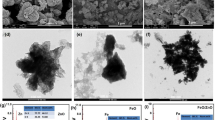
Abstract
Nanogenerators (NGs) which harvest energy from mechanical vibration have attracted more attention in the past decade. Piezoelectric materials are the most promising candidates for developing NGs. Flexible free-standing nano-ZnO/PVDF composite films are prepared by incorporating different amounts of nano-ZnO fillers in PVDF matrix using sol–gel technique. Poled films show enhanced dielectric constant. The above free-standing films, with appropriate contacts, are subjected to energy harvesting studies. The output voltage increases with nano-ZnO loading in the PVDF matrix and shows enhanced effect for the poled films. Piezoelectric properties are investigated by measuring the piezoelectric charge constant (d 33) and piezoelectric voltage constant (g 33). A maximum AC output voltage ~4 V and output power of the order of few nanowatts are recorded for the nanogenerator which is used to light a red LED using a rectifying circuit through the discharging of a capacitor.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.H. Kim, B. Kumar, K.Y. Lee, H.K. Park, J.H. Lee, H.H. Lee, H. Jun, D. Lee, S.W. Kim, Piezoelectric two-dimensional nanosheets/anionic layer heterojunction for efficient direct current power generation. Sci. Rep. 3, 1–6 (2017)
L. Chen, X. Xu, P. Zeng, J. Ma, Integration of energy harvester for self-powered wireless sensor network nodes. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2014, 1–7 (2014)
T. Huang, C. Wang, H. Yu, H. Wang, Q. Zhang, M. Zhu, Human walking-driven wearable all-fiber triboelectric nanogenerator containing electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride piezoelectric nanofibers. Nano Energy 14, 226–235 (2015)
K.-I. Park, S. Xu, Y. Liu, G.-T. Hwang, S.-J.L. Kang, Z.L. Wang, K.J. Lee, Piezoelectric BaTiO3 thin film nanogenerator on plastic substrates. Nano Lett. 10(12), 4939–4943 (2010)
Z.-H. Lin, Y. Yang, J.M. Wu, Y. Liu, F. Zhang, Z.L. Wang, BaTiO3 nanotubes-based flexible and transparent nanogenerators. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 3, 3599–3604 (2012)
G. Zhu, R. Yang, S. Wang, Z.L. Wang, Flexible high-output nanogenerator based on lateral ZnO nanowire array. Nano Lett. 10, 3151–3155 (2010)
K.Y. Lee, M.K. Gupta, S.W. Kim, Transparent flexible stretchable piezoelectric and triboelectric nanogenerators for powering portable electronics. Nano Energy 14, 139–160 (2014)
Y.K.A. Low, L.Y. Tan, L.P. Tan, F.Y.C. Boey, K.W. Ng, Increasing solvent polarity and addition of salts promote β-phase poly(vinylidene fluoride) formation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 128, 2902–2910 (2013)
V. Strashilov, G. Alexieva, B. Vincent, V.S. Nguyen, D. Rouxel, Structural impact on piezoelectricity in PVDF and P(VDF-TrFE) thin films. Appl. Phys. A 118, 1469–1477 (2015)
Y.-J. Lee, J. Wang, S.R. Cheng, J.W.P. Hsu, Solution processed ZnO hybrid nanocomposite with tailored work function for improved electron transport layer in organic photovoltaic devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 9128–9133 (2013)
W.K. Choi, D.H. Park, B.W. Kwon, D.I. Son, US Patent No. WO2012165753 A1, Application No. PCT/KR2012/001433 (2012)
C.J.L. Constantino, A.E. Job, R.D. Simoes, J.A. Giacometti, V. Zucolotto, O.N. Oliveira Jr., G. Gozzi, D.L. Chinaglia, Phase transition in poly(vinylidene fluoride) investigated with micro-Raman spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 59, 275–279 (2005)
S. Satapathy, S. Pawar, P.K. Gupta, K.B.R. Varma, Effect of annealing on phase transition in poly(vinylidene fluoride) films prepared using polar solvent. Bull. Mater. Sci. 34, 727–733 (2011)
T. Boccaccio, A. Bottino, G. Capannelli, P. Piaggio, Characterization of PVDF membranes by vibrational spectroscopy. J. Membr. Sci. 210, 315–329 (2002)
Y. Bormashenko, R. Pogreb, O. Stanevsky, E. Bormashenko, Vibrational spectrum of PVDF and its interpretation. Polym. Testing 23, 791–796 (2004)
B. Mattsson, H. Ericson, L.M. Torell, F. Sundholm, Degradation of a fuel cell membrane, as revealed by micro-Raman spectroscopy. Electrochim. Acta 45, 1405–1408 (2000)
B. Mattsson, H. Ericson, L.M. Torell, F. Sundholm, Micro-Raman investigations of PVDF-based proton-conducting membranes. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 37, 3317–3327 (1999)
M.T. Riosbaas, K.J. Loh, G.O. Bryan, B.R. Loyol, In situ phase change characterization of PVDF thin films using Raman spectroscopy. Proc. SPIE 9061, 90610Z (2014). doi:10.1117/12.2045430
A. Kaschner, U. Haboeck, M. Strassburg, M. Strassburg, G. Kaczmarczyk, A. Hoffmann, C. Thomsen, A. Zeuner, H.R. Alves, D.M. Hofmann, B.K. Meyer, Nitrogen-related local vibrational modes in ZnO:N. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 1909–1911 (2002)
B. Cheng, Y. Xiao, G. Wu, L. Zhang, The vibrational properties of one-dimensional ZnO: Ce nanostructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 416–418 (2004)
C. Bundesmann, N. Ashkenov, M. Schubert, D. Spemann, T. Butz, E.M. Kaidashev, M. Lorenz, M. Grundmann, Raman scattering in ZnO thin films doped with Fe, Sb, Al, Ga, and Li. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 1974–1976 (2003)
J. Bird, Electrical Circuit Theory and Technology (Routledge, Abingdon, 2014), p. 567
A.R. West, D.C. Sinclair, N. Hirose, Characterization of electrical materials, especially ferroelectrics, by impedance spectroscopy. J. Electroceram. 1, 65–71 (1997)
J.S. Harrison, Z. Ounaies, Piezoelectric Polymers Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology (Wiley, New York, 2002), pp. 474–498
K.S. Ramadan, D. Sameoto, S. Evoy, A review of piezoelectric polymers as functional materials for electromechanical transducers. Smart Mater. Struct. 23, 033001 (2014)
H. Landolt, R. Börnstein, H. Fischer, O. Madelung, G. Deuschle, Landolt-Bornstein: Numerical Data and Functional Relationships in Science and Technology, ed. by O. Madelung. New Series, Group III, Vol. 17 (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1987), p. 164
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Board of Research in Nuclear Sciences (BRNS), Government of India, for the financial assistance to carry out this research program. R.B. wishes to thank the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, while S.D. wishes to thank the BRNS, Government of India, for their fellowships.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhunia, R., Das, S., Dalui, S. et al. Flexible nano-ZnO/polyvinylidene difluoride piezoelectric composite films as energy harvester. Appl. Phys. A 122, 637 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0161-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0161-1