Abstract
Objectives
Core biopsy underestimates invasion in more than 20% of patients with preoperatively diagnosed ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) without evidence of invasion (pure DCIS). The aim of the current study was to evaluate the efficacy of preoperative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to discriminate between patients with DCIS who are at high risk of invasive breast cancer and patients at low risk.
Methods
One hundred and twenty-five patients, preoperatively diagnosed with pure DCIS (128 lesions; 3 bilateral) by core-needle biopsy, were prospectively included. Clinical, mammographic, histological (core biopsy) and MRI features were assessed. All patients underwent breast surgery. Analyses were performed to identify features associated with presence of invasion.
Results
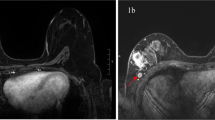
Eighteen lesions (14.1%) showed invasion on final histology. Seventy-three lesions (57%) showed suspicious enhancement on MRI with a type 1 (n = 12, 16.4%), type 2 (n = 19, 26.0%) or type 3 curve, respectively (n = 42, 57.5%). At multivariate analysis, the most predictive features for excluding presence of invasive disease were absence of enhancement or a type 1 curve on MRI (negative predictive value 98.5%; AZ 0.80, P = 0.00006).
Conclusion
Contrast medium uptake kinetics at MRI provide high negative predictive value to exclude presence of invasion and may be useful in primary surgical planning in patients with a preoperative diagnosis of pure DCIS.
Key Points
• It is important to determine invasion in breast DCIS.
• MRI contrast medium uptake kinetics can help exclude the presence of invasion.
• However, the positive predictive value for the presence of invasion is limited.
• MRI features were more accurate at predicting invasion than mammographic features alone.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leonard GD, Swain SM (2004) Ductal carcinoma in situ, complexities and challenges. J Natl Cancer Inst 96:906–920
Virnig BA, Tuttle TM, Shamliyan T, Kane RL (2010) Ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast: a systematic review of incidence, treatment, and outcomes. J Natl Cancer Inst 102:170–178
Brennan ME, Turner RM, Ciatto S et al (2011) Ductal carcinoma in situ at core-needle biopsy: meta-analysis of underestimation and predictors of invasive breast cancer. Radiology 260:119–128
Pandelidis S, Heiland D, Jones D, Stough K, Trapeni J, Suliman Y (2003) Accuracy of 11-gauge vacuum-assisted core biopsy of mammographic breast lesions. Ann Surg Oncol 10:43–47
Jackman RJ, Burbank F, Parker SH et al (2001) Stereotactic breast biopsy of nonpalpable lesions: determinants of ductal carcinoma in situ underestimation rates. Radiology 218:497–502
Lomoschitz FM, Helbich TH, Rudas M et al (2004) Stereotactic 11-gauge vacuum-assisted breast biopsy: influence of number of specimens on diagnostic accuracy. Radiology 232:897–903
Sakorafas GH, Farley DR, Peros G (2008) Recent advances and current controversies in the management of DCIS of the breast. Cancer Treat Rev 34:483–497
Intra M, Rotmensz N, Veronesi P et al (2008) Sentinel node biopsy is not a standard procedure in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast: the experience of the European institute of oncology on 854 patients in 10years. Ann Surg 247:315–319
Yi M, Krishnamurthy S, Kuerer HM et al (2008) Role of primary tumor characteristics in predicting positive sentinel lymph nodes in patients with ductal carcinoma in situ or microinvasive breast cancer. Am J Surg 196:81–87
Sakr R, Bezu C, Raoust I et al (2008) The sentinel lymph node procedure for patients with preoperative diagnosis of ductal carcinoma in situ: risk factors for unsuspected invasive disease and for metastatic sentinel lymph nodes. Int J Clin Pract 62:1730–1735
Ansari B, Ogston SA, Purdie CA, Adamson DJ, Brown DC, Thompson AM (2008) Meta-analysis of sentinel node biopsy in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Br J Surg 95:547–554
Goyal A, Douglas-Jones A, Monypenny I, Sweetland H, Stevens G, Mansel RE (2006) Is there a role of sentinel lymph node biopsy in ductal carcinoma in situ?: analysis of 587 cases. Breast Cancer Res Treat 98:311–314
Lee JW, Han W, Ko E et al (2008) Sonographic lesion size of ductal carcinoma in situ as a preoperative predictor for the presence of an invasive focus. J Surg Oncol 98:15–20
O’Flynn EA, Morel JC, Gonzalez J et al (2009) Prediction of the presence of invasive disease from the measurement of extent of malignant microcalcification on mammography and ductal carcinoma in situ grade at core biopsy. Clin Radiol 64:178–183
Patani N, Cutuli B, Mokbel K (2008) Current management of DCIS: a review. Breast Cancer Res Treat 111:1–10
Meijnen P, Oldenburg HS, Loo CE, Nieweg OE, Peterse JL, Rutgers EJ (2007) Risk of invasion and axillary lymph node metastasis in ductal carcinoma in situ diagnosed by core-needle biopsy. Br J Surg 94:952–956
Doyle B, Al Mudhaffer M, Kennedy MM et al (2009) Sentinel lymph node biopsy in patients with a needle core biopsy diagnosis of ductal carcinoma in situ: is it justified? J Clin Pathol 62:534–538
