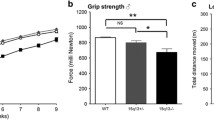
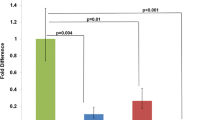
Abstract
Megencephaly, enlarged brain, occurs in several acquired and inherited human diseases including Sotos syndrome, Robinow syndrome, Canavan’s disease, and Alexander disease. This defect can be distinguished from macrocephaly, an enlarged head, which usually occurs as a consequence of congenital hydrocephalus. The pathology of megencephaly in humans has not been well defined, nor has the defect been reported to occur spontaneously in any other species. In this report we describe a recessive mutation in the mouse that results in a 25% increase in brain size in the first 8 months of life. We have determined that the megencephaly is characterized by overall hypertrophy of the brain, and not by hyperplasia of particular cell types or by hypertrophy of a singular tissue compartment. Edema and hydrocephalus are absent. This mutation has been mapped to mid-distal mouse Chromosome (Chr) 6 in a region homologous with human Chr 12.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adomato, B.T., O’Brien, J.S., Lampert, P.W., Roe, T.F., Neustein, H.B. (1972). Cerebral spongy degeneration of infancy: a biochemical and ultrastructural study of affected twins. Neurology 22, 202–210.
Alexander, W.S. (1949). Progressive fibroid degeneration of fibrillary astrocytes associated with mental retardation in hydrocephalic infant. Brain 72, 373–381.
Belknap, J.K., Phillips, T.J., O’Toole, L.A. (1992). Quantitative trait loci associated with brain weight in the BXD/Ty recombinant inbred mouse strains. Brain Res. Bull. 29, 337–344.
Bignami, A. (1968). Unilateral megalencephaly with nerve cell hypertrophy. An anatomical and quantitative histochemical study. Brain Res. 9, 103–114.
Carson, M.J., Behringer, R.R., Brinster, R.L., McMorris, F.A. (1993). Insulin-like growth factor I increases brain growth and central nervous system myelination in transgenic mice. Neuron 10, 729–740.
Davisson, M.T. (1990). The Jackson Laboratory mouse mutant resource. Lab. Anim. 19, 23–29.
DeMyer, W. (1986). Megalencephaly: types, clinical syndromes, and management. Pediatr. Neurol. 2, 321–328.
DeMyer, W.E. (1972). Megalencephaly in children: clinical syndromes, genetic patterns, and differential diagnosis for other causes of megalocephaly. Neurology 22, 634–643.
Dietrich, W., Katz, H., Lincoln S. E, Shin, H.-S., Friedman J, Dracopoli, N.C. S, L.E. (1992). A genetic map of the mouse suitable for typing intraspecific crosses. Genetics 131, 423–447.
Donahue, L.R., Beamer, W.G. (1993). Growth hormone deficiency in ‘little’ mice results in aberrant body composition, reduced insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3), but does not affect IGFBP-2, -1, or -4. J. Endocrinol. 136, 91–104.
Fuller, J.L. (1979). Fuller BWS lines: history and results. In Development and Evolution of Brain Size. ME. Hahn, C. Jensen, B.C. Dudek, eds. (New Yoifc Academic Press), pp. 187–204.
Gooskens, R.H.J.M., WUlemse, J., Bijlsma, J.B., Hanlo, P.W. (1988). Megalencephaly: definition and classification. Brain Dev. 10, 1–7.
Johnson, K.R., Cook, S.A. (1994). Identification and genetic mapping of 151 dispersed members of 16 ribosomal protein multigene families in the mouse. Mamm. Genome 5, 670–687.
Klocke K., Roberds, S.L., Tamkun, M.M., Gronemeir, M., Augustin, A., Albrecht, B., Pongs, O., Jockusch, H. (1993). Chromosomal mapping in the mouse of eight K+channel genes representing the four Shaker-like subfamilies Shaker, Shab, Shaw, and Shal. Genomics 18, 568–574.
Labarca, C, Paigen, K. (1980). A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal. Biochem. 102, 344–352.
Lock, L.F., Gilbert, D.J., Street, V.A., Migeon, M.B., Jenkins, N.A., Copeland, N.G., Tempel, B.L. (1994). Voltage-gated potassium channel genes are clustered in paralogous regions of the mouse genome. Genomics 20, 354–362.
Lorber, J., Priestley, B.L. (1981). Children with large heads: a practical approach to diagnosis in 557 children, with special reference to 109 children with megalencephaly. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 23, 494–504.
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J. (1951). Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
Manly, K.F. (1993). A Macintosh program for storage and analysis of experimental genetic mapping data. Mamm. Genome 4, 303–313.
Mathews, L.S., Hammer, R.E., Behringer, R.R., D’Ercole, A.J., Bell, G.I., Brinster, R.L., Palmiter, R.D. (1988). Growth enhancement of transgenic mice expressing human insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology 123, 2827–2833.
Meisler, M.H., Barrow, L.L., Canessa, CM., Rossier, B.C. (1994). SCNNI, an epithelial cell sodium channel gene in the conserved linkage group on mouse Chromosome 6 and human Chromosome 12. Genomics 24, 185–186.
Moore, K. (1995). Mouse Genome Informatics Project, Chromosome 6 Committee Report; Mouse Genome Database (MGD). (Bar Harbor, Me.: The Jackson Laboratory), World Wide Web (URL:http://www. informatics.jax.org/).
Pettit, R.E., Kilroy, A.W., Allen, J.H. (1980). Macrocephaly with head growth parallel to normal growth pattern. Arch. Neurol. 37, 518–521.
Robinow, M., Silverman, F.N., Smith, H.D. (1969). A newly recognized dwarfing syndrome. Am. J. Dis. Child. 117, 645–651.
Roderick, T.H., Wimer, R.E., Wimer, C.C., Schwartzkroin, P.A. (1973). Genetic and phenotypic variation in weight of brain and spinal cord between inbred strains of mice. Brain Res. 64, 345–353.
Roderick, T.H., Wimer, R.E., Wimer, C.C. (1976). Genetic manipulation of neuroanatomical traits. In Knowing, Thinking and Believing, L. Petrinovich, J.L. McGaugh, eds. (New York: Plenum Publishing Corp), pp. 143–178.
Storer, J.B. (1967). Relation of lifespan to brain weight, body weight, and metabolic rate among inbred mouse strains. Exp. Gerontol. 2, 173–182.
Street, V.A. (1995). Molecular genetic analysis of distal mouse Chromosome 6 defines gene order and positions of the deafwaddler and opisthotonos mutations. Genomics 29, 129–130.
Wahlsten, D. (1974). Heritable aspects of anomalous myelinated fibre tracts in the forebrain of the laboratory mouse. Brain Res. 68, 1–18.
Whinship, I.M. (1985). Sotos syndrome-autosomal dominant inheritance substantiated. Clin. Genet. 28, 243–246.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Donahue, L.R., Cook, S.A., Johnson, K.R. et al. Megencephaly: a new mouse mutation on chromosome 6 that causes hypertrophy of the brain. Mammalian Genome 7, 871–876 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003359900259
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003359900259