Abstract.
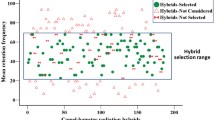
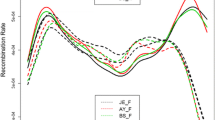
A dog whole-genome radiation hybrid (WGRH) panel including 126 clones was constructed by fusing dog fibroblasts irradiated at 5000 rads with thymidine kinase-deficient hamster cells. The average retention frequency of the panel designated as RHDF5000 is 21%, and its resolution power is estimated at 600 kb. The data provided by typing 400 markers were used to estimate linkage power changes subsequent to panel reduction. These changes were analyzed by recomputing typing data from five reduced panels. From these simulations, the parameters allowing investigation of the evolution of the linkage power in the course of panel reduction were determined. Guidelines for constructing a WGRH panel are proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 23 February 1999 / Accepted: 11 May 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vignaux, F., Hitte, C., Priat, C. et al. Construction and optimization of a dog whole-genome radiation hybrid panel. 10, 888–894 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003359901109
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003359901109