Abstract
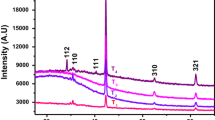
In the nanoscale architecture, expected morphology plays an important role in the fabrication of supercapacitive devices due to their highly porous properties. Herein, a well-defined rutile TiO2 architecture was successfully prepared by spray pyrolysis technique (SPT), by changing the concentration of the spraying solution from 0.01 to 0.1 M at 723 K deposition temperature onto stainless steel substrates. The thermal decomposition behavior of the precursor is analyzed using thermogravimetric analyzer. As-deposited thin film electrodes exhibits rutile tetragonal crystalline structure confirmed using XRD. FT-IR study indicate the presence of Ti=O stretching vibration in the range 400–1000 cm−1. The obtained nanostructures merely changes by changing the concentration of spraying solution and process parameters as strongly evidenced using SEM. TEM image and SAED pattern confirms the formation of nanorods and rutile tetragonal structure of TiO2. EDAX confirms formation of pristine TiO2. Wettability of samples shows angle of contact changes by changing the sample thickness and surface roughness of the samples. Optimized electrode shows maximum specific capacitance 273.84 F/g at 2 mV/s in 1 M KOH. Maximum values of specific energy (SE), specific power (SP) and efficiency as observed using galvanostatic charge–discharge are 04.32 Wh/Kg, 70.27 KW/Kg and 90.37%, respectively.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Wang, L. Zhang, J. Zhang, A review of electrode materials for electrochemical supercapacitors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 797 (2012)
C. Largoet, C. Portet, J. Chmiola, P. Taberna, Y. Gogotsi, P. Simon, Relation between the Ion size and pore size for an electric double-layer capacitor. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 2730 (2008)
R. Kotz, M. Carlen, Principles and applications of electrochemical capacitors. Electrochem. Acta 45, 2483 (2000)
A. Burke, Ultracapacitors: why, how, and where is the technology. J. Power Sources 91, 37 (2000)
B.E. Conway, Electrochemical supercapacitors (Kluwer Academic/Plenum, New York, 1999)
H.P. Deshmukh, P.S. Shinde, P.S. Patil, Structural, optical and electrical characterization of spray-deposited TiO2 thin films. Mater. Sci. Engg. B 130, 220 (2006)
H. Zhan, Y. Zhong, Z. He, L. Zhang, J. Wang, J. Zang, C. Cao, Three-dimensional nanoporous TiO2 network films with excellent electrochemical capacitance performance. Alloys Compd. 597, 1 (2014)
D. Zhang, G. Li, X. Yang, J.C. Yu, A micrometer-size TiO2 single-crystal photocatalyst with remarkable 80% level of reactive facets. Chem. Commun. 29, 4381 (2009)
J. Fu, Photocatalytic properties of glass ceramics containing anatase-type TiO2. Mater. Lett. 68, 419 (2012)
Z. Liu, M. Misra, Dye-sensitized photovoltaic wires using highly ordered TiO2 nanotube arrays. ACS Nano 4, 2196 (2010)
B.Y. Fugare, B.J. Lokhande, Spray pyrolysed titanium oxide thin films using different ingredients for supercapacitive charaterizations. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 5788 (2016)
G. Du, B. Wan, Z. Guo, J. Shen, Y. Li, H. Liu, Effect of annealing on electrochemical performance of anodized TiO2 nanotubes for lithium ion batteries. Adv. Sci. Lett. 4, 469 (2011)
Y. Xia, P. Yang, Y. Sun, Y. Wu, B. Mayers, B. Gates, Y. Yin, F. Kim, H. Yan, One- dimensional nanostructures: synthesis, characterization, and applications. Adv. Mater. 15, 353 (2003)
Y. Leprince-Wang, K. Yu-Zhang, Study of the growth morphology of TiO2 thin films by AFM and TEM. Surf. Coat. Technol. 140, 155 (2001)
R.C. Weast (Ed), Hand book of chemistry and physics, 67th edn. CRC, Boca Rotan, p. B-140, (1986–1987)
N-G Park, Van de Lagemaat, Frank AJ, Comparison of dye-sensitized rutile-and anatase-based TiO2 solar cells, J. Phys. Chem. B, 104, 8989, (2000)
R. Mechiakh, N. Ben Sedrine, R. Chitourou, R. Bensaha, Correlation between microstructure and optical properties of nano-crystalline TiO2 thin films prepared by sol–gel dip coating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 670 (2010)
G.H. Kim, S.D. Kim, S.H. Park, Plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition of TiO2 films on silica gel powders at atmospheric pressure in a circulating fluidized bed reactor. Chem. Eng. Process: Proc. Intens. 48, 1135 (2009)
M.W. Pyun, E.J. Kim, D.H. Yoo, S.H. Hann, Oblique angle deposition of TiO2 thin films prepared by electron-beam evaporation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 1149 (2010)
