Abstract
Objectives
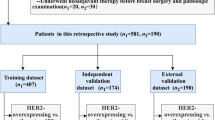
This study aims to explore values of multi-parametric MRI–based radiomics for detecting the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation and resistance (T790M) mutation in lung adenocarcinoma (LA) patients with spinal metastasis.
Methods
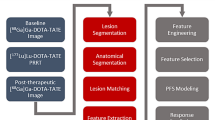
This study enrolled a group of 160 LA patients from our hospital (between Jan. 2017 and Feb. 2021) to build a primary cohort. An external cohort was developed with 32 patients from another hospital (between Jan. 2017 and Jan. 2021). All patients underwent spinal MRI (including T1-weighted (T1W) and T2-weighted fat-suppressed (T2FS)) scans. Radiomics features were extracted from the metastasis for each patient and selected to develop radiomics signatures (RSs) for detecting the EGFR and T790M mutations. The clinical-radiomics nomogram models were constructed with RSs and important clinical parameters. The receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve was used to evaluate the predication capabilities of each model. Calibration and decision curve analyses (DCA) were constructed to verify the performance of the models.
Results
For detecting the EGFR and T790M mutation, the developed RSs comprised 9 and 4 most important features, respectively. The constructed nomogram models incorporating RSs and smoking status showed favorite prediction efficacy, with AUCs of 0.849 (Sen = 0.685, Spe = 0.885), 0.828 (Sen = 0.964, Spe = 0.692), and 0.778 (Sen = 0.611, Spe = 0.929) in the training, internal validation, and external validation sets for detecting the EGFR mutation, respectively, and with AUCs of 0.0.842 (Sen = 0.750, Spe = 0.867), 0.823 (Sen = 0.667, Spe = 0.938), and 0.800 (Sen = 0.875, Spe = 0.800) in the training, internal validation, and external validation sets for detecting the T790M mutation, respectively.
Conclusions
Radiomics features from the spinal metastasis were predictive on both EGFR and T790M mutations. The constructed nomogram models can be potentially considered as new markers to guild treatment management in LA patients with spinal metastasis.
Key Points
• To our knowledge, this study was the first approach to detect the EGFR T790M mutation based on spinal metastasis in patients with lung adenocarcinoma.
• We identified 13 MRI features that were strongly associated with the EGFR T790M mutation.
• The proposed nomogram models can be considered as potential new markers for detecting EGFR and T790M mutations based on spinal metastasis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AIC:
-
Akaike information criterion
- AUC:
-
Area under the ROC curve
- BM:
-
Bone metastasis
- CEA:
-
Carcinoembryonic antigen
- CYFRA:
-
Cytokeratin
- DCA:
-
Decision curve analysis
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- EGFR-TKIs:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- GLCM:
-
Gray-level co-occurrence matrix
- ICC:
-
Intraclass correlation coefficient
- LA:
-
Lung adenocarcinoma
- LASSO:
-
Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- NSE:
-
Neuron-specific enolase
- PS:
-
Performance status
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
- RS:
-
Radiomics signature
- T1W:
-
T1-weighted
- T2FS:
-
Fat-suppressed T2-weighted
References
Rebuzzi SE, Alfieri R, La Monica S, Minari R, Petronini PG, Tiseo M (2020) Combination of EGFR-TKIs and chemotherapy in advanced EGFR mutated NSCLC: review of the literature and future perspectives. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 146:102820
Guo Y, Song J, Wang Y et al (2020) Concurrent genetic alterations and other biomarkers predict treatment efficacy of EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer: a review. Front Oncol 10:610923
Yun CH, Mengwasser KE, Toms AV et al (2008) The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:2070–2075
Ma C, Wei S, Song Y (2011) T790M and acquired resistance of EGFR TKI: a literature review of clinical reports. J Thorac Dis 3:10–18
Ohashi K, Maruvka YE, Michor F, Pao W (2013) Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant disease. J Clin Oncol 31:1070–1080
Vaclova T, Grazini U, Ward L et al (2021) Clinical impact of subclonal EGFR T790M mutations in advanced-stage EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancers. Nat Commun 12:1780
Wu SG, Liu YN, Tsai MF et al (2016) The mechanism of acquired resistance to irreversible EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-afatinib in lung adenocarcinoma patients. Oncotarget 7:12404–12413
Yu HA, Arcila ME, Rekhtman N et al (2013) Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin Cancer Res 19:2240–2247
