Abstract.
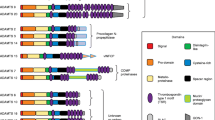
Thrombospondins are a family of extracellular, adhesive proteins that are widely expressed in vertebrates. Five distinct gene products, designated thrombospondin-1 through -4 and cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP), have been identified. With the exception of thrombospondin-4, the structure and location of thrombospondin genes have been determined in the human and/or mouse genomes. In this study, the structure and location of the murine thrombospondin-4 gene and the location of the human thrombospondin-4 gene are reported. The murine thrombospondin-4 gene is approximately 4.5 kb in length and includes 22 exons. Interspecific backcross analysis of progeny derived from matings of (C57BL/6J ×Mus spretus)F1× C57BL/6J mice indicates that the thrombospondin-4 gene is tightly linked to the Dhfr locus on murine Chromosome (Chr) 13. The human gene maps to Chr 5 in band q13 by in situ hybridization to human metaphase chromosomes. The thrombospondin-4 promoter is similar to promoters of some housekeeping, growth control, and other thrombospondin genes in that it contains multiple GC box sequences and lacks a CAAT box. The presence of multiple E-box sequence motifs is consistent with thrombospondin-4 expression in muscle and bone tissue.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 18 May 1998 / Accepted: 24 May 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Newton, G., Weremowicz, S., Morton, C. et al. The thrombospondin-4 gene. 10, 1010–1016 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003359901149
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003359901149