Abstract
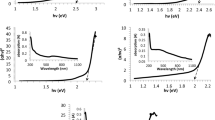
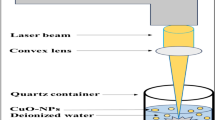
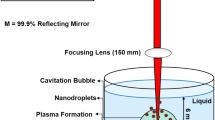
Large-scale commercial production of nanoparticles via efficient, economical, and environmentally friendly methods is a challenging endeavour. The laser ablation method being a green and potential route of nanoparticles synthesis can be exploited to achieve this end. In this work, we report the ablation of a copper target submerged in distilled water by pulsed Nd:YAG laser. The influence of ablation time on the structure and optical properties of grown copper oxide nanoparticles are studied. Such nanoparticle composition and structure is determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared, and Raman analyses. Results from transmission electron microscopy images established that synthesised nanoparticles are a spherical shape with average sizes of 24–37 nm. Fluorescence spectra revealed the enhancement of nanoparticle concentration and reduction in the sizes with increasing ablation time, where the optimum ablation time is demonstrated to be 60 min. Photoluminescence spectra exhibited a prominent visible peak (green), which blueshifted from 542 to 537 nm, confirming the shrinkage of copper oxide particle size at higher ablation time. The XRD pattern showed that the prepared nanoparticles possess a single phase of monocline cupric oxide nanostructure.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.B. Gawande, A. Goswami, F.X. Felpin, T. Asefa, X. Huang, R. Silva, X. Zou, R. Zboril, R.S. Varma, Chem. Rev. 116, 3722 (2016)
N.R. Dhineshbabu, V. Rajendran, N. Nithyavathy, R. Vetumperumal, Appl. Nanosci. 6, 933 (2016)
D.S. Murali, S. Kumar, R.J. Choudhary, A.D. Wadikar, M.K. Jain, A. Subrahmanyam, AIP Adv. 5, 1 (2015)
M.A. Gondal, T.F. Qahtan, M.A. Dastageer, T.A. Saleh, Y.W. Maganda (ed.), High-Capacity Opt. Networks Enabling Technol. (HONET-CNS) (IEEE, Piscataway, 2013), pp. 146–150
A.N. Abd, R.a. Ismail, N.F. Habubi, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 10 (2015)
V. Amendola, M. Meneghetti, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11, 3805 (2009)
A. Baladi, R.S. Mamoory, N. Group, Int. J. Mod. Phys. Conf. Ser. 5, 58 (2012)
A.R. Sadrolhosseini, S. Abdul Rashid, A. Zakaria, K. Shameli, J. Nanomater. 2016, 1 (2016)
R. Mahfouz, F.J. Cadete Santos Aires, A. Brenier, B. Jacquier, J.C. Bertolini, Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 5181 (2008)
K.S. Khashan, G.M. Sulaiman, F.A. Abdulameer, Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 41, (2016)
M. Muniz-Miranda, C. Gellini, A. Simonelli, M. Tiberi, F. Giammanco, E. Giorgetti, Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 110, 829 (2013)
M. Gondal, T.F. Qahtan, M. Dastageer, Y.W. Maganda, D.H. Anjum, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 13, 5759 (2013)
M.A. Gondal, T.F. Qahtan, M.A. Dastageer, T.A. Saleh, Y.W. Maganda, D.H. Anjum, Appl. Surf. Sci. 286, 149 (2013)
K. Amikura, T. Kimura, M. Hamada, N. Yokoyama, J. Miyazaki, Y. Yamada, Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 6976 (2008)
P.V. Kazakevich, A.V. Simakin, V.V. Voronov, G.A. Shafeev, Appl. Surf. Sci. 252, 4373 (2006)
R.K. Swarnkar, S.C. Singh, R. Gopal, Bull. Mater. Sci. 34, 1363 (2011)
S.A. Abdulateef, M.Z. MatJafri, A.F. Omar, N.M. Ahmed, S.A. Azzez, I.M. Ibrahim, B.E.B. Al-Jumaili, AIP Conf. Proc. 1733, 20035 (2016)
T. Tsuji, T. Hamagami, T. Kawamura, J. Yamaki, M. Tsuji, Appl. Surf. Sci. 243, 214 (2005)
S. Hamad, G.K. Podagatlapalli, S.P. Tewari, S.V. Rao, Pramana 82, 331 (2014)
D.C. Onwudiwe, T.P.J. Krüger, A. Jordaan, C.A. Strydom, Appl. Surf. Sci. 321, 197 (2014)
J. Xiao, P. Liu, C.X. Wang, G.W. Yang, Prog. Mater Sci. 87, 140 (2017)
A. Nath, A. Khare, J. Appl. Phys. 110, 043111 (2011)
S. Chandra, A. Kumar, P.K. Tomar, J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 18, 149 (2014)
S. Muthukumaran, R. Gopalakrishnan, Opt. Mater. (Amst). 34, 1946 (2012)
E. Kayahan, N. Ceylan, K. Esmer, Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 2808 (2008)
B.E.B. Al-Jumaili, Z.A. Talib, A. Ramizy, N.M. Ahmed, L.Y. Josephine, S.B. Paiman, I.B. Muhd, S.A. Abdulateef, J. Nanomater. 2016, 1–8 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia under Research University Grant Scheme Grant No. GP-IPB/2014/9449900 and the MHESR of Iraq for financial.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Jumaili, B.E.B., Talib, Z.A., Zakaria, A. et al. Impact of ablation time on Cu oxide nanoparticle green synthesis via pulsed laser ablation in liquid media. Appl. Phys. A 124, 577 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1995-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1995-5