Abstract
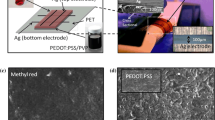
We propose a novel bilayer resistive switching device based on N,N′-bis (3-methylphenyl)-N,N′-diphenylbenzidine (TPD) and poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly(styrenesulfonate)/poly(vinyl alcohol) (PEDOT:PSS/PVOH) composite. The bilayer structure of TPD and (PEDOT:PSS/PVOH) is fabricated on indium tin oxide (ITO)-coated polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrate through all-printed technology. Here, the ITO acts as a bottom electrode and the top electrode is patterned using silver (Ag) epoxy. The fabricated device has a high resistance state (HRS) of 97.23 kΩ and a low resistance state (LRS) of 3.38 kΩ at read voltage of 0.58 V, which achieved Roff/Ron resistance ratio of ~ 28.7. The proposed device maintained its stability for more than 300 endurance cycles and retention time of more than 104 s. To ensure the resistive switching behavior, the proposed resistive memory device is electrically and mechanically tested. To conform the proper fabrication, FESEM is used for the surface morphology and cross section. The results suggest that the proposed device can be used in future printed resistive switching devices.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Chua, Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Cir. Theory 18, 507–519 (1971)
D.B. Strukov, G.S. Snider, D.R. Stewart, R.S. Williams, The missing memristor found. Nature 453, 80 (2008)
S. Shin, K. Kim, S.-M. Kang, Compact models for memristors based on charge-flux constitutive relationships. Trans. Comp.-Aided Des. Integ. Cir. Syst. 29, 590–598 (2010)
G.U. Siddiqui, M.M. Rehman, K.H. Choi, Enhanced resistive switching in all-printed, hybrid and flexible memory device based on perovskite ZnSnO3 via PVOH polymer. Polymer 100, 102–110 (2016)
S. Ali, J. Bae, C.H. Lee, K.H. Choi, Y.H. Doh, All-printed and highly stable organic resistive switching device based on graphene quantum dots and polyvinylpyrrolidone composite. Org. Electron. 25, 225–231 (2015)
S. Ali, J. Bae, C.H. Lee, S. Shin, N.P. Kobayashi, Ultra-low power non-volatile resistive crossbar memory based on pull up resistors. Org. Electron. 41, 73–78 (2017)
J.J. Yang, D.B. Strukov, D.R. Stewart, Memristive devices for computing. Nat. Nanotechnol. 8, 13 (2012)
J. Rajendran, H. Manem, R. Karri, G.S. Rose, Memristor based programmable threshold logic array. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Nanoscale Architectures, IEEE Press, Anaheim, California, 2010, pp. 5–10
S. Ali, A. Hassan, G. Hassan, J. Bae, C.H. Lee, Flexible frequency selective passive circuits based on memristor and capacitor. Org. Electron. 51, 119–127 (2017)
M.G. Bray, D.H. Werner, Passive switching of electromagnetic devices with memristors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 073504 (2010)
S.H. Jo, T. Chang, I. Ebong, B.B. Bhadviya, P. Mazumder, W. Lu, Nanoscale memristor device as synapse in neuromorphic systems. Nano Lett. 10, 1297–1301 (2010)
M. Prezioso, F. Merrikh-Bayat, B.D. Hoskins, G.C. Adam, K.K. Likharev, D.B. Strukov, Training and operation of an integrated neuromorphic network based on metal-oxide memristors. Nature 521, 61 (2015)
J. Borghetti, Z. Li, J. Straznicky, X. Li, D.A.A. Ohlberg, W. Wu, D.R. Stewart, R.S. Williams, A hybrid nanomemristor/transistor logic circuit capable of self-programming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 1699–1703 (2009)
S. Ali, J. Bae, C.H. Lee, Printed non-volatile resistive switches based on zinc stannate (ZnSnO3). Curr. Appl. Phys. 16, 757–762 (2016)
N.M. Muhammad, N. Duraisamy, K. Rahman, H.W. Dang, J. Jo, K.H. Choi, Fabrication of printed memory device having zinc-oxide active nano-layer and investigation of resistive switching. Curr. Appl. Phys. 13, 90–96 (2013)
G. Ghosh, M.K. Orlowski, Correlation between set and reset voltages in resistive RAM cells. Curr. Appl. Phys. 15, 1124–1129 (2015)
S.B. Lee, S.H. Chang, H.K. Yoo, M.J. Yoon, S.M. Yang, B.S. Kang, Reversible changes between bipolar and unipolar resistance-switching phenomena in a Pt/SrTiOx/Pt cell. Curr. Appl. Phys. 12, 1515–1517 (2012)
M.K. Hota, M.K. Bera, B. Kundu, S.C. Kundu, C.K. Maiti, A natural silk fibroin protein-based transparent bio-memristor. Adv. Func. Mater. 22, 4493–4499 (2012)
