Abstract
Objective
To assess the value of the liver and spleen viscoelastic parameters at multifrequency MR elastography to determine the degree of portal hypertension and presence of high-risk oesophageal varices in patients with cirrhosis.
Methods
From January to September 2012, 36 consecutive patients with cirrhosis evaluated for transplantation were prospectively included. All patients underwent hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) measurements and endoscopy to assess oesophageal varices. Multifrequency MR elastography was performed within the liver and spleen. The shear, storage and loss moduli were calculated and compared to the HVPG with Spearman coefficients and multiple regressions. Patients with and without severe portal hypertension and high-risk varices were compared with Mann–Whitney tests, logistic regression and ROC analysis.
Results
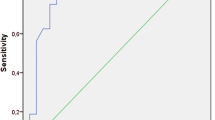
The liver storage and loss moduli and the spleen shear, storage and loss moduli correlated with the HVPG. At multiple regression, only the liver and the spleen loss modulus correlated with the HVPG (r = 0.44, p = 0.017, and r = 0.57, p = 0.002, respectively). The spleen loss modulus was the best parameter for identifying patients with severe portal hypertension (p = 0.019, AUROC = 0.81) or high-risk varices (p = 0.042, AUROC = 0.93).
Conclusions
The spleen loss modulus appears to be the best parameter for identifying patients with severe portal hypertension or high-risk varices.
Key points
1. Noninvasive HVPG assessment can be performed with liver and spleen MR elastography
2. The spleen loss modulus enables the detection of high-risk oesophageal varices
3. The spleen loss modulus enables the detection of severe portal hypertension




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MR:
-
magnetic resonance
- HVPG:
-
hepatic venous pressure gradient
- G*:
-
complex shear modulus
- Gd:
-
storage modulus
- Gl:
-
loss modulus
- ROC:
-
receiver-operating characteristics
- INR:
-
international normalised ratio
- GGT:
-
gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
- AP:
-
alkaline phosphatase
- AST:
-
aspartate aminotransferase
- ALT:
-
alanine aminotransferase
- AUROC:
-
area under the ROC curve
References
Bosch J, Abraldes JG, Berzigotti A, Garcia-Pagan JC (2009) The clinical use of HVPG measurements in chronic liver disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 6:573–582
Ripoll C, Groszmann R, Garcia-Tsao G et al (2007) Hepatic venous pressure gradient predicts clinical decompensation in patients with compensated cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 133:481–488
de Franchis R, Baveno VF (2010) Revising consensus in portal hypertension: report of the Baveno V consensus workshop on methodology of diagnosis and therapy in portal hypertension. J Hepatol 53:762–768
Groszmann RJ, Wongcharatrawee S (2004) The hepatic venous pressure gradient: anything worth doing should be done right. Hepatology 39:280–282
Thomopoulos KC, Labropoulou-Karatza C, Mimidis KP, Katsakoulis EC, Iconomou G, Nikolopoulou VN (2003) Non-invasive predictors of the presence of large oesophageal varices in patients with cirrhosis. Dig Liver Dis 35:473–478
Schepis F, Camma C, Niceforo D et al (2001) Which patients with cirrhosis should undergo endoscopic screening for esophageal varices detection? Hepatology 33:333–338
Pilette C, Oberti F, Aube C et al (1999) Non-invasive diagnosis of esophageal varices in chronic liver diseases. J Hepatol 31:867–873
Madhotra R, Mulcahy HE, Willner I, Reuben A. Prediction of esophageal varices in patients with cirrhosis. J Clin Gastroenterol;34:81–85
Giannini E, Botta F, Borro P et al (2003) Platelet count/spleen diameter ratio: proposal and validation of a non-invasive parameter to predict the presence of oesophageal varices in patients with liver cirrhosis. Gut 52:1200–1205
Cottone M, D’Amico G, Maringhini A et al (1986) Predictive value of ultrasonography in the screening of non-ascitic cirrhotic patients with large varices. J Ultrasound Med 5:189–192
Berzigotti A, Rossi V, Tiani C et al (2011) Prognostic value of a single HVPG measurement and Doppler-ultrasound evaluation in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. J Gastroenterol 46:687–695
Sebastiani G, Tempesta D, Fattovich G et al (2010) Prediction of oesophageal varices in hepatic cirrhosis by simple serum non-invasive markers: Results of a multicenter, large-scale study. J Hepatol 53:630–638
Thabut D, Trabut JB, Massard J et al (2006) Non-invasive diagnosis of large oesophageal varices with FibroTest in patients with cirrhosis: a preliminary retrospective study. Liver Int 26:271–278
Berzigotti A, Gilabert R, Abraldes JG et al (2008) Noninvasive prediction of clinically significant portal hypertension and esophageal varices in patients with compensated liver cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol 103:1159–1167
Castera L, Pinzani M, Bosch J (2012) Non invasive evaluation of portal hypertension using transient elastography. J Hepatol 56:696–703
