Thermophoresis diffusion coefficient
- F :
-
Dimensionless velocity
- M:
-
Magnetic parameter
- A:
-
Ratio of velocities
- Rd:
-
Radiation parameter
- Pr:
-
Prandtl number
- N b :
-
Brownian motion parameter
- N T :
-
Thermophoresis parameter
- S c :
-
Schmidt number
- β :
-
Biot number
- Nu x :
-
Local Nusselt number
- Re x :
-
Local Reynolds number
- k∗:
-
Coefficient of mean absorption
- a, c :
-
Positive constants
- τ :
-
Surface shear stress
- σ∗:
-
Stefan–Boltzmann constant parameter
- \(\theta\) :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- \(\Phi\) :
-
Dimensionless concentration
- \(\eta\) :
-
Dimensionless space variable
- \(\nu\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity
- ∞:
-
Condition at the free stream
- w :
-
Condition at the surface
References
T. Hayat, M. Rashid, M. Imtiaz, A. Alsaedi, Nanofluid flow due to rotating disk with variable thickness and homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 113, 96–105 (2017)
D.H. Doh, M. Muthtamilselvan, Thermophoretic particle deposition on magnetohydrodynamic flow of micropolar fluid due to a rotating disk. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 130, 350–359 (2017)
T. Hayat, S. Qayyum, M. Imtiaz, A. Alsaedi, Flow between two stretchable rotating disks with Cattaneo-Christov heat flux model. Result Physics. 7, 126–133 (2017)
C. Yin, L. Zheng, C. Zhang, X. Zhang, Flow and heat transfer of nanofluids over a rotating disk with uniform stretching rate in the radial direction. Propuls. Power Res. 6, 25–30 (2017)
M. Turkyilmazoglu, Effects of uniform radial electric field on the MHD heat and fluid flow due to a rotating disk. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 51, 233–240 (2012)
S.J. Xun, L. Zheng, X. Chen, X. Zhang, Flow and heat transfer of Ostwald-de Waele fluid over a variable thickness rotating disk with index decreasing. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 103, 1214–1224 (2016)
R. Muhammad, M.I. Khan, N.B. Khan, M. Jameel, Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) radiated nanomaterial viscous material flow by a curved surface with second order slip and entropy generation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 189, 105294 (2020)
M.I. Khan, F. Shah, M. Waqas, T. Hayat, A. Alsaedi, The role of γAl2O3−H2O and γAl2O3−C2H6O2 nanomaterials in Darcy-Forchheimer stagnation point flow: an analysis using entropy optimization. Int. J. Thermal Sci. 140, 20–27 (2019)
T. Hayat, F. Shah, M.I. Khan, M.I. Khan, A. Alsaedi, Entropy analysis for comparative study of effective Prandtl number and without effective Prandtl number via γAl2O3−H2O and γAl2O3−C2H6O2 nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 266, 814–823 (2018)
R.A. Kareem, J.A. Gbadeyan, Entropy generation and thermal criticality of generalized Couette hydromagnetic flow of two-step exothermic chemical reaction in a channel. Int J Thermofluids 5–6, 100037 (2020)
Z.Y. Xie, Y.J. Jian, Entropy generation of two-layer magnetohydrodynamic electroosmotic flow through micro parallel channels. Energy 139, 1080–1093 (2017)
M.M. Rashidi, N. Kavyani, S. Abelman, Investigation of entropy generation in MHD and slip flow over a rotating porous disk with variable properties. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 70, 892–917 (2014)
S. Qayyum, M. Ijaz Khan, T. Hayat, A. Alsaedi, M. Tamoor, Entropy generation in dissipative flow of Williamson fluid between two rotating disks. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 127, 933–942 (2018)
T. Hayat, M.I. Khan, S. Qayyum, M.I. Khan, A. Alsaedi, Entropy generation for flow of Sisko fluid due to rotating disk. J. Mol. Liq. 264, 375–385 (2018)
S.U. Khan, M.M. Bhatti, S. Qaisar, I.A. Khan, Swimming of micro-organism over an oscillatory stretched surface filled with a magnetic third-grade nanofluid: an application of activation energy. Chin. J. Phys. 65, 64–74 (2020)
S. Hussain, A. Shah, S. Ayub, A. Ullah, An approximate analytical solution of the Allen-Cahn equation using homotopy perturbation method and homotopy analysis method. Heliyon 5, e03060 (2019)