G. Zhou, B. Sun, A. Zhou, B. Wu, H. Huang, A larger nonvolatile bipolar resistive switching memory behaviour fabricated using eggshells. Curr. Appl. Phys. 17, 235–239 (2017)
M.M. Rehman, G.U. Siddiqui, J.Z. Gul, S.-W. Kim, J.H. Lim, K.H. Choi, Resistive Switching in all-printed, flexible and hybrid MoS2-PVA nanocomposite based memristive device fabricated by reverse offset. Sci. Rep. 6, 36195 (2016)
I. Mihalache, L.M. Veca, M. Kusko, D. Dragoman, Memory effect in carbon quantum DOT–PEG1500N composites. Curr. Appl. Phys. 14, 1625–1632 (2014)
R. Muhammad Muqeet, S. Ghayas Uddin, D. Yang Hoi, C. Kyung, Hyun, Highly flexible and electroforming free resistive switching behavior of tungsten disulfide flakes fabricated through advanced printing technology. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 32, 095001 (2017)
B. De Salvo, J. Buckley, D. Vuillaume, Recent results on organic-based molecular memories. Curr. Appl. Phys. 11, e49–e57 (2011)
J.J. Yang, M. Feng, D.P. Matthew, A.A.O. Douglas, R.S. Duncan, L. Chun Ning, R.S. Williams, The mechanism of electroforming of metal oxide memristive switches. Nanotechnology 20, 215201 (2009)
Z.-M. Liao, C. Hou, Q. Zhao, D.-S. Wang, Y.-D. Li, D.-P. Yu, Resistive switching and metallic-filament formation in Ag2S nanowire transistors. Small 5, 2377–2381 (2009)
S. Larentis, F. Nardi, S. Balatti, D.C. Gilmer, D. Ielmini, Resistive switching by voltage-driven ion migration in bipolar RRAM—part II: modeling. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 59, 2468–2475 (2012)
B. Geffroy, P. le Roy, C. Prat, Organic light-emitting diode (OLED) technology: materials, devices and display technologies. Polym. Int. 55, 572–582 (2006)
Y. Shirota, H. Kageyama, Charge carrier transporting molecular materials and their applications in devices. Chem. Rev. 107, 953–1010 (2007)
U. Schubert, N. Huesing, A. Lorenz, Hybrid inorganic-organic materials by sol-gel processing of organofunctional metal alkoxides. Chem. Mater. 7, 2010–2027 (1995)
C.-H. Huang, J.-S. Huang, S.-M. Lin, W.-Y. Chang, J.-H. He, Y.-L. Chueh, ZnO1–x nanorod arrays/ZnO Thin Film bilayer structure: from homojunction diode and high-performance memristor to complementary 1D1R application. ACS Nano 6, 8407–8414 (2012)
Y.C. Bae, A.R. Lee, J.B. Lee, J.H. Koo, K.C. Kwon, J.G. Park, H.S. Im, J.P. Hong, Oxygen ion drift-induced complementary resistive switching in homo TiOx/TiOy/TiOx and hetero TiOx/TiON/TiOx triple multilayer frameworks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 22, 709–716 (2012)
U. Bauer, L. Yao, A.J. Tan, P. Agrawal, S. Emori, H.L. Tuller, S. van Dijken, G.S.D. Beach, Magneto-ionic control of interfacial magnetism. Nat. Mater. 14, 174 (2014)
S.-M. Lin, J.-Y. Tseng, T.-Y. Su, Y.-C. Shih, J.-S. Huang, C.-H. Huang, S.-J. Lin, Y.-L. Chueh, Tunable multilevel storage of complementary resistive switching on single-step formation of ZnO/ZnWOx bilayer structure via interfacial engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 6, 17686–17693 (2014)
Z. Hu, Q. Li, M. Li, Q. Wang, Y. Zhu, X. Liu, X. Zhao, Y. Liu, S. Dong, Ferroelectric memristor based on Pt/BiFeO3/Nb-doped SrTiO3 heterostructure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 102901 (2013)
G. Hassan, S. Ali, J. Bae, C.H. Lee, Flexible resistive switching device based on poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrene sulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS)/poly(4-vinylphenol) (PVP) composite and methyl red heterojunction. Appl. Phys. A 123, 256 (2017)
K. Zhang, K. Sun, F. Wang, Y. Han, Z. Jiang, B. Wang, K. Liu, H.S.P. Wong, Electrochemical metallization and trapping/detrapping resistive switching mechanism in Al/VOx/Cu RRAM. ECS Solid State Lett. 3, Q63–Q66 (2014)
Y. Sun, C. Song, J. Yin, X. Chen, Q. Wan, F. Zeng, F. Pan, Guiding the growth of a conductive filament by nanoindentation to improve resistive switching. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 9, 34064–34070 (2017)
S. Ali, J. Bae, C.H. Lee, Organic diode with high rectification ratio made of electrohydrodynamic printed organic layers. Electron. Mater. Lett. 12, 270–275 (2016)
