Abstract
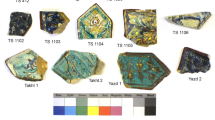
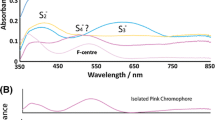
Ceramic tiles used to manufacture artistic panels during the XVI to the XVIII centuries were decorated with high-lead soda-lime glazes, incorporating a diversity of chromophore cations, as ascertained by SRXRF (synchrotron radiation X-ray fluorescence). Previous X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) studies have shown that sodium and lead are hosted by the glassy matrix in those glazes. However, the possible role of calcium as a modifier of the tetrahedral silica network is not fully clarified, despite being recognized that calcium cations alter some fundamental properties of glazes, namely transparency. An X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) study of glazes with varied colorings was therefore undertaken at Ca K- and L-edges. Well crystallized oxide minerals were used to model distinct coordination environments by oxygen atoms – close to octahedral geometry in calcite and dodecahedral in gypsum – while fluorite was chosen to mimic ideal cubic coordination. A first XAS approach suggested a minor variation in the energy separation between L2–L3 absorption edges when comparing blue and yellow glazes, irrespective of the period of manufacture. A further study on the X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) carried out at the K-edge corroborated this difference and, along with the theoretical spectra modeling performed with the FEFF code, allowed interpreting of the Ca 1s absorption spectra of glazes as arising from a non-regular high-coordination environment within the silica matrix.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.M. Santos Simões, “Azulejaria” in Portugal along XV and XVI centuries. A General Introduction (Fundação Calouste Gulbenkian, Portugal, 1990) [in Portuguese]
J. Molera, T. Pradell, N. Salvadó, M. Vendrell-Saz, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 2871 (1999)
L. Cormier, L. Galoisy, J.-M. Delaye, D. Ghaleb, G. Calas, Comptes Rendues de l’Acad. Sc. Paris t.2, IV, 249 (2001)
L. Cormier, D.R. Neuville, Chem. Geol. 213, 103 (2004)
M.O. Figueiredo, T.P. Silva, J.P. Veiga, Appl. Phys. A 83, 209 (2006)
M.O. Figueiredo, J.P. Veiga, T.P. Silva, J.P. Mirão, S. Pascarelli, Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 238, 134 (2005)
H. Effenberger, K. Mereiter, I. Zemann, Z. Kristallogr. 156, 233 (1981)
R.W.G. Wyckoff, Crystal Structures, 2nd edn. (Wiley, New York, 1964), Vol. 1, pp. 239–241
P. Pederson, D. Semmingsen, Acta Cryst. B 38, 1074 (1982)
P. Chevallier, P. Dehz, F. Legrand, A. Erko, Y. Agafonov, L.A. Panchenko, A. Yashkin, J. Trace Microprobe Techniques 14, 517 (1996)
J.X. Wang, D. Piccot, P. Chevallier, F. Legrand, K. Abbas, Note CEA-N-2756 (1993)
M.J. Carmezim, M.O. Figueiredo, Adv. Mater. Forum I 230–232, 311 (2002)
J. Susini, M. Salomé, B. Fayard, R. Ortega, B. Kaulich, Surf. Rev. Lett. 9, 203 (2002)
M.O. Figueiredo, J.P. Veiga, T.P. Silva, J.P. Mirão, S. Pascarelli, Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 238, 134 (2005)
M.O. Figueiredo, AIP Conf. Proc. 882, 205 (2007)
A.L. Ankudinov, J.J. Rehr, Phys. Rev. B 62, 2437 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
PACS
61.43.Fs; 41.60.Ap; 61.10.Ht
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Veiga, J., Figueiredo, M. Calcium in ancient glazes and glasses: a XAFS study. Appl. Phys. A 92, 229–233 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-008-4496-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-008-4496-0