Abstract
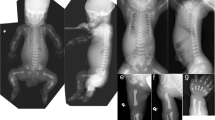
Rbt (Rabo torcido) is a new semidominant mouse mutant with a variety of skeletal abnormalities. Heterozygous Rbt mutants display homeotic anteroposterior patterning problems along the axial skeleton that resemble Polycomb group and trithorax gene mutations. In addition, the Rbt mutant displays strong similarities to the phenotype observed in Ts (Tail-short), indicating also a homeotically transformed phenotype in these mice. We have mapped the Rbt locus to an interval of approximately 6 cM on mouse Chromosome (Chr) 11 between microsatellite markers D11Mit128 and D11 Mit 103. The Ts locus was mapped within a shorter interval of approximately 3 cM between D11Mit128 and D11Mit203. This indicates that Rbt and Ts may be allelic mutations. Sox9, the human homolog of which is responsible for the skeletal malformation syndrome campomelic dysplasia, was mapped proximal to D11Mit128. It is, therefore, unlikely that Ts and Rbt are mouse models for this human skeletal disorder.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akasaka, T., Kanno, M., Balling, R., Mieza, M.A., Taniguchi, M., Koseki, H. (1996). A role for mel-18, a polycomb group-related vertebrate gene, during the anteroposterior specification of the axial skeleton. Development 122, 1513–1522.
Alkema, M.J., van der Lugt, N.M.T., Bobeldijk, R.C., Berns, A., van Lohuizen, M. (1995). Transformation of axial skeleton due to overex-pression of bmi-1 in transgenic mice. Nature 374, 724–727.
Bedell, M.A., Jenkins, N.A., Copeland, N.G. (1996). Good genes in bad neighbourhoods. Nature Genet. 380, 229–232.
Breen, M, Deakin, L., MacDonald, B., Miller, S., Sibson, R., Tarttelin, E., Avner, P., Bourgade, F., Guénet, J.-L., Montagutelli, X., Poirier, C., Simon, D., Tailor, D., Bishop, M., Kelly, M., Rysavy, F., Rastan, S., Norris, D., Shepherd, D., Abbott, C, Pilz, A., Hodge, S., Jackson, I., Boyd, Y., Blair, H., Maslen, G., Todd, J.A., Read, P.W., Stoye, J., Ashworth, A., McCarthy, L., Cox, R., Schalkwyk, L., Lehrach, H., Klose, J., Gangadharan, I., Brown, S. (1994). Towards high resolution maps of the mouse and human genomes. A facility for ordering markers to 0.1 cM resolution. Hum. Mol. Genet. 3, 621–627.
Brunk, B.P., Martin, E.C., Adler, P.N. (1991). Drosophila genes posterior sex combs and suppressor two of zeste encode proteins with homology to the murine bmi-1 oncogene. Nature 353, 351–355.
Candia, A.F., Hu, J., Crosby, J., Lalley, P.A., Noden, D., Nadeau, J.H., Wright, C.V.E. (1992). Moxl and Mox2 define a novel homeobox gene subfamily and are differentially expressed during early mesodermal patterning in mouse embryos. Development 116, 1123–1136.
Deol, M.S. (1961). Genetical studies on the skeleton of the mouse. XXVIII. Tail-short. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 155, 78–95.
Dietrich, W., Katz, H., Lincoln, S.E., Shin, H.-S., Friedman, J., Dracopoli, N., Lander, E.S. (1992). A genetic map of the mouse suitable for typing intraspecific crosses. Genetics 131, 423–447.
Dietrich, F.D., Miller, J., Steen, R., Merchant, M.A., Damron-Boles, D., Husain, Z., Dredge, R., Daly, M.J., Ingalls, K.A., O’Connor, T.J., Evans, CA., DeAngelis, M.M., Levinson, D.M., Kruglyak, L., Goodman, N., Copeland, N.G., Jenkins, N.A., Hawkins, T.L., Stein, L., Page, D.C., Lander, E.S. (1996). Comprehensive genetic map of the mouse genome. Nature 380, 149–152.
Faust, C., Schumacher, A., Hildener, B., Magnuson, T. (1995). The eed mutation disrupts anterior mesoderm production in mice. Development 121, 273–285.
Foster, J.W., Dominguez-Steglich, M.A., Guioli, S., Kwok, C., Weiler, P.A., Stevanovic, M., Weissenbach, J., Mansour, S., Young, I.D., Goodfellow, P.N., Brook, J.D., Schafer, A.J. (1994). Campomelic dysplasia and autosomal sex reversal caused by mutations in an SRY-related gene. Nature 372, 525–530.
Hearne, C.M., McAleer, M.A., Love, J.M., Aitman, T.J., Cornall, R.J., Ghosh, S., Knight, A.M., Prins, J.-B., Todd, J.A. (1991). Additional microsatellite markers for mouse genome mapping. Mamm. Genome 1, 273–282.
Hobert, O., Sures, I., Ciossek, T., Fuchs, M., Ullrich, A. (1996). Isolation and developmental expression analysis of Enx-1. A novel mouse Polycomb group gene. Mech. Dev. 55, 171–184.
