Abstract.
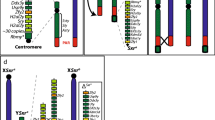
Common laboratory strains such as C57BL/6J carry a single Csf2ra gene that maps to the distal end of Chromosome (Chr) 19. Here we report that several species of wild mice contain multiple Csf2ra genes. Using interspecific backcross mapping and in situ hybridization, we demonstrate that one of these species, Mus spretus, carries four Csf2ra genes dispersed among the distal tips of Chrs 4, 10, 13, and 19. Our data further suggest that these additional Csf2ra genes are not generated by retrotransposition, but rather by nonhomologous subtelomeric exchanges that could be mediated in part by ribosomal genes located at the subtelomeric regions of Chrs 4, 13, and 19. Although we do not know whether these additional Csf2ra genes are functionally active, our studies suggest that subtelomeric exchange provides a potent means for rapid gene amplification in the mouse.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 23 May 2001 / Accepted: 7 August 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brannan, C., Disteche, C., Park, L. et al. Autosomal telomere exchange results in the rapid amplification and dispersion of Csf2ra genes in wild-derived mice. Mammalian Genome 12, 882–886 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-001-2084-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-001-2084-0