Abstract
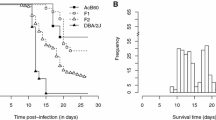
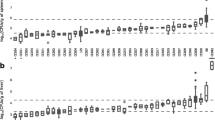
The extreme susceptibility to infection with Salmonella Typhimurium of wild-derived MOLF/Ei mice has been linked to one genomic region on Chromosome 1 (Ity3). A member of the Toll-like receptors family, Tlr5, located on distal Chromosome 1, was previously shown to be a candidate gene for Ity3 based on expression studies and sequencing analysis. The candidacy of Tlr5 as a Salmonella-susceptibility gene was evaluated functionally by comparing Tlr5 C57BL/6J and MOLF/Ei alleles in vitro and in vivo. In vitro studies showed that the MOLF/Ei Tlr5 allele is more transcriptionally active when the gene is removed from its natural genomic environment. This observation was supported by in vivo studies in B6.MOLF-Ity3 congenic mice that showed that mice homozygous for the MOLF/Ei allele at Ity3, including Tlr5, had an increased response to flagellin as measured by IL-6 and CXCL-1 secretion in the serum compared with parental MOLF/Ei mice. Despite the fact that both MOLF/Ei and B6.MOLF-Ity/Ity3 mice are more susceptible to Salmonella Typhimurium infection than B6.MOLF-Ity mice, they exhibit a different phenotype with respect to Tlr5 expression and Tlr5 signaling, supporting the prediction that Tlr5 is not primarily involved in the disease phenotype underlying the Ity3 locus in MOLF/Ei mice.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abiola O, Angel JM, Avner P, Bachmanov AA, Belknap JK, et al. (2003) The nature and identification of quantitative trait loci: a community’s view. Nat Rev Genet 4(11): 911–916
Adamo R, Sokol S, Soong G, Gomez MI, Prince A (2004) Pseudomonas aeruginosa flagella activate airway epithelial cells through asialoGM1 and Toll-like receptor 2 as well as Toll-like receptor 5. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 30(5): 627–634
Akira S, Takeda K (2004) Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 4(7): 499–511
Bambou J-C, Giraud A, Menard S, Begue B, Rakotobe S, et al. (2004) In vitro and ex vivo activation of the TLR5 signaling pathway in intestinal epithelial cells by a commensal Escherichia coli strain. J Biol Chem 279(41): 42984–42992
Barton GM, Medzhitov R (2003) Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Science 300(5625): 1524–1525
Chini BA, Fiedler MA, Milligan L, Hopkins T, Stark JM (1998) Essential roles of NF-κB and C/EBP in the regulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 after respiratory syncytial virus infection of human respiratory epithelial cell cultures. J Virol 72(2): 1623–1626
Didierlaurent A, Ferrero I, Otten LA, Dubois B, Reinhardt M, et al. (2004) Flagellin promotes myeloid differentiation factor 88-dependent development of Th2-type response. J Immunol 172(11): 6922–6930
Donnelly MA, Steiner TS (2002) Two nonadjacent regions in enteroaggregative Escherichia coli flagellin are required for activation of Toll-like receptor 5. J Biol Chem 277(43): 40456–40461
Ducut Sigala JL, Bottero V, Young DB, Shevchenko A, Mercurio F, et al. (2004) Activation of transcription factor NF-κB requires ELKS, an IκB kinase regulatory subunit. Science 304(5679): 1963–1967
Dunstan SJ, Hawn TR, Hue NT, Parry CP, Ho VA, et al. (2005) Host susceptibility and clinical outcomes in toll-like receptor 5-deficient patients with typhoid fever in Vietnam. J Infect Dis 191(7): 1068–1071
Eaves-Pyles T, Murthy K, Liaudet L, Virag L, Ross G, et al. (2001) Flagellin, a novel mediator of Salmonella-induced epithelial activation and systemic inflammation: IκBκ degradation, induction of nitric oxide synthase, induction of proinflammatory mediators, and cardiovascular dysfunction. J Immunol 166(2): 1248–1260
Gewirtz AT, Rao AS, Simon PO Jr, Merlin D, Carnes D, et al. (2000) Salmonella typhimurium induces epithelial IL-8 expression via Ca2+-mediated activation of the NF-κB pathway. J Clin Invest 105(1): 79–92