Hochmair MJ, Buder A, Schwab S et al (2019) Liquid-biopsy-based identification of EGFR T790M mutation-mediated resistance to afatinib treatment in patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC, and subsequent response to osimertinib. Target Oncol 14:75–83
Jenkins S, Yang JC, Ramalingam SS et al (2017) Plasma ctDNA analysis for detection of the EGFR T790M mutation in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 12:1061–1070
Uramoto H, Mitsudomi T (2007) Which biomarker predicts benefit from EGFR-TKI treatment for patients with lung cancer? Br J Cancer 96:857–863
Kuchuk M, Kuchuk I, Sabri E, Hutton B, Clemons M, Wheatley-Price P (2015) The incidence and clinical impact of bone metastases in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 89:197–202
Tsuya A, Kurata T, Tamura K, Fukuoka M (2007) Skeletal metastases in non-small cell lung cancer: a retrospective study. Lung Cancer 57:229–232
Zhou Y, Yu QF, Peng AF, Tong WL, Liu JM, Liu ZL (2017) The risk factors of bone metastases in patients with lung cancer. Sci Rep 7:8970
Oliveira MB, Mello FC, Paschoal ME (2016) The relationship between lung cancer histology and the clinicopathological characteristics of bone metastases. Lung Cancer 96:19–24
Sugiura H, Yamada K, Sugiura T, Hida T, Mitsudomi T (2008) Predictors of survival in patients with bone metastasis of lung cancer. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466:729–736
Kagohashi K, Satoh H, Ishikawa H, Ohtsuka M, Sekizawa K (2003) Bone metastasis as the first manifestation of lung cancer. Int J Clin Pract 57:184–186
Cetin K, Christiansen CF, Jacobsen JB, Nørgaard M, Sørensen HT (2014) Bone metastasis, skeletal-related events, and mortality in lung cancer patients: a Danish population-based cohort study. Lung Cancer 86:247–254
Saad F, Lipton A, Cook R, Chen YM, Smith M, Coleman R (2007) Pathologic fractures correlate with reduced survival in patients with malignant bone disease. Cancer 110:1860–1867
Hsiao KC, Chu PY, Chang GC, Liu KJ (2020) Elevated expression of lumican in lung cancer cells promotes bone metastasis through an autocrine regulatory mechanism. Cancers (Basel) 12:233
Krawczyk P, Nicoś M, Ramlau R et al (2014) The incidence of EGFR-activating mutations in bone metastases of lung adenocarcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res 20:107–112
Malapelle U, Pisapia P, Rocco D et al (2016) Next generation sequencing techniques in liquid biopsy: focus on non-small cell lung cancer patients. Transl Lung Cancer Res 5:505–510
Malapelle U, Mayo de-Las-Casas C, Rocco D et al (2017) Development of a gene panel for next-generation sequencing of clinically relevant mutations in cell-free DNA from cancer patients. Br J Cancer 116:802–810
Merker JD, Oxnard GR, Compton C et al (2018) Circulating tumor DNA analysis in patients with cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology and College of American Pathologists Joint Review. J Clin Oncol 36:1631–1641
Shen TX, Liu L, Li WH et al (2019) CT imaging-based histogram features for prediction of EGFR mutation status of bone metastases in patients with primary lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Imaging 19:34
Michalopoulos GD, Yolcu YU, Ghaith AK, Alvi MA, Carr CM, Bydon M (2021) Diagnostic yield, accuracy, and complication rate of CT-guided biopsy for spinal lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurointerv Surg 13:841–847
Huang WL, Chen YL, Yang SC et al (2017) Liquid biopsy genotyping in lung cancer: ready for clinical utility? Oncotarget 8:18590–18608
Cook GJR, Goh V (2020) Molecular imaging of bone metastases and their response to therapy. J Nucl Med 61:799–806
Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H (2016) Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 278:563–577
Rogers W, Thulasi Seetha S, Refaee TAG et al (2020) Radiomics: from qualitative to quantitative imaging. Br J Radiol 93:20190948
Liu Y, Kim J, Balagurunathan Y et al (2016) Radiomic features are associated with EGFR mutation status in lung adenocarcinomas. Clin Lung Cancer 17:441–448 e446
Gevaert O, Echegaray S, Khuong A et al (2017) Predictive radiogenomics modeling of EGFR mutation status in lung cancer. Sci Rep 7:41674
Yuan M, Pu XH, Xu XQ et al (2017) Lung adenocarcinoma: assessment of epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status based on extended models of diffusion-weighted image. J Magn Reson Imaging 46:281–289
Zhang L, Chen B, Liu X et al (2018) Quantitative biomarkers for prediction of epidermal growth factor receptor mutation in non-small cell lung cancer. Transl Oncol 11:94–101
