Abstract
Objectives
Different compositions of the extra cellular matrix with changing concentrations of more or less hydrophilic components like proteins may have a major influence on the diffusion phenomena found in gliomas.
Methods
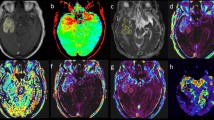
24 patients (14 male / 10 female) with histologically confirmed non necrotic glioma underwent preoperative MRI, including magnetisation transfer (MTR), triple echo T2 weighted (T2W) and diffusion weighted (DWI) sequences. Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), quantitative T2 and MTR maps were calculated and regions of interest (