Gewirtz AT, Navas TA, Lyons S, Godowski PJ, Madara JL (2001a) Cutting edge: bacterial flagellin activates basolaterally expressed TLR5 to induce epithelial proinflammatory gene expression. J Immunol 167(4): 1882–1885
Gewirtz AT, Simon PO Jr, Schmitt CK, Taylor LJ, Hagedom CH, et al. (2001b) Salmonella typhimurium translocates flagellin across intestinal epithelia, inducing a proinflammatory response. J Clin Invest 107(1): 99–109
Glazier AM, Nadeau JH, Aitman TJ (2002) Finding genes that underlie complex traits. Science 298(5602): 2345–2349
Guenet JL, Bonhomme F (2003) Wild mice: an ever-increasing contribution to a popular mammalian model. Trends Genet 19: 24
Haehnel V, Schwarzfischer L, Fenton MJ, Rehli M (2002) Transcriptional regulation of the human Toll-like receptor 2 gene in monocytes and macrophages. J Immunol 168(11): 5629–5637
Hawn TR, Verbon A, Lettinga KD, Zhao LP, Li SS, et al. (2003) A common dominant TLR5 stop codon polymorphism abolishes flagellin signaling and is associated with susceptibility to Legionnaires’ disease. J Exp Med 198(10): 1563–1572
Hayashi F, Smith KD, Ozinsky A, Hawn TR, Yi EC, et al. (2001) The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. Nature 410(6832): 1099–1103
Heinz S, Haehnel V, Karaghiosoff M, Schwarzfischer L, Muller M, et al. (2003) Species-specific regulation of Toll-like receptor 3 genes in men and mice. J Biol Chem 278(24): 21502–21509
Hromas R, Orazi A, Neiman RS, Maki R, Van Beveren C, et al. (1993) Hematopoietic lineage- and stage-restricted expression of the ETS oncogene family member PU.1. Blood 82(10): 2998–3004
Kadowaki N, Ho S, Antonello S, Malefyt RW, Kastelein RA, et al. (2001) Subsets of human dendritic cell precursors express different Toll-like receptors and respond to different microbial antigens. J Exp Med 194(6): 863–870
Klemsz MJ, McKercher SR, Celada A, Van Beveren C, Maki RA (1990) The macrophage and B cell-specific transcription factor PU.1 is related to the ets oncogene. Cell 61(1): 113–124
Kunsch C, Lang R, Rosen CA, Shannon MF (1994) Synergistic transcriptional activation of the IL-8 gene by NF-κB p65 (RelA) and NF-IL-6. J Immunol 153(1): 153–164
Liaudet L, Murthy KGK, Mabley JG, Pacher P, Soriano FG, et al. (2002) Comparison of inflammation, organ damage, and oxidant stress induced by Salmonella enterica serovar Muenchen flagellin and serovar enteritidis lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun 70(1): 192–198
Liaudet L, Szabo C, Evgenov OV, Murthy KG, Pacher P, et al. (2003) Flagellin from Gram-negative bacteria is a potent mediator of acute pulmonary inflammation in sepsis. Shock 19(2): 131–137
Maaser C, Heidemann J, von Eiff C, Lugering A, Spahn TW, et al. (2004) Human intestinal microvascular endothelial cells express Toll-like receptor 5: a binding partner for bacterial flagellin. J Immunol 172(8): 5056–5062
McSorley SJ, Ehst BD, Yu Y, Gewirtz AT (2002) Bacterial flagellin is an effective adjuvant for CD4+ T cells in vivo. J Immunol 169(7): 3914–3919
Means TK, Hayashi F, Smith KD, Aderem A, Luster AD (2003) The Toll-like receptor 5 stimulus bacterial flagellin induces maturation and chemokine production in human dendritic cells. J Immunol 170(10): 5165–5175
Moser M, Murphy KM (2000) Dendritic cell regulation of TH1–TH2 development. Nat Immunol 1(3): 199–205
O’Brien AD, Rosenstreich DL, Scher I, Campbell GH, MacDermott RP, et al. (1980) Genetic control of susceptibility to Salmonella typhimurium in mice: role of the LPS gene. J Immunol 124(1): 20–24
Quandt K, Frech K, Karas H, Wingender E, Werner T (1995) MatInd and MatInspector: new fast and versatile tools for detection of consensus matches in nucleotide sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res 23(23): 4878–4884
