Abstract
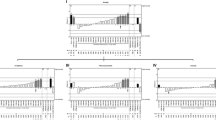
We measured fear conditioning (FC) in a panel of chromosome substitution strains (CSS) created using the C57BL/6J (B6) and A/J (AJ) inbred strains. Mice were trained to associate a specific context and tone with a foot shock. FC was measured by observing freezing behavior during re-exposure to the context and tone. Freezing to context was more than twofold greater in the AJ strain relative to the B6 strain. Among the CSS we identified four strains with higher (CSS-6, -10, -11, and -18) and two strains with lower (CSS-7 and -14) freezing to context. CSS-10 and -18 also showed higher freezing to tone, while CSS-12 showed less freezing to tone. CSS-1 has been implicated in open-field (OF) and light-dark box (LDB); we observed significant activity differences prior to training but no differences in FC. Chromosomes 6 and 10 have been associated with differences in anxiety-like behaviors, suggesting the existence of pleiotropic alleles that influence both learned and innate fear. By utilizing a genetic reference population, we have identified chromosomes that pleiotropically influence multiple phenotypes hypothesized to reflect a common ethologic construct that has been termed emotionality. The CSS provide a straightforward means of isolating the underlying genetic factors.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belknap JK (2003) Chromosome substitution strains: some quantitative considerations for genome scans and fine mapping. Mamm Genome 14:723–732
Caldarone B, Saavedra C, Tartaglia K, Wehner JM, Dudek BC, et al. (1997) Quantitative trait loci analysis affecting contextual conditioning in mice [see comments]. Nat Genet 17:335–337
Davis M (1992) The role of the amygdala in fear-potentiated startle: implications for animal models of anxiety. Trends Pharmacol Sci 13:35–41
Dexter WR, Merrill HK (1969) Role of contextual discrimination in fear conditioning. J Comp Physiol Psychol 69:677–681
Fendt M, Fanselow MS (1999) The neuroanatomical and neurochemical basis of conditioned fear. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:743–760
Fernandez-Teruel A, Escorihuela RM, Gray JA, Aguilar R, Gil L, Gimenez-Llort L, Tobena A, Bhomra A, Nicod A, Mott R, Driscoll P, Dawson GR, Flint J (2002) A quantitative trait locus influencing anxiety in the laboratory rat. Genome Res 12, 618–626
Gershenfeld HK, Neumann PE, Mathis C, Crawley JN, Li X, et al. (1997) Mapping quantitative trait loci for open-field behavior in mice. Behavior Genet 27:201–210
Gershenfeld HK, Paul SM (1997) Mapping quantitative trait loci for fear-like behaviors in mice. Genomics 46:1–8
Henderson ND, Turri MG, DeFries JC, Flint J (2004) QTL analysis of multiple behavioral measures of anxiety in mice. Behav Genet 34:267–293
Hettema JM, Annas P, Neale MC, Kendler KS, Fredrikson M (2003) A twin study of the genetics of fear conditioning. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60:702–708
Klemenhagen KC, Gordon JA, David DJ, Hen R, Gross CT (2006) Increased fear response to contextual cues in mice lacking the 5-HT1A receptor. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:101–111
LaBar KS, LeDoux JE, Spencer DD, Phelps EA (1995) Impaired fear conditioning following unilateral temporal lobectomy in humans. J Neurosci 15:6846–6855
LaBar KS, Gatenby JC, Gore JC, LeDoux JE, Phelps EA (1998) Human amygdala activation during conditioned fear acquisition and extinction: a mixed-trial fMRI study. Neuron 20:937–945
LeDoux JE (2000) Emotion circuits in the brain. Annu Rev Neurosci 23:155–184
Lissek S, Powers AS, McClure EB, Phelps EA, Woldehawariat G, et al. (2005) Classical fear conditioning in the anxiety disorders: a meta-analysis. Behav Res Therapy 43:1391–1424
McNish KA, Gewirtz JC, Davis M (1997) Evidence of contextual fear after lesions of the hippocampus: a disruption of freezing but not fear-potentiated startle. J Neurosci 17:9353–9360
Owen EH, Christensen SC, Paylor R, Wehner JM (1997) Identification of quantitative trait loci involved in contextual and auditory-cued fear conditioning in BXD recombinant inbred strains. Behav Neurosci 111:292–300
Phillips RG, LeDoux JE (1992) Differential contribution of amygdala and hippocampus to cued and contextual fear conditioning. Behav Neurosci 106:274–285
Ponder CA, Kliethermes CL, Drew MR, Muller J, Das K, et al. (2007) Selection for contextual fear conditioning affects anxiety-like behaviors and gene expression. Genes Brain Behav (in press)
Radcliffe RA, Lowe MV, Wehner JM (2000) Confirmation of contextual fear conditioning QTLs by short-term selection. Behav Genetics 30:183–191
Richardson MP, Strange BA, Dolan RJ (2004) Encoding of emotional memories depends on amygdala and hippocampus and their interactions. Nat Neurosci 7:278–285
Risbrough VB, Brodkin JD, Geyer MA (2003) GABA-A and 5-HT1A receptor agonists block expression of fear-potentiated startle in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:654–663
Santos JM, Gâargaro AC, Oliveira AR, Masson S, Brandäao ML (2005) Pharmacological dissociation of moderate and high contextual fear as assessed by freezing behavior and fear-potentiated startle. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 15:239–246
Singer JB, Hill AE, Burrage LC, Olszens KR, Song J, et al. (2004) Genetic dissection of complex traits with chromosome substitution strains of mice. Science 304:445–448
Singer JB, Hill AE, Nadeau JH, Lander ES (2005) Mapping quantitative trait loci for anxiety in chromosome substitution strains of mice. Genetics 169:855–862
Stylianou IM, Tsaih SW, Dipetrillo K, Ishimori N, Li R, et al. (2006) Complex genetic architecture revealed by analysis of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in chromosome substitution strains and f2 crosses. Genetics 174:999–1007
Talbot CJ, Radcliffe RA, Fullerton J, Hitzemann R, Wehner JM, et al. (2003) Fine scale mapping of a genetic locus for conditioned fear. Mamm Genome 14:223–230
Wehner JM, Radcliffe RA, Rosmann ST, Christensen SC, Rasmussen DL, et al. (1997) Quantitative trait locus analysis of contextual fear conditioning in mice [see comment]. Nat Genetics 17:331–334
Zhang S, Lou Y, Amstein TM, Anyango M, Mohibullah N, et al. (2005) Fine mapping of a major locus on chromosome 10 for exploratory and fear-like behavior in mice. Mamm Genome 16:306–318
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by K01MH70933, T32GM07088 and a NARSAD young investigator award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ponder, C.A., Munoz, M., Gilliam, T.C. et al. Genetic architecture of fear conditioning in chromosome substitution strains: relationship to measures of innate (unlearned) anxiety-like behavior. Mamm Genome 18, 221–228 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-007-9013-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-007-9013-9