T. Hayat, M.I. Khan, S. Qayyum, A. Alsaedi, Entropy generation in flow with silver and copper nanoparticles. Colloids Surf., A 539, 335–346 (2018)
P.A. Naik, Z. Jian, M. Ghoreishi, Estimating the approximate analytical solution of HIV viral dynamic model by using homotopy analysis method. Chaos Solitons Fract. 131, 109500 (2020)
M.I. Khan, M. Waqas, T. Hayat, A. Alsaedi, A comparative study of Casson fluid with homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 498, 85–90 (2017)
M.R. Shirkhani, H.A. Hoshyar, I. Rahimipetroudi, H. Akhavan, D.D. Ganji, Unsteady time-dependent incompressible Newtonian fluid flow between two parallel plates by homotopy analysis method (HAM), homotopy perturbation method (HPM) and collocation method (CM). Propuls. Power Res. 7, 247–256 (2018)
R. Muhammad, M.I. Khan, M. Jameel, N.B. Khan, Fully developed Darcy-Forchheimer mixed convective flow over a curved surface with activation energy and entropy generation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 188, 105298 (2020)
Z. Un Nisa, N.A. Shah, I. Tlili, S. Ullah, M. Nazar, Natural convection flow of second grade fluid with thermal radiation and damped thermal flux between vertical channels. Alexandria Eng. J. 58, 1119–1125 (2019)
M.I. Khan, F. Alzahrani, A. Hobiny, Heat transport and nonlinear mixed convective nanomaterial slip flow of Walter-B fluid containing gyrotactic microorganisms. Alexandria Eng. J. 59, 1761–1769 (2020)
I. Tlili, M. Bilal, M.Z.A. Qureshi, Z. Abdelmalek, Thermal analysis of magnetized pseudoplastic nano fluid flow over 3D radiating non-linear surface with passive mass flux control and chemically responsive species. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 8125–8135 (2020)
F. Haq, S. Kadry, Y.M. Chu, M. Khan, M.I. Khan, Modeling and theoretical analysis of gyrotactic microorganisms in radiated nanomaterial Williamson fluid with activation energy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 10468–10477 (2020)
R. Ahmed, N. Ali, K. Al-Khaled, S.U. Khan, I. Tlili, Finite difference simulations for non-isothermal hydromagnetic peristaltic flow of a bio-fluid in a curved channel: applications to physiological systems. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 195, 105672 (2020)
M.I. Khan, S. Kadry, Y.M. Chu, W.A. Khan, A. Kumar, Exploration of Lorentz force on a paraboloid stretched surface in flow of Ree-Eyring nanomaterial. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 10265–10275 (2020)
M.S. Hashmi, K. Al-Khaled, N. Khan, S.U. Khan, I. Tlili, Buoyancy driven mixed convection flow of magnetized Maxell fluid with homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions with convective boundary conditions. Results Phys. 19, 103379 (2020)
M.I. Khan, F. Alzahrani, A. Hobiny, Z. Ali, Estimation of entropy generation in Carreau-Yasuda fluid flow using chemical reaction with activation energy. J Mater Res. Technol. 9, 9951–9964 (2020)
S.A. Shehzad, M.G. Reddy, P. VIjayakumari, I. Tlili, Behavior of ferromagnetic Fe2SO4 and titanium alloy Ti6Al4v nanoparticles in micropolar fluid flow. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer. 117, 104769 (2020)
S. Xun, J. Zhao, L. Zheng, X. Chen, X. Zhang, Flow and heat transfer of Ostwald-de Waele fluid over a variable thickness rotating disk with index decreasing. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 103, 1214–1224 (2016)
H.I. Andersson, E. de Korte, R. Meland, Flow of a power-law fluid over a rotating disk revisited. Fluid Dyn. Res. 28, 75–88 (2001)
C.Y. Ming, L.C. Zheng, X.X. Zhang, Steady flow and heat transfer of the powerlaw fluid over a rotating disk. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 38, 280–284 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M.W.A., Shah, F., Khan, M.I. et al. Fully developed entropy-optimized MHD nanofluid flow by a variably thickened rotating surface. Appl. Phys. A 126, 890 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-04068-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-04068-2