Abstract
Objectives
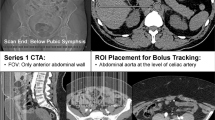
Preoperative planning of deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP) flaps has become increasingly important in radiology services as multidetector CT angiography (CTA) has been proven to be the technique of choice. We aim to optimise the process, checking the value of the “Navarra criteria,” assessing radiological and surgical concordance.
Methods
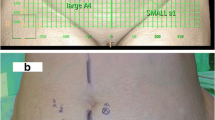
Preoperative CTA was obtained in 105 DIEP flaps involving 101 women (mean age 49.1 years). A main perforator pedicle and an alternative were chosen, applying a modification of the “Navarra criteria,” assessing the correlation between the main perforator chosen by the radiologist and the one that was ultimately used to perform the flap using the Kappa index.
Results
In 100 of the 105 DIEP flaps (95.2 %), the perforator pedicles chosen were ultimately used to raise the flap. Four of the perforator pedicles that were not used were dismissed due to avoidable errors in the radiological approach. Concordance was very high, with a Kappa index of 0.93 (95 % CI: 0.87–0.99). CT room time was less than 12 minutes, and reading time was 10 minutes.
Conclusions
The application of the “Navarra criteria” in preoperative planning of DIEP flaps improves radiological and surgical concordance as well as the reading process.
Key Points
• DIEP flap is one of the best techniques for breast reconstruction.
• Preoperative planning is essential in DIEP flaps.
• CTA is the best option for the preoperative planning of DIEP flaps.
• “Navarra criteria” allow radiologists to choose the best perforator to form flaps.
• Modified “Navarra criteria” improves radiological and surgical concordance.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CDS:
-
Colour Doppler sonography
- CTA:
-
Multidetector computed tomography angiography
- DIEA:
-
Deep inferior epigastric artery
- DIEP:
-
Deep inferior epigastric perforator
- MIP:
-
Maximum intensity projection
- MPR:
-
Multiplanar reconstruction
- MRA:
-
Magnetic resonance angiography
- SIEA:
-
Superficial inferior epigastric artery
- TRAM:
-
Transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous
- VR:
-
Volume rendering
References
Alonso-Burgos A, García-Tutor E, Bastarrika G et al (2006) Preoperative planning of deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flap reconstruction with multislice-CT angiography: imaging findings and initial experience. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 59:585–593
Masia J, Clavero JA, Larranaga JR et al (2006) Multidetector-row computed tomography in the planning of abdominal perforator flaps. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 59:594–599
Rozen WM, Phillips TJ, Ashton MW et al (2007) Pr15 The branching pattern of the DIEA for perforator flaps: the importance of preoperative CT angiography. ANZ J Surg 77:A65
Rozen WM, Stella DL, Ashton MW et al (2007) Three-dimensional CT angiography: a new technique for imaging microvascular anatomy. Clin Anat 20:1001–1003
Rosson GD, Williams CG, Fishman EK et al (2007) 3D CT angiography of abdominal wall vascular perforators to plan DIEAP flaps. Microsurgery 27:641–646
Rozen WM, Phillips TJ, Ashton MW et al (2007) Preoperative imaging for DIEA perforator flaps: a comparative study of CT angiography and Doppler ultrasound. ANZ J Surg 77:A64
Castro J, Garcia-Tutor E, Alonso A et al (2008) Análisis of deep inferior epigastric vessels with 3D CT angiography, color Doppler ultrasound and Doppler in DIEP flaps: preliminary results. Cir plast Iberolatinoam 34:223–234
Rozen WM, Anavekar NS, Ashton MW, Stella DL, Grinsell D, Bloom R et al (2008) Does the preoperative imaging of perforators with CT angiography improve operative outcomes in breast reconstruction? Microsurgery 28:516–523
Granzow JW, Levine JL, Chiu ES, Allen RJ (2006) Breast reconstruction using perforator flaps. J Surg Oncol 94:441–454, Review
Moon HK, Taylor GI (1988) The vascular anatomy of rectus abdominus musculocutaneous flaps based on the deep superior epigastric system. Plast Reconstr Surg 82:815–832
Lindsey JT (2007) Integrating the DIEP and muscle-sparing (MS-2) free TRAM techniques optimises surgical outcomes: presentation of an algorithm for microsurgical breast reconstruction based on perforator anatomy. Plast Reconstr Surg 119:18–27
Garvey PB, Buchel EW, Pockaj BA, Casey WJ III, Gray RJ, Hernández JL et al (2006) DIEP and pedicled TRAM flaps: a comparison of outcomes. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:1711–1719