Colecchia A, Montrone L, Scaioli E et al (2012) Measurement of spleen stiffness to evaluate portal hypertension and the presence of esophageal varices in patients with HCV-related cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 143:646–654
Berzigotti A, Seijo S, Arena U et al (2013) Elastography, spleen size, and platelet count identify portal hypertension in patients with compensated cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 144:102–111, e1
Sharma P, Kirnake V, Tyagi P et al (2013) Spleen stiffness in patients with cirrhosis in predicting esophageal varices. Am J Gastroenterol 108:1101–1107
Takuma Y, Nouso K, Morimoto Y et al (2013) Measurement of spleen stiffness by acoustic radiation force impulse imaging identifies cirrhotic patients with esophageal varices. Gastroenterology 144:92–101, e2
Bavu E, Gennisson JL, Couade M et al (2011) Noninvasive in vivo liver fibrosis evaluation using supersonic shear imaging: a clinical study on 113 hepatitis C virus patients. Ultrasound Med Biol 37:1361–1373
Huwart L, Sempoux C, Vicaut E et al (2008) Magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 135:32–40
Nedredal GI, Yin M, McKenzie T et al (2011) Portal hypertension correlates with splenic stiffness as measured with MR elastography. J Magn Reson Imaging 34:79–87
Yin M, Kolipaka A, Woodrum DA et al (2013) Hepatic and splenic stiffness augmentation assessed with MR elastography in an in vivo porcine portal hypertension model. J Magn Reson Imaging 38:809–15
Talwalkar JA, Yin M, Venkatesh S et al (2009) Feasibility of in vivo MR elastographic splenic stiffness measurements in the assessment of portal hypertension. AJR Am J Roentgenol 193:122–127
Yin M, Talwalkar JA, Glaser KJ et al (2011) Dynamic postprandial hepatic stiffness augmentation assessed with MR elastography in patients with chronic liver disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol 197:64–70
Sinkus R, Siegmann K, Xydeas T, Tanter M, Claussen C, Fink M (2007) MR elastography of breast lesions: understanding the solid/liquid duality can improve the specificity of contrast-enhanced MR mammography. Magn Reson Med 58:1135–1144
Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R (1973) Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg 60:646–649
Wiesner RH, McDiarmid SV, Kamath PS et al (2001) MELD and PELD: application of survival models to liver allocation. Liver Transpl 7:567–580
Qureshi W, Adler DG, Davila R et al (2005) ASGE Guideline: the role of endoscopy in the management of variceal hemorrhage, updated July 2005. Gastrointest Endosc 62:651–655
Garteiser P, Sahebjavaher RS, Ter Beek L et al (2013) Rapid acquisition of multifrequency, multislice and multidirectional magnetic resonance elastography data with a fractionally encoded gradient echo sequence. NMR Biomed 26:1326–35
Carrion JA, Navasa M, Bosch J, Bruguera M, Gilabert R, Forns X (2006) Transient elastography for diagnosis of advanced fibrosis and portal hypertension in patients with hepatitis C recurrence after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 12:1791–1798
Vizzutti F, Arena U, Romanelli RG et al (2007) Liver stiffness measurement predicts severe portal hypertension in patients with HCV-related cirrhosis. Hepatology 45:1290–1297
Hirooka M, Ochi H, Koizumi Y et al (2011) Splenic elasticity measured with real-time tissue elastography is a marker of portal hypertension. Radiology 261:960–8
Huwart L, Peeters F, Sinkus R et al (2006) Liver fibrosis: non-invasive assessment with MR elastography. NMR Biomed 19:173–179
Chen S, Sanchez W, Callstrom MR, Gorman B, Lewis JT, Sanderson SO et al (2013) Assessment of liver viscoelasticity by using shear waves induced by ultrasound radiation force. Radiology 266:964–970
Deffieux T, Gennisson JL, Bercoff J, Tanter M (2011) On the effects of reflected waves in transient shear wave elastography. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 58:2032–2035
Arena U, Platon ML, Stasi C et al (2013) Liver stiffness is influenced by a standardized meal in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus at different stages of fibrotic evolution. Hepatology 58:65–72
Acknowledgements
We thank Lucile Dehec, Ariane Metei, Maryse Moinat, Maryvonne Monroty and Irène Rua for their help in identifying the patients.
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Bernard E Van-Beers. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. The authors state that this work has not received any funding. No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper. Institutional review board approval was obtained. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study. Methodology: prospective, diagnostic or prognostic study, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ronot, M., Lambert, S., Elkrief, L. et al. Assessment of portal hypertension and high-risk oesophageal varices with liver and spleen three-dimensional multifrequency MR elastography in liver cirrhosis. Eur Radiol 24, 1394–1402 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3124-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3124-y