Abstract
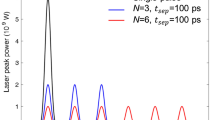
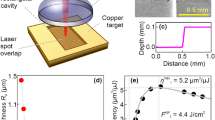
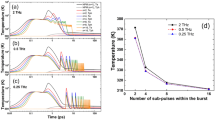
This paper deals with the unique phenomena occurring during the multi-burst mode picosecond (ps) laser ablation of metals through modeling and experimental studies. The two-temperature model (TTM) is used and expanded to calculate the ablation depth in the multi-burst mode. A nonlinear increment of ablation volume is found during the multi-burst laser ablation. The deactivation of ablated material and the application of temperature-dependent electron-phonon coupling are demonstrated to be important to provide reliable results. The simulation results based on this expanded laser ablation model are experimentally validated. A significant increase of ablation rate is found in the multi-burst mode, compared with the single-pulse mode under the same total fluence. This numerical model provides a physical perspective into the energy transport process during multi-burst laser ablation and can be used to study the pulse-to-pulse separation time effect on the ablation rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Nolte, C. Momma, H. Jacobs, A. Tünnermann, B.N. Chichkov, B. Wellegehausen, H. Welling, Ablation of metals by ultrashort laser pulses. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 14, 2716 (1997)
J. Jandeleit, A. Horn, E.W. Kreutz, R. Poprawe, Micromachining of metals and ceramics by nano- and picosecond laser radiation. Proc. SPIE 3223, 34 (1997)
F. Dausinger, H. Hügel, V. Konov, Micro-machining with ultrashort laser pulses: From basic understanding to technical applications. Proc. SPIE 5147, 106 (2003)
M. Lapczyna, K.P. Chen, P.R. Herman, H.W. Tan, R.S. Marjoribanks, Ultra high repetition rate (133 MHz) laser ablation of aluminum with 1.2-ps pulses. Appl. Phys. A 69, S883 (1999)
R. Le Harzic, D. Breitling, S. Sommer, C. Föhl, K. König, F. Dausinger, E. Audouard, Processing of metals by double pulses with short laser pulses. Appl. Phys. A 81, 1121 (2005)
A. Semerok, C. Dutouquet, Ultrashort double pulse laser ablation of metals. Thin Solid Films 453–454, 501 (2004)
O. Andrusyak, M. Bubelnik, J. Mares, T. McGovern, C.W. Siders, Single-pulse and burst-mode ablation of gold films measured by quartz crystal microbalance. Proc. SPIE 5647, 61 (2005)
A.A. Andreev, J. Limpouch, A.B. Iskakov, H. Nakano, Enhancement of x-ray line emission from plasmas produced by short high-intensity laser double pulses. Phys. Rev. E 65, 026403 (2002)
C. Lehane, H.S. Kwok, Enhanced drilling using a dual-pulse Nd:YAG laser. Appl. Phys. A 73, 45 (2001)
A.C. Forsman, P.S. Banks, M.D. Perry, E.M. Campbell, A.L. Dodell, M.S. Armas, Double-pulse machining as a technique for the enhancement of material removal rates in laser machining of metals. J. Appl. Phys. 98, 033302 (2005)
G.W. Rieger, M. Taschuk, Y.Y. Tsui, R. Fedosejevs, Comparative study of laser-induced plasma emission from microjoule picosecond and nanosecond KrF-laser pulses. Spectrochim. Acta, Part B 58, 497 (2003)
A. Ancona, F. Röser, K. Rademaker, J. Limpert, S. Nolte, A. Tünnermann, High speed laser drilling of metals using a high repetition rate, high average power ultrafast fiber CPA system. Opt. Express 16, 8958 (2008)
C. Cheng, X. Xu, Mechanisms of decomposition of metal during femtosecond laser ablation. Phys. Rev. B 72, 165415 (2005)
B. Wu, Y.C. Shin, A simple model for high fluence ultra-short pulsed laser metal ablation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 247, 4079 (2007)
B.H. Christensen, K. Vestentoft, P. Balling, Short-pulse ablation rates and the two-temperature model. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253, 6347 (2007)
F. Vidal, T.W. Johnston, S. Laville, O. Barthelemy, M. Chaker, B.L. Drogoff, J. Margot, M. Sabsabi, Critical-point phase separation in laser ablation of conductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 2573 (2001)
T.Q. Qiu, C.L. Tien, Heat transfer mechanisms during short-pulse laser heating of metals. ASME J. Heat Transfer 115, 835 (1993)
S.I. Anisimov, V.V. Zhakhovski, N.A. Inogamov, K. Nishihara, Yu.V. Petrov, V.A. Khokhlov, Ablated matter expansion and crater formation under the action of ultrashort laser pulse. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 103, 183 (2006)
B. Sallé, O. Gobert, P. Meynadier, M. Perdrix, G. Petite, A. Semerok, Femtosecond and picosecond laser microablation: ablation efficiency and laser microplasma expansion. Appl. Phys. A 69, S381 (1999)
A. Semerok, B. Sallé, J.F. Wagner, G. Petite, O. Gobert, P. Meynadier, M. Perdrix, Microablation of pure metals: laser plasma and crater investigations. Proc. SPIE 4423, 153 (2001)
S.S. Wellershoff, J. Hohlfeld, J. Güdde, E. Matthias, The role of electron-phonon coupling in femtosecond laser damage of metals. Appl. Phys. A 69, S99 (1999)
J.K. Chen, W.P. Latham, J.E. Beraun, The role of electron-phonon coupling in ultrafast laser heating. J. Laser Appl. 17, 63 (2005)
N.N. Nedialkov, S.E. Imamova, P.A. Atanasov, Ablation of metals by ultrashort laser pulses. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 37, 638 (2004)
K. Furusawa, K. Takahashi, H. Kumagai, K. Midorikawa, M. Obara, Ablation characteristics of Au, Ag, and Cu metals using a femtosecond Ti:sapphire laser. Appl. Phys. A 69, S359 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, W., Shin, Y.C. & King, G. Modeling of multi-burst mode pico-second laser ablation for improved material removal rate. Appl. Phys. A 98, 407–415 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-009-5405-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-009-5405-x