Abstract
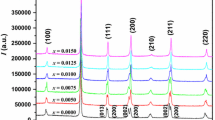
(1−x−y)Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3–xBi0.5K0.5TiO3– yBi0.5Li0.5TiO3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics have been prepared by an ordinary sintering technique, and their structure, electrical properties, and temperature characteristics have been studied systematically. The ceramics can be well-sintered at 1050–1150 °C. The increase in K+ concentration decreases the grain-growth rate and promotes the formation of grains with a cubic shape, while the addition of Li+ decreases greatly the sintering temperature and assists in the densification of BNT-based ceramics. The results of XRD diffraction show that K+ and Li+ diffuse into the Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3 lattices to form a solid solution with a pure perovskite structure. As x increases from 0.05 to 0.50, the ceramics transform gradually from rhombohedral phase to tetragonal phase and consequently a morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) is formed at 0.15≤x≤0.25. The concentration y of Li+ has no obvious influence on the crystal structure of the ceramics. Compared with pure Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3, the partial substitution of K+ and Li+ for Na+ lowers greatly the coercive field E c and increases the remanent polarization P r of the ceramics. Because of the MPB, lower E c and large P r, the piezoelectricity of the ceramics is improved significantly. For the ceramics with the compositions near the MPB (x=0.15–0.25 and y=0.05–0.10), the piezoelectric properties become optimum: piezoelectric coefficient d 33=147–231 pC/N and planar electromechanical coupling factor k P=20.2–41.0%. In addition, the ceramics exhibit relaxor characteristic, which probably results from the cation disordering in the 12-fold coordination sites. The depolarization temperature T d shows a strong dependence on the concentration x of K+ and reaches the lowest values at the MPB. The temperature dependences of the ferroelectric and dielectric properties at high temperatures may imply that the ceramics may contain both the polar and non-polar regions at temperatures above T d.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.A. Smolenskii, V.A. Isupov, A.I. Agranovskaya, N.N. Krainik, Sov. Phys. Solid State 2, 2651 (1961)
T. Takennaka, K. Maruyama, K. Sakata, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 30, 2236 (1991)
A. Herabut, A. Safari, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80(11), 2954 (1997)
A. Sasaki, T. Chiba, Y. Mamiya, E. Otsuki, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 38(9B), 5564 (1999)
K. Yoshii, Y. Hiruma, H. Nagata, T. Takenaka, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 45(5B), 4493 (2006)
S. Zhao, G. Li, A. Ding, T. Wang, Q.R. Yin, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 39, 2277 (2006)
Z. Yang, B. Liu, L. Wei, Y. Hou, Mater. Res. Bull. 43, 81 (2008)
B.J. Chu, D.R. Chen, G.R. Li, Q.R. Yin, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 22, 2115 (2002)
G. Fan, W. Lu, X. Wang, F. Liang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 202908 (2007)
Y.M. Li, W. Chen, J. Zhou, Q. Xu, H.J. Sun, R.X. Xu, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 112, 5 (2004)
K. Pengpat, S. Hauphimol, S. Eitssayeam, U. Intutha, G. Rujijangul, T. Tunkasiri, J. Electroceram. 16, 301 (2006)
D. Lin, D. Xiao, J. Zhu, P. Yu, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26, 3247 (2006)
X.X. Wang, X.G. Tang, H.L.W. Chan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 91 (2004)
J. Shieh, K.C. Wu, C.S. Chen, Acta Mater. 55(9), 3081 (2007)
S. Zhang, T.R. Shrout, H. Nagata, Y. Hiruma, T. Takenaka, IEEE Trans. Ultrason., Ferroelect., Freq. Contr. 54(5), 910 (2007)
Y. Makiuchi, R. Aoyagi, Y. Hiruma, H. Nagata, T. Takenaka, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 44, 4350 (2005)
Y. Li, W. Chen, Q. Xu, J. Zhou, X. Gu, S. Fang, Mater. Chem. Phys. 94, 328 (2005)
X.X. Wang, S.H. Choy, X.G. Tang, H.L.W. Chan, J. Appl. Phys. 97, 104101 (2005)
D. Lin, K.W. Kwok, H.L.W. Chan, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40, 5354 (2007)
Y.Q. Yao, T.Y. Tseng, C.C. Chou, H.H.D. Chen, J. Appl. Phys. 102, 094102 (2007)
D. Lin, D. Xiao, J. Zhu, P. Yu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 062901 (2006)
E. Fukuchi, T. Kimura, T. Tani, Y. Saito, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 85(6), 1461 (2002)
Y. Hiruma, R. Aoyagi, H. Nagata, T. Takenaka, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. A 44(7), 5040 (2005)
C. Karthik, N. Ravishankar, K.B.R. Varma, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 042905 (2006)
N. Setter, L.E. Cross, J. Appl. Phys. 51, 4356 (1980)
J.K. Lee, J.Y. Yi, K.S. Hong, J. Sol. Stat. Chem. 177, 2850 (2004)
J. Suchanicz, J. Kusz, H. Böhm, H. Duda, J.P. Mercurio, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 22, 1559 (2003)
J. Suchanicz, J. Kusz, H. Böhm, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 97, 154 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, D., Zheng, Q., Xu, C. et al. Structure, electrical properties and temperature characteristics of Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3–Bi0.5K0.5TiO3–Bi0.5Li0.5TiO3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. Appl. Phys. A 93, 549–558 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-008-4667-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-008-4667-z