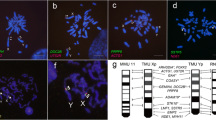
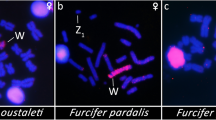
A combination of FISH and RH mapping was used to study the evolution of sex chromosome genes in the pig. In total, 19 genes were identified, including 3 PAR genes (STS, KAL, PRK). The gene order of the porcine X Chromosome (Chr) closely resembled the human X Chr (PRK/STS/KAL–AMELX–EIF2s3X/ZFX–USP9X–DBX–SMCX), suggesting that the porcine X has undergone very little rearrangement during evolution. For the porcine Y Chr, two linkage groups of 10 NRY genes were found, and the following order was established: Ypter–(AMELY–EIF2S3Y/ZFY–USP9Y–DBY/UTY)–(TSPY–SMCY–UBE1Y–SRY)–CEN. This gene order showed greater conservation with the murine Y than with the human Y Chr. In addition, all porcine Y Chr genes mapped to Yp, which is similar to the mouse and included EIF2s3Y and UBE1Y, which are not present in humans. Interestingly, complete conservation of X/Y homologous gene order was found between the pig X and Y Chrs, indicating that the porcine Y Chr has not undergone extensive reorganisation with respect to the X. This suggests that the order of the X/Y homologous genes of the porcine X and Y Chrs may closely resemble the ancestral gene order of the eutherian sex chromosomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quilter, C., Blott, S., Mileham, A. et al. A mapping and evolutionary study of porcine sex chromosome gene . Mamm Genome 13, 588–594 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-002-3026-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-002-3026-1