Abstract
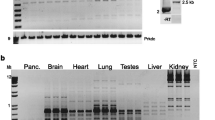
We have cloned and sequenced the mouse transcript homologous to human polycystic kidney disease 1 (PKD1). The predicted protein is 79% identical to human PKD1 and shows the presence of most of the domains identified in the human sequence. Since the mouse homolog is transcribed from a unique gene and there are no transcribed, closely related copies as has been observed for human PKD1, we have been able to investigate alternative splicing of the transcript. At the junction of exons 12 and 13, several different splicing variants lead to a predicted protein that would be secreted. These forms are predominantly found in newborn brain, while in kidney the transcript homologous to the previously described human RNA predominates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American PKD1 Consortium (1995) Analysis of the genomic sequence for the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (PKD1) gene predicts the presence of a leucine-rich repeat. Hum Mol Gene 4, 575–582
Claros MG, von Heijne G (1994) TopPred II: an improved software for membrane protein structure predictions. Comput Appl Biosci 10, 685–686
Duan DS, Werner S, Williams LT (1992) A naturally occurring secreted form of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor 1 binds basic FGF in preference over acidic FGF. J Biol Chem 267, 16076–16080
European Polycystic Kidney Disease Consortium (1994) The polycystic kidney disease 1 gene encodes a 14 kb transcript and lies within a duplicated region on chromosome 16. Cell 77, 881–894
Hughes J, Ward CJ, Peral B, Aspinwall R, Clark K, Sanmillan JL, Gamble V. Harris PC (1995) The polycystic kidney disease 1 (PKD1) gene encodes a novel protein with multiple cell recognition domains. Nature Genet 10, 151–160
International Polycystic Kidney Disease Consortium (1995) Polycystic kidney disease: the complete structure of the PKD1 gene and its protein. Cell 81, 289–298
Kozak M (1987) At least six nucleotides preceding the AUG initiator codon enhance translation in mammalian cells. J Mol Biol 196, 947–950
Mochizuki T, Wu GQ, Hayashi T, Xenophontos SL, Veldhuisen B, Saris JJ, Reynolds DM, Cai YQ, Gabow PA, Pierides A, Kimberling WJ, Breuning MH, Deltas CC, Peters DJM, Somlo S (1996) PKD2, a gene for polycystic kidney disease that encodes an integral membrane protein. Science 272, 1339–1342
Mosley B, Beckmann MP, March CJ, Idzerda RL, Gimpel SD, VandenBos T, Friend D, Alpert A, Anderson D, Jackson J et al. (1989) The murine interleukin-4 receptor: molecular cloning and characterization of secreted and membrane bound forms. Cell 59, 335–348
Moy GW, Mendoza LM, Schulz JR, Swanson WJ, Glabe CG, Vacquier VD (1996) The sea-urchin sperm receptor for egg jelly is a modular protein with extensive homology to the human polycystic kidney disease protein, PKD1. J Cell Biol 133, 809–817
Olsson PG, Lohntag C, Horsley S, Kearney L, Harris PC, Frischauf AM (1996) The mouse homolog of the polycystic kidney disease gene (PKD1) is a single copy gene. Genomics 34, 233–235
Peral B, Gamble V, Millan JLS, Strong C, Sloanestanley J, Moreno F, Harris PC (1995) Splicing mutations of the polycystic kidney disease 1 (PKD1) gene induced by intronic deletion. Hum Mol Genet 4, 569–574
Peral B, Ong ACM, Sanmillan JL, Gamble V, Rees L, Harris PC (1996a) A stable, nonsense mutation associated with a case of infantile onset polycystic kidney disease 1 (PKD1). Hum Mol Genet 5, 539–542
Peral B, Sanmillan JL, Ong ACM, Gamble V, Ward CJ, Strong C, Harris PC (1996b) Screening the 3s′ region of the polycystic kidney disease 1 (PKD1) gene reveals 6 novel mutations. Am J Hum Genet 58, 86–96
Petch LA, Harris J, Raymond VW, Blasband A, Lee DC, Earp HS (1990) A truncated, secreted form of the epidermal growth factor receptor is encoded by an alternatively spliced transcript in normal rat tissue. Mol Cell Biol 10, 2973–2982
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989). Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. (Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press)
Schneider MC, Zhang F, Geng L, Pohlschmidt M, Zhou J, Zhao H, Torosian S, Lohntag C, Kovats S, Frischauf A, Reeders ST, Fu YH (1994) Identification of the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease gene. Am J Hum Genet 55, 37
Turco AE, Rossetti S, Bresin E, Corra S, Gammaro L, Maschio G, Pignatti PF (1995) A novel nonsense mutation in the PKD1 gene (C3817T) is associated with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) in a large 3-generation italian family. Hum Mol Genet 4, 1331–1335
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Löhning, C., Nowicka, U. & Frischauf, AM. The mouse homolog of PKD1: Sequence analysis and alternative splicing. Mammalian Genome 8, 307–311 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003359900429
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003359900429