Houston, C.S., Opitz, J.M., Spranger, J.W., Macpherson, R.I., Reed, M.H., Gilbert, E.F., Herrmann, J., Schinzel, A. (1983). The campomelic syndrome: review, report of 17 cases, and follow-up on the currently 17-year old boy first reported by Maroteaux et al. in 1971. Am. J. Med. Genet. 15, 3–28.
Kessel, Gruss, (1991). Homeotic transformations of murine vertebrae and concomitant alteration of Hox codes induced by retinoic acid. Cell 67, 89–104.
Krumlauf, R. (1994). Hox genes in vertebrate development. Cell 78, 191–201.
Lyon, M.F., Rastan, S., Brown, S.D.M. (1996). Genetic Variants and Strains of the Laboratory Mouse. (Oxford: Oxford University Press).
McGinnis, W., Krumlauf, R. (1992). Homeobox genes and axial patterning. Cell 68, 283–302.
Morgan, W.C. (1950). A new tail-short mutation in the mouse. J. Hered. 41, 208–215.
Müller, J., Gaunt, S., Lawrence P.A. (1995). Function of the Polycomb protein is conserved in mice and flies. Development 121, 2847–2852.
Nomura, M., Takihara, Y., Shimada, K. (1994). Isolation and characterization of retinoic acid-inducible cDNA clones in F9 cells: one of the early inducible clones encodes a novel protein sharing several highly homologous regions with a Drosophila Polyhomeotic protein. Differentiation 57, 39–50.
Orlando, V., Paro, R. (1995). Chromatin multiprotein complexes involved in the maintenance of transcription patterns. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 5, 174–179.
Paterson, H.F. (1980). In vivo and in vitro studies on early embryonic lethal Tail-short (Ts) in the mouse. J. Exp. Zool. 211, 247–256.
Pearce, J.J.H., Singh, P.B., Gaunt, S.J. (1992). The mouse has a Polycomb-like chromobox gene. Development 114, 912–929.
Schmitt, K., Foster, J.W., Feakes, R.W., Knights, C, Davis, M.E., Spillet, D.J., Goodfellow P.N. (1996). Construction of a mouse whole-genome radiation hybrid panel and application to MMU11. Genomics 34, 193–197.
Simon, J., (1995). Locking in stable states of gene expression: transcriptional control during Drosophila development. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 7, 376–385.
Sweet, H.O., Roderick, T.H., Davisson, M.T. (1979). Chr 11 linkage. Mouse News Lett. 60, 51.
Tagava, M., Sakamoto, T., Shigemoto, K., Matsubara, H., Tamura, Y., Ito, T., Nakamura, I., Okitsu, A., Imai, K., Taniguchi, M. (1990). Expression of novel DNA-binding protein with zinc finger structure in various tumor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 20021–20026.
Tommerup, N., Schempp, W., Meinecke, P., Pedersen, S., Bolund, L., Brandt, C., Goodpasture, C., Guldberg, P., Held, K.R., Reinwein, H., Saugstad, O.D., Scherer, G., Skjeldal, O., Toder, R., Westvik, J., van der Hagen, C.B., Wolf, U. (1993). Assignment of an autosomal sex reversal locus (SRAl) and campomelic dysplasia (CMPD1) to 17q24.3-q25.1. Nature Genet, 4, 170–174.
Van der Lugt, N.M.T., Domen, J., Linders, K., van Roon, M., Robanus-Maandag, E., te Riele, H., van der Falk, M., Deschamps, J., Sofroniew, M., van Lohuizen, M., Burns, A. (1994). Posterior transformation, neurological abnormalities, and severe hematopoietic defects in mice with a targeted deletion of bmi-1 proto-oncogene. Genes & Dev. 8, 757–769.
Wagner, T., Wirth, J., Meyer, J., Zabel, B., Held, M., Zimmer, J., Pasantes, J., Dagna Bricarelli, F., Keutel, J., Hustert, E., Wolf, U., Tommerup, N., Schempp, W., Scherer, G. (1994). Autosomal sex reversal and campomelic dysplasia are caused by mutations in and around the SRY-related gene SOX9. Cell 79, 1111–1120.
Wirth, J., Wagner, T., Meyer, J., Pfeiffer, R.A., Tietze, H.U., Schempp, W., Scherer, G. (1996). Translocation breakpoints in three patients with campomelic dysplasia and autosomal sex reversal map more than 130 kb from SOX9. Hum. Genet. 97, 186–193.
Wright, E., Hargrave, M.R., Christiansen, J., Cooper, L., Kun, J., Evans, T., Gangadharan, U., Greenfield, A., Koopman, P. (1995). The Sry-related gene Sox9 is expressed during chondrogenesis in mouse embryos. Nature Genet. 9, 15–20.
Yu, B.D., Hess, J.L., Horning, S.E., Brown, G.A.J., Korsmeyer, S.J. (1995). Alterered Hox expression and segmentation identity in MII-mutant mice. Nature 378, 505–508.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hustert, E., Scherer, G., Olowson, M. et al. Rbt (rabo torcido), a new mouse skeletal mutation involved in anteroposterior patterning of the axial skeleton, maps close to the ts (tail-short) locus and distal to the sox9 locus on chromosome 11. Mammalian Genome 7, 881–885 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003359900261
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003359900261