Thoma A, Veltri K, Khuthaila D, Rockwell G, Duku E (2004) Comparison of the deep inferior epigastric perforator flap and free transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap in postmastectomy reconstruction: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 113:1650–1661
Phillips TJ, Stella DL, Rozen WM, Ashton M, Taylor GI (2008) Abdominal wall CT angiography: a detailed account of a newly established preoperative imaging technique. Radiology 249:32–44
Cina A, Barone-Adesi L, Rinaldi P, Cipriani A, Salgarello M, Masetti R et al (2013) Planning deep inferior epigastric perforator flaps for breast reconstruction: a comparison between multidetector computer tomography and magnetic resonance angiography. Eur Radiol 23:2333–2343
Greenspun D, Vasile J, Levine JL, Erhard H, Studinger R, Chernyak V et al (2010) Anatomic imaging of abdominal perforator flaps without ionizing radiation: seeing is believing with magnetic resonance imaging angiography. J Reconstr Microsurg 26:37–44
Rozen WM, Stella DL, Bowden J, Taylor GI, Ashton MW (2009) Advances in the pre-operative planning of deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flaps: magnetic resonance angiography. Microsurgery 29:119–123
Rozen WM, Garcia-Tutor E, Alonso-Burgos A et al (2010) Planning and optimising DIEP flaps with virtual surgery: the Navarra experience. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 63:289–297
Rozen WM, Ashton MW, Taylor GI (2008) Reviewing the vascular supply of the anterior abdominal wall: redefining anatomy for increasingly refined surgery. Clin Anat 21:89–98
Blondeel PN, Arnstein M, Verstraete K, Depuydt K, Van Landuyt KH, Monstrey SJ, Kroll SS (2000) Venous congestion and blood flow in free transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous and deep inferior epigastric perforator flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg 106:1295–1299
Elder EE, Brandberg Y, Björklund T, Rylander R, Lagergren J, Jurell G et al (2005) Quality of life and patient satisfaction in breast cancer patients after immediate breast reconstruction: A prospective study. Breast 14:201–208
Khoo A, Kroll SS, Reece GP, Miller MJ, Evans GR, Robb GL (1998) A comparison of resource costs of immediate and delayed breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 101:964–968, Discussion 969–970
Blondeel PN, Morris SF, Hallock GG, Neligan PC (2006) Perforator flaps, anatomy, technique & clinical applications. St Louis Quality Medical Publishing
Giunta RE, Geisweid A, Feller AM (2000) The value of preoperative Doppler sonography for planning free perforator flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg 105:2381–2386
Rozen WM, Ashton MW, Pan WR, Taylor GI (2007) Raising perforator flaps for breast reconstruction: the intramuscular anatomy of the deep inferior epigastric artery. Plast Reconstr Surg 120:1443–1449
Clavero JA, Masia J, Larrañaga J, Monillm JM, Pons G, Siurana S, Alomar X (2008) MDCT in the preoperative planning of abdominal perforator surgery for postmastectomy breast reconstruction. Am J Roentgenol 191:670–676
Masia J, Larranaga J, Clavero JA, Vives L, Pons G, Pons JM (2008) The value of the multidetector row computed tomography for the preoperative planning of deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flap: our experience in 162 cases. Ann Plast Surg 60:29–36
Keys KA, Louie O, Said HK, Neligan PC, Mathes DW (2013) Clinical utility of CT angiography in DIEP breast reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 66:e61–e65
Granzow JW, Levine JL, Chiu ES, Allen RJ (2006) Breast reconstruction using perforator flaps. Review. J Surg Oncol 94:441–454
Acknowledgements
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Dr. Emilio Garcia-Tutor (consulta@drgarciatutor.es). The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. The authors state that this work has not received any funding. One of the authors, Gil Rodríguez Caravaca, has significant statistical expertise. Institutional Review Board approval was obtained, as it is an observational study, which does not change the usual diagnosis and treatment sequences. All of the information and images of patients used for the study was anonymous. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study. Some study subjects have been previously reported as a poster in ECR 2013 with DOI: 10.1594/ecr2013/C-1030. Methodology: prospective, observational, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Casares Santiago, M., García-Tutor, E., Rodríguez Caravaca, G. et al. Optimising the preoperative planning of deep inferior epigastric perforator flaps for breast reconstruction. Eur Radiol 24, 2097–2108 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3243-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3243-5