Berg WA, Gutierrez L, NessAiver MS et al (2004) Diagnostic accuracy of mammography, clinical examination, US, and MR imaging in preoperative assessment of breast cancer. Radiology 233:830–849
Medeiros LR, Duarte CS, Rosa DD et al (2011) Accuracy of magnetic resonance in suspicious breast lesions: a systematic quantitative review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 126:273–285
Kuhl CK, Schrading S, Bieling HB et al (2007) MRI for diagnosis of pure ductal carcinoma in situ: a prospective observational study. Lancet 370:485–492
Brem RF, Fishman M, Rapelyea JA (2007) Detection of ductal carcinoma in situ with mammography, breast specific gamma imaging, and magnetic resonance imaging: a comparative study. Acad Radiol 14:945–950
Schouten van der Velden AP, Boetes C, Bult P, Wobbes T (2006) The value of magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis and size assessment of in situ and small invasive breast carcinoma. Am J Surg 192:172–178
Jansen SA, Newstead GM, Abe H, Shimauchi A, Schmidt RA, Karczmar GS (2007) Pure ductal carcinoma in situ: kinetic and morphologic MR characteristics compared with mammographic appearance and nuclear grade. Radiology 245:684–691
Groves AM, Warren RM, Godward S, Rajan PS (2005) Characterization of pure high-grade DCIS on magnetic resonance imaging using the evolving breast MR lexicon terminology: can it be differentiated from pure invasive disease? Magn Reson Imaging 23:733–738
Neubauer H, Li M, Kuehne-Heid R, Schneider A, Kaiser WA (2003) High grade and non-high grade ductal carcinoma in situ on dynamic MR mammography: characteristic findings for signal increase and morphological pattern of enhancement. Br J Radiol 76:3–12
Rahbar H, Partridge SC, Eby PR et al (2011) Characterization of ductal carcinoma in situ on diffusion weighted breast MRI. Eur Radiol 21:2011–2019
Mossa-Basha M, Fundaro GM, Shah BA, Ali S, Pantelic MV (2010) Ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast: MR imaging findings with histopathologic correlation. Radiographics 30:1673–1687
Hwang ES, Kinkel K, Esserman LJ, Lu Y, Weidner N, Hylton NM (2003) Magnetic resonance imaging in patients diagnosed with ductal carcinoma-in-situ: value in the diagnosis of residual disease, occult invasion, and multicentricity. Ann Surg Oncol 10:381–388
Van Goethem M, Schelfout K, Kersschot E et al (2007) MR mammography is useful in the preoperative locoregional staging of breast carcinomas with extensive intraductal component. Eur J Radiol 62:273–282
Esserman LJ, Kumar AS, Herrera AF et al (2006) Magnetic resonance imaging captures the biology of ductal carcinoma in situ. J Clin Oncol 24:4603–4610
American College of Radiology (2003) Breast imaging reporting and data system. American College of Radiology, Reston
Kuhl CK, Mielcareck P, Klaschik S et al (1999) Dynamic breast MR imaging: are signal intensity time course data useful for differential diagnosis of enhancing lesions? Radiology 211:101–110
Liberman L, Dershaw DD, Rosen PP, Abramson AF, Deutch BM, Hann LE (1994) Stereotaxic 14-gauge breast biopsy: how many core biopsy specimens are needed? Radiology 192:793–795
Liberman L, Evans WP III, Dershaw DD et al (1994) Radiography of microcalcifications in stereotaxic mammary core biopsy specimens. Radiology 190:223–225
Egan RL (1982) Multicentric breast carcinomas: clinical-radiographic-pathologic whole organ studies and 10-year survival. Cancer 49:1123–1130
Metz CE (1986) ROC methodology in radiologic imaging. Invest Radiol 21:720–733
Silverstein MJ, Recht A, Lagios MD et al (2009) Special report: Consensus conference III. Image-detected breast cancer: state-of-the-art diagnosis and treatment. J Am Coll Surg 209:504–520
Van Goethem M, Schelfout K, Kersschot E et al (2005) Comparison of MRI features of different grades of DCIS and invasive carcinoma of the breast. JBR-BTR 88:225–232
Facius M, Renz DM, Neubauer H et al (2007) Characteristics of ductal carcinoma in situ in magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Imaging 31:394–400
Menell JH, Morris EA, Dershaw DD, Abramson AF, Brogi E, Liberman L (2005) Determination of the presence and extent of pure ductal carcinoma in situ by mammography and magnetic resonance imaging. Breast J 11:382–390
Bazzocchi M, Zuiani C, Panizza P et al (2006) Contrast-enhanced breast MRI in patients with suspicious microcalcifications on mammography: results of a multicenter trial. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186:1723–1732
Meijnen P, Oldenburg HS, Peterse JL, Bartelink H, Rutgers EJ (2008) Clinical outcome after selective treatment of patients diagnosed with ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Ann Surg Oncol 15:235–243
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported in part by the Dutch Cancer Foundation (NKB 2004–3082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deurloo, E.E., Sriram, J.D., Teertstra, H.J. et al. MRI of the breast in patients with DCIS to exclude the presence of invasive disease. Eur Radiol 22, 1504–1511 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2394-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2394-5