L.S.C. Pingree, B.A. MacLeod, D.S. Ginger, The changing face of PEDOT:PSS films: substrate, bias, and processing effects on vertical charge transport. J Phys Chem C 112, 7922–7927 (2008)
G.-F. Wang, X.-M. Tao, R.-X. Wang, Fabrication and characterization of OLEDs using PEDOT:PSS and MWCNT nanocomposites. Composit Sci Technol 68, 2837–2841 (2008)
X. Zhang, J. Wu, J. Wang, J. Zhang, Q. Yang, Y. Fu, Z. Xie, Highly conductive PEDOT:PSS transparent electrode prepared by a post-spin-rinsing method for efficient ITO-free polymer solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 144, 143–149 (2016)
X. Crispin, F.L.E. Jakobsson, A. Crispin, P.C.M. Grim, P. Andersson, A. Volodin, C. van Haesendonck, M. Van der Auweraer, W.R. Salaneck, M. Berggren, The origin of the high conductivity of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)—poly(styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT—PSS) plastic electrodes. Chem. Mater. 18, 4354–4360 (2006)
M.E. Londoño, J.M. Jaramillo, R. Sabater, J.M. Vélez, Dielectric properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels prepared by freezing/thawing technique. E.I.A. Revista 18, 105–114 (2012)
R. Scholz, L. Gisslén, C. Himcinschi, I. Vragović, E.M. Calzado, E. Louis, E. San Fabián, M.A. Maroto, Díaz-García, asymmetry between absorption and photoluminescence line shapes of TPD: spectroscopic fingerprint of the twisted biphenyl core. J Phys Chem A 113, 315–324 (2009)
L. Ma, Z. Wu, T. Lei, Y. Yu, F. Yuan, S. Ning, B. Jiao, X. Hou, Theoretical insight into the deep-blue amplified spontaneous emission of new organic semiconductor molecules. Org. Electron. 15, 3144–3153 (2014)
J. Ouyang, C.W. Chu, F.C. Chen, Q. Xu, Y. Yang, Polymer optoelectronic devices with high conductivity poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene) anodes. J Macromol Sci Part A 41, 1497–1511 (2004)
L. Keun Woo, K. Kyung Min, L. Junwye, A. Rashid, K. Byeonghoon, P. Sung Kye, L. Seok Kiu, P. Sung Ha, K. Hyun Jae, A two-dimensional DNA lattice implanted polymer solar cell. Nanotechnology 22, 375202 (2011)
Y. Sun, M. Tai, C. Song, Z. Wang, J. Yin, F. Li, H. Wu, F. Zeng, H. Lin, F. Pan, Competition between Metallic and Vacancy defect conductive filaments in a CH3NH3PbI3-based memory device. J Phys Chem C 122, 6431–6436 (2018)
P. Matyba, H. Yamaguchi, M. Chhowalla, N.D. Robinson, L. Edman, Flexible and metal-free light-emitting electrochemical cells based on graphene and PEDOT-PSS as the electrode materials. ACS Nano 5, 574–580 (2011)
S. Ali, J. Bae, C.H. Lee, N.P. Kobayashi, S. Shin, A. Ali, Resistive switching device with highly asymmetric current-voltage characteristics: a solution to backward sneak current in passive crossbar arrays. Nanotechnology 29, 455201 (2018)
M.M. Rehman, B.-S. Yang, Y.-J. Yang, K.S. Karimov, K.H. Choi, Effect of device structure on the resistive switching characteristics of organic polymers fabricated through all printed technology. Curr. Appl. Phys. 17, 533–540 (2017)
P. Singh, P.K. Rout, M. Singh, R.K. Rakshit, A. Dogra, Ferroelectric memory resistive behavior in BaTiO3/Nb doped SrTiO3 heterojunctions. Thin Solid Films 643, 60–64 (2017)
Z. Yongdan, L. Meiya, H. Zhongqiang, L. Xiaolian, W. Qiangwen, F. Xiaoli, G. Kaimo, Nonvolatile resistive switching behaviour and the mechanism in Nd:BiFeO 3 /Nb:SrTiO 3 heterostructure. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 46, 215305.` (2013)
M.N. Awais, M. Mustafa, M.N. Shehzad, U. Farooq, M.T. Hamayun, K.H. Choi, Resistive-switching and current-conduction mechanisms in F8BT polymer resistive switch. Micro Nano Lett 11, 712–714 (2016)
I. Stoica, E. Angheluta, M. Ivan, A. Farcas, D. Dorohoi, Electro-optical and morphological characterization of PVA foils with sulfathiazole. Digest J Nanomater Biostruct 6, 1667–1674 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (NRF-2016R1A2B4015627).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M.U., Hassan, G., Raza, M.A. et al. Bipolar resistive switching device based on N,N′-bis(3-methylphenyl)-N,N′-diphenylbenzidine and poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrene sulfonate)/poly(vinyl alcohol) bilayer stacked structure. Appl. Phys. A 124, 726 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2142-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2142-z