Qureshi ST, Lariviere L, Sebastiani G, Clermont S, Skamene E, et al. (1996) A high-resolution map in the chromosomal region surrounding the Lps locus. Genomics 31(3): 283–294
Reed KA, Hobert ME, Kolenda CE, Sands KA, Rathman M, et al. (2002) The Salmonella typhimurium flagellar basal body protein FliE is required for flagellin production and to induce a proinflammatory response in epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 277(15): 13346–13353
Rehli M, Poltorak A, Schwarzfischer L, Krause SW, Andreesen R, et al. (2000) PU.1 and interferon consensus sequence-binding protein regulate the myeloid expression of the human Toll-like receptor 4 gene. J Biol Chem 275(13): 9773–9781
Roger T, David J, Glauser MP, Calandra T (2001) MIF regulates innate immune responses through modulation of Toll-like receptor 4. Nature 414(6866): 920–924
Sancho-Shimizu V, Malo D (2006) Sequencing, expression and functional analyses support the candidacy of Ncf2 in suspectibility to Salmonella Typhimurium infection in wild-dervied mice. J Immunol (In press)
Schmausser B, Andrulis M, Endrich S, Lee SK, Johenhans C, et al. (2004) Expression and subcellular distribution of toll-like receptors TLR4, TLR5 and TLR9 on the gastric epithelium in Helicobacter pylori infection. Clin Exp Immunol 136(3): 521–526
Sebastiani G, Olien L, Gauthier S, Skamene E, Morgan K, et al. (1998) Mapping of genetic modulators of natural resistance to infection with Salmonella typhimurium in wild-derived mice. Genomics 47(2): 180–186
Sebastiani G, Blais V, Sancho V, Vogel SN, Stevenson MM, et al. (2002) Host immune response to Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection in mice derived from wild strains. Infect Immun 70(4): 1997–2009
Sebastiani G, Leveque G, Lariviere L, Laroche L, Skamene E, et al. (2000) Cloning and characterization of the murine Toll-like receptor 5 (Tlr5) gene: sequence and mRNA expression studies in Salmonella-susceptible MOLF/Ei mice. Genomics 64(3): 230–240
Slack JL, Schooley K, Bonnert TP, Mitcham JL, Qwarnstrom EE, et al. (2000) Identification of two major sites in the type I interleukin-1 receptor cytoplasmic region responsible for coupling to pro-inflammatory signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 275(7): 4670–4678
Sundquist M, Rydstrom A, Wick MJ (2004) Immunity to Salmonella from a dendritic point of view. Cell Microbiol 6(1): 1–11
Vidal S, Malo D, Vogan K, Skamene E, Gros P (1993) Natural resistance to to infection with intracellular parasites: isolation of a candidate for Bcg. Cell 73: 469–485
Vidal S, Tremblay M, Govoni G, Gauthier S, Sebastiani G, et al. (1995) The Ity/Lsh/Bcg locus: natural resistance to infection with intracellular parasites is abrogated by disruption of the Nramp1 gene. J Exp Med 182: 655–666
Way SS, Thompson LJ, Lopes JE, Hajjar AM, Kollmann TR, et al. (2004) Characterization of flagellin expression and its role in Listeria monocytogenes infection and immunity. Cell Microbiol 6(3): 235
Zeng H, Carlson AQ, Guo Y, Yu Y, Collier-Hyams LS, et al. (2003) Flagellin is the major proinflammatory determinant of enteropathogenic Salmonella. J Immunol 171(7): 3668–3674
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Line Lariviere for excellent technical services and Silvia Vidal for helpful discussions. This work was supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI). D.M. is a scholar of CIHR and an International Research Scholar of the HHMI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Isabelle Angers and Vanessa Sancho this authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Angers, I., Sancho-Shimizu, V., Descoteaux, A. et al. Tlr5 is not primarily associated with susceptibility to Salmonella Typhimurium infection in MOLF/Ei mice. Mamm Genome 17, 385–397 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-005-0132-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-005-0132-x