Pinheiro G, Pereira T, Dias C et al (2020) Identifying relationships between imaging phenotypes and lung cancer-related mutation status: EGFR and KRAS. Sci Rep 10:3625
Wang G, Wang B, Wang Z et al (2021) Radiomics signature of brain metastasis: prediction of EGFR mutation status. Eur Radiol 31:4538–4547
Chen BT, Jin T, Ye N et al (2021) Predicting survival duration with MRI radiomics of brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. Front Oncol 11:621088
Jiang X, Ren M, Shuang X et al (2021) Multiparametric MRI-based radiomics approaches for preoperative prediction of EGFR mutation status in spinal bone metastases in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. J Magn Reson Imaging 54:497–507
Fan Y, Dong Y, Yang H et al (2021) Subregional radiomics analysis for the detection of the EGFR mutation on thoracic spinal metastases from lung cancer. Phys Med Biol 66
van Griethuysen JJM, Fedorov A, Parmar C et al (2017) Computational radiomics system to decode the radiographic phenotype. Cancer Res 77:e104–e107
Koo TK, Li MY (2016) A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J Chiropr Med 15:155–163
Sauerbrei W, Royston P, Binder H (2007) Selection of important variables and determination of functional form for continuous predictors in multivariable model building. Stat Med 26:5512–5528
Pan W (2001) Akaike’s information criterion in generalized estimating equations. Biometrics 57:120–125
Ruopp MD, Perkins NJ, Whitcomb BW, Schisterman EF (2008) Youden Index and optimal cut-point estimated from observations affected by a lower limit of detection. Biom J 50:419–430
DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL (1988) Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics 44:837–845
Cao R, Dong Y, Wang X et al (2022) MRI-based radiomics nomogram as a potential biomarker to predict the EGFR mutations in exon 19 and 21 based on thoracic spinal metastases in lung adenocarcinoma. Acad Radiol 29:e9–e17
Parekh V, Jacobs MA (2016) Radiomics: a new application from established techniques. Expert Rev Precis Med Drug Dev 1:207–226
Mohammadi A, Afshar P, Asif A et al (2019) Lung cancer radiomics: highlights from the IEEE Video and Image Processing Cup 2018 Student Competition. IEEE Signal Process Mag 36:164–173
Li S, Luo T, Ding C, Huang Q, Guan Z, Zhang H (2020) Detailed identification of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung adenocarcinoma: combining radiomics with machine learning. Med Phys 47:3458–3466
Liu G, Xu Z, Ge Y et al (2020) 3D radiomics predicts EGFR mutation, exon-19 deletion and exon-21 L858R mutation in lung adenocarcinoma. Transl Lung Cancer Res 9:1212–1224
Wu S, Shen G, Mao J, Gao B (2020) CT radiomics in predicting EGFR mutation in non-small cell lung cancer: a single institutional study. Front Oncol 10:542957
Shi Z, Zheng X, Shi R et al (2017) Radiological and clinical features associated with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status of exon 19 and 21 in lung adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep 7:364
Wang Y, Wei Y, Ma X, Ma X, Gong P (2018) Association between advanced NSCLC T790 M EGFR-TKI secondary resistance and prognosis: a observational study. Medicine (Baltimore) 97:e11346
Lambin P, Leijenaar RTH, Deist TM et al (2017) Radiomics: the bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14:749–762
Funding
The study was funded by the Climbing Fund of National Cancer Center (NCC201806B011), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81872363), PhD Start-up Fund of Liaoning Province (2021-BS-044), China National Natural Science Foundation (31770147), Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (2021-MS-205), and Medical-Engineering Joint Fund for Cancer Hospital of China Medical University and Dalian University of Technology (LD202029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Xiran Jiang, PhD.
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Statistics and biometry
No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Methodology
• retrospective
• diagnostic or prognostic study
• multicenter study
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 17 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Y., Dong, Y., Wang, H. et al. Development and externally validate MRI-based nomogram to assess EGFR and T790M mutations in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma. Eur Radiol 32, 6739–6751 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-022-08955-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-022-08955-5