Abstract.
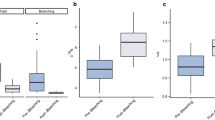
This study investigated the variation of bioerosional processes in relation to disturbances of reefal communities due to eutrophication. La Saline fringing reef (Reunion Island) is subjected to nutrient inputs from the adjacent land. Bioerosion by grazers, microborers, and macroborers was measured using experimental substrata exposed for 1 year in three sites characterized by different levels of nutrient input and benthic community response. The relationship between bioerosion and epilithic algal cover of hard substrata and the interactions between the various agents of bioerosion were analyzed with parametric statistics. Significant variations in bioerosion were found among sites, ranging from 1.63 to 3.52 kg CaCO3 m–2 year–1 for grazing rates, from 6.73 to 32.25 g m–2 year–1 for macroboring rates, and from 43.78 to 67.56 g m–2 year–1 for microboring rates. One of the major factors controlling these variations appeared to be changes in the epilithic algal cover on substrata in response to changes in reefal water chemistry. In low nutrient areas, where dead corals were colonized mainly by algal turfs, erosion by microorganisms was low (43.78 g m–2 year–1) due to intense grazing (3.52 kg m–2 year–1). In reef zones receiving high nutrient inputs, the development of encrusting calcareous algae and macroalgae was associated with the lowest grazing (1.63 kg m–2 year–1) and macroboring (6.73 g m–2 year–1) rates recorded among sites. In contrast, high microboring rates (57.54 and 67.56 g m–2 year–1) were found in enriched areas in association with high macroalgal cover.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chazottes, .V., Le Campion-Alsumard, .T., Peyrot-Clausade, .M. et al. The effects of eutrophication-related alterations to coral reef communities on agents and rates of bioerosion (Reunion Island, Indian Ocean). Coral Reefs 21, 375–390 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-002-0259-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-002-0259-0