Abstract
Objectives
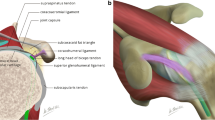
To evaluate the localisation, frequency and amount of extravasation in patients with extra-articular contrast material leak into locations unrelated to the injection path in shoulder magnetic resonance (MR) arthrography and associated shoulder disorders.
Methods
The sites of extravasation were determined on the shoulder MR arthrography of 40 patients. The extravasations were measured on three vertical planes of the MR arthrography. Sufficient joint distension was assessed according to the transverse diameters of the axillary recess on coronal MR images.
Results
Extravasation of the contrast material occurred through the subscapular recess, the synovium of the biceps, and the axillary recess. In four cases, extravasations were observed in more than one anatomic location. The most common site of extravasation was along the subscapularis muscle. Superior labrum anterior-posterior (SLAP) lesions were found to be most frequently associated with extravasations. The amount of extravasation was significantly higher in patients with adhesive capsulitis compared with the patients with a different diagnosis (p = 0.022).
Conclusions
The extravasations adjacent to the axillary recess do not always indicate glenohumeral ligament pathology. Massive subscapular extravasations were most frequently associated with adhesive capsulitis and SLAP lesions, and might be considered in the MR arthrography report.
Key Points
• Contrast material extravasation may reduce the diagnostic value of shoulder MR arthrography.
• The extravasations may occur into locations unrelated to the injection path.
• The extravasations adjacent to axillary recess can be misleading for HAGL lesion.
• Massive subscapular extravasations were frequently associated with adhesive capsulitis and SLAP lesions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mohana-Borges AV, Chung CB, Resnick D (2004) MR imaging and MR arthrography of the postoperative shoulder: spectrum of normal and abnormal findings. Radiographics 24:69–85
Waldt S, Burkart A, Imhoff AB, Bruegel M, Rummeny EJ, Woertler K (2005) Anterior shoulder instability: accuracy of MR arthrography in the classification of anteroinferior labroligamentous injuries. Radiology 237:578–583
Waldt S, Bruegel M, Mueller D et al (2007) Rotator cuff tears: assessment with MR arthrography in 275 patients with arthroscopic correlation. Eur Radiol 17:491–498
Sanders TG, Tirman PFJ, Linares R, Feller JF, Richardson R (1999) Glenolabral articular disruption lesion: MR arthrography with arthroscopic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 172:171–175
Gokalp G, Dusak A, Yazici Z (2010) Efficacy of ultrasonography-guided shoulder MR arthrography using a posterior approach. Skeletal Radiol 39:575–579
Ogul H, Bayraktutan U, Ozgokce M et al (2014) Ultrasound-guided shoulder MR arthrography: comparison of rotator interval and posterior approach. Clin Imaging 38:11–17
Porat S, Leupold JA, Burnett KR, Nottage WM (2008) Reliability of non-imaging-guided glenohumeral joint injection through rotator interval approach in patients undergoing diagnostic MR arthrography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 191:W96–W99
Tian CY, Shang Y, Zheng ZZ (2012) Glenoid bone lesions: comparison between 3D VIBE images in MR arthrography and nonarthrographic MSCT. J Magn Reson Imaging 36:231–236
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods of assessing agreement between methods of clinical measurements. Lancet 1:307–310
British Standards Institution (1979) Precision of test methods, I: guide for the determination and reproducibility for a standard test method. British Standard 5497
Efron B, Tibshirani R (1986) The bootstrap method for standard errors, confidence intervals and other measures of statistical accuracy. Stat Sci 1:1–35
Catalano OA, Manfredi R, Vanzulli A et al (2007) MR arthrography of the glenohumeral joint: modified posterior approach without imaging guidance. Radiology 242:550–554
Rutten MJ, Collins JM, Maresch BJ et al (2009) Glenohumeral joint injection: a comparative study of ultrasound and fluoroscopically guided techniques before MR arthrography. Eur Radiol 19:722–730
Hodler J (2008) Technical errors in MR arthrography. Skeletal Radiol 37:9–18
Lee MH, Ahn JM, Muhle C et al (2003) Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder: diagnosis using magnetic resonance arthrography, with arthroscopic findings as the standard. J Comput Assist Tomogr 27:901–906
Hall FM (2005) Frozen shoulder. Radiology 235:713–714
Hashimoto T, Suzuki K, Nobuhara K (1995) Dynamic analysis of intraarticular pressure in the glenohumeral joint. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 4:209–218
Ng AW, Chu CM, Lo WN, Lai YM, Kam CK (2009) Assessment of capsular laxity in patients with recurrent anterior shoulder dislocation using MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol 192:1690–1695
Jung JY, Jee WH, Chun HJ, Kim YS, Chung YG, Kim JM (2006) Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder: evaluation with MR arthrography. Eur Radiol 16:791–796
Kim KC, Rhee KJ, Shin HD (2009) Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder: dimensions of the rotator interval measured with magnetic resonance arthrography. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 18:437–442
Chung CB, Sorenson S, Dwek JR, Resnick D (2004) Humeral avulsion of the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament: MR arthrography and clinical correlation in 17 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 183:355–359
Grossman MG, Tibone JE, McGarry MH, Schneider DJ, Veneziani S, Lee TQ (2005) A cadaveric model of the throwing shoulder: a possible etiology of superior labrum anterior-to-posterior lesions. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87:824–831
Waldt S, Burkart A, Lange P, Imhoff AB, Rummeny EJ, Woertler K (2004) Diagnostic performance of MR arthrography in the assessment of superior labral anteroposterior lesions of the shoulder. AJR Am J Roentgenol 182:1271–1278
Holzapfel K, Waldt S, Bruegel M et al (2010) Inter- and intraobserver variability of MR arthrography in the detection and classification of superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) lesions: evaluation in 78 cases with arthroscopic correlation. Eur Radiol 20:666–673
Acknowledgements
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Mecit Kantarci. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. The authors state that this work has not received any funding. No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper. Institutional Review Board approval was obtained. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study. Methodology: cross-sectional study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogul, H., Kantarci, M., Topal, M. et al. Extra-articular contrast material leaks into locations unrelated to the injection path in shoulder MR arthrography. Eur Radiol 24, 2606–2613 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3270-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3270-2