Abstract
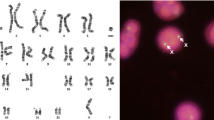
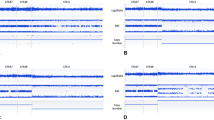
Chromosomal aberrations in the horse are known to cause congenital abnormalities, embryonic loss, and infertility. While diagnosed mainly by karyotyping and FISH in the horse, the use of SNP array comparative genome hybridization (SNP-CGH) is becoming increasingly common in human diagnostics. Normalized probe intensities and allelic ratios are used to detect changes in copy number genome-wide. Two horses with suspected chromosomal abnormalities and six horses with FISH-confirmed aberrant karyotypes were chosen for genotyping on the Equine SNP50 array. Karyotyping of the first horse indicated mosaicism for an additional small, acrocentric chromosome, although the identity of the chromosome was unclear. The second case displayed a similar phenotype to human disease caused by a gene deletion and so was chosen for SNP-CGH due to the ability to detect changes at higher resolutions than those achieved with conventional karyotyping. The results of SNP-CGH analysis for the six horses with known chromosomal aberrations agreed completely with previous karyotype and FISH analysis. The first undiagnosed case showed a pattern of altered allelic ratios without a noticeable shift in overall intensity for chromosome 27, consistent with a mosaic trisomy. The second case displayed a more drastic change in both values for chromosome 30, consistent with a complete trisomy. These results indicate that SNP-CGH is a viable method for detection of chromosomal aneuploidies in the horse.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brooks SA, Gabreski N, Miller D, Brisbin A, Brown HE, Streeter C, Mezey J, Cook D, Antczak DF (2010) Whole-genome SNP association in the horse: identification of a deletion in myosin Va responsible for Lavender Foal Syndrome. PLoS Genet 6:e1000909
Candille SI, Kaelin CB, Cattanach BM, Yu B, Thompson DA, Nix MA, Kerns JA, Schmutz SM, Millhauser GL, Barsh GS (2007) A β-defensin mutation causes black coat color in domestic dogs. Science 318:1418–1423
Conlin LK, Thiel BD, Bonnemann CG, Medne L, Ernst LM, Zackai EH, Deardorff MA, Krantz ID, Hakonarson H, Spinner NB (2010) Mechanisms of mosaicism, chimerism, and uniparental disomy identified by single nucleotide polymorphism array analysis. Hum Mol Genet 19:1263–1275
Faas BH, Feenstra I, Eggink AJ, Kooper AJ, Pfundt R, van Vugt JM, de Leeuw N (2012) Non-targeted whole genome 250 K SNP array analysis as replacement for karyotyping in fetuses with structural ultrasound anomalies: evaluation of a one-year experience. Prenat Diagn 32:362–370
ISCNH (1997) International system for cytogenetic nomenclature of the domestic horse. Chromosome Res 5:433–443
Lear TL, Bailey E (2008) Equine clinical cytogenetics: the past and future. Cytogenet Genome Res 120:42–49
Lear TL, Brandon R, Bell K (1999a) Localization of ten horse microsatellite markers by FISH. Anim Genet 30:235
Lear TL, Cox JH, Kennedy GA (1999b) Autosomal trisomy in a thoroughbred colt: 65,XY,+31. Equine Vet J 31:85–88
Lear TL, Brandon R, Piumi F, Terry RR, Guerin G, Thomas S, Bailey E (2001) Mapping of 31 horse genes in BACs by FISH. Chromosome Res 9:261–262
Lear TL, Lundquist J, Zent WW, Fishback WD Jr, Clark A (2008) Three autosomal chromosome translocations associated with repeated early embryonic loss (REEL) in the domestic horse (Equus caballus). Cytogenet Genome Res 120:117–122
McCue ME, Bannasch DL, Petersen JL, Gurr J, Bailey E, Binns MM, Distl O, Guérin G, Hasegawa T, Hill EW, Leeb T, Lindgren G, Penedo MC, Røed KH, Ryder OA, Swinburne JE, Tozaki T, Valberg SJ, Vaudin M, Lindblad-Toh K, Wade CM, Mickelson JR (2012) A high density SNP array for the domestic horse and extant Perissodactyla: utility for association mapping, genetic diversity, and phylogeny studies. PLoS Genet 8:e1002451
Peiffer DA, Le JM, Steemers FJ, Chang W, Jenniges T, Garcia F, Haden K, Li J, Shaw CA, Belmont J, Cheung SW, Shen RM, Barker DL, Gunderson KL (2006) High-resolution genomic profiling of chromosomal aberrations using infinium whole-genome genotyping. Genome Res 16:1136–1148
R Development Core Team (2009) ISBN 3-900051-07-0. http://www.R-project.org/. Accessed 01 Nov 2012
Seabright M (1971) A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet 2:971–972
Srebniak MI, Boter M, Oudesluijs GO, Cohen-Overbeek T, Govaerts LC, Diderich KE, Oegema R, Knapen MF, van de Laar IM, Joosten M, Van Opstal D, Galjaard RH (2012) Genomic SNP array as a gold standard for prenatal diagnosis of foetal ultrasound abnormalities. Mol Cytogenet 5:14
Wang K, Li M, Hadley D, Liu R, Glessner J, Grant S, Hakonarson H, Bucan M (2007) PennCNV: an integrated hidden Markov model designed for high-resolution copy number variation detection in whole-genome SNP genotyping data. Genome Res 17:1665–1674
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the owners of the horses used in this study for providing samples, and Julie Fronczek, Suellen Charter, and the rest of the Cytogenetics Laboratory at the San Diego Zoo’s Institute for Conservation Research for cell culture assistance. TLL acknowledges Judy Lundquist for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holl, H.M., Lear, T.L., Nolen-Walston, R.D. et al. Detection of two equine trisomies using SNP-CGH. Mamm Genome 24, 252–256 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-013-9450-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-013-9450-6