C. Sima, C. Grigoriu, Electrical properties of ultrathin titanium dioxide films on silicon. Thin Solid Films, 518, 1314, (2009)
T. Paulmier, J.M. Bell, P.M. Fredericks, Plasma electrolytic deposition of titanium dioxide nanorods and nano-particles. Mater. Process. Technol. 208, 117 (2008)
I. OjaAcik, A. Junolainen, V. Mikli, M. Danielson, M. Krunks, Growth of ultra-thin TiO2 films by spray pyrolysis on different substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 1391 (2009)
D. Mardare, F. Iacomi, N. Cornel, M. Girtan, D. Luca, Undoped and Cr-doped TiO2 thin films obtained by spray pyrolysis. Thin Solid Films 518, 4586 (2010)
D. Perednis, L. Gauckler, Thin film deposition using spray pyrolysis. Electroceram. 14, 103 (2005)
R.W. Schwartz, T. Schneller, R. Waser, C R Chim., Chemical solution deposition of electronic oxide films, 7, 433 (2004)
R.S. Mane, Y.H. Hwang, C.D. Lokhande, S.D. Sartale, S.H. Han, Room temperature synthesis of compact TiO2 thin films for 3-D solar cells by chemical arrested route. Appl. Surf. Sci. 246, 271 (2005)
L. Castaneda, J.C. Alonso, A. Ortiz, E. Andrade, J.M. Saniger, J.G. Banuelos, Spray pyrolysis deposition and characterization of titanium oxide thin films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 77, 938 (2002)
W. Wu-Qiang, H.S. Rao, H.L. Feng, X.D. Guo, S. Cheng-Yong, Morphology-controlled cactus-like branched anatase TiO2 arrays with high light-harvesting efficiency for dye-sensitized solar cells. Power Sourc. 260, 6 (2014)
A. Moses Ezhil Raj, V. Agnes, V. BenaJothy, C. Sanjeeviraja, Low temperature TiO2 rutile phase thin film synthesis by chemical spray pyrolysis (CSP) of titanyl acetylacetonate. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 13, 391 (2010)
E. Bae, N. Murakami, T. Ohno, Exposed crystal surface-controlled TiO2 nanorods having rutile phase from TiCl3 under hydrothermal conditions. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 300, 72 (2009)
M.M. Viana, V.F. Soares, N.D.S. Mohallem, Synthesis and characterization of TiO2 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 36, 2047 (2010)
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-ray diffraction, 2nd edn. (Addison-Wesely publishing company, Reading, 1978)
M.M. Ba-Abbad, A.M.H. Kadhum, A.B. Mohammad, M.S. Takriff, K. Sopian, Synthesis and catalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles for photochemical oxidation of concentrated chlorophenols under direct solar radiation. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 7, 4878 (2012)
Y. Wang, L. Zhang, K. Deng, X. Chen, Z. Zou, Low temperature synthesis and photocatalytic activity of rutile TiO2 nanorod superstructures. J Phys Chem C 111, 2709 (2007)
J.W. Lang, L.B. Kong, W.J. Wu, Y.C. Lau, L. Kong, Facile approach to prepare loose-packed NiO nano-flakes materials for supercapacitors, Chem. Comm. 5, 4213 (2008)
D. Quere., Wetting and roughness, Annu. Rev. Mater. Res., 38, 71, (2008)
P.D. Cozzoli, A. Kornowski, H. Weller, Low-temperature synthesis of soluble and processable organic-capped anatase TiO2 nanorods. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 14539 (2003)
M. Salari, K. Konstantinov, H.K. Liu, Enhancement of the capacitance in TiO2 nanotubes through controlled introduction of oxygen vacancies. Mater. Chem. 21, 5128 (2011)
B.J. Lokhande, R.C. Ambare, R.S. Mane, S.R. Bharadwaj, Boron-doped cadmium oxide composite structures and their electrochemical measurements. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 2978 (2013)
K.K. Liu, Z.L. Hu, R. Xue, J.R. Zhang, Z.J. Zhu, Power Sourc. 176, 862 (2008)
Y. Xie, D. Fu, Supercapacitance of ruthenium oxide deposited on titania and titanium substrates. Mater. Chem. Phys. 122, 27 (2010)
J.S. Ye, H.F. Cui, X. Liu, T.M. Lim, W.D. Zhang, F.S. Sheu, Preparation and characterization of aligned carbon nanotube–ruthenium oxide nanocomposites for supercapacitors. Small 1, 560 (2005)
T. Berger, T. Lana-Villarreal, D. Monllor-Satoca, R. G´omez, An electrochemical study on the nature of trap states in nanocrystalline rutile thin films. J. Phys. Chem. C 111(27), 9936 (2007)
Acknowledgement
Authors are grateful to DST-SERB for providing financial support through the Project Scheme SB/EMEQ-331/2013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fugare, B.Y., Lokhande, B.J. The influence of concentration on the morphology of TiO2 thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis for electrochemical study. Appl. Phys. A 123, 394 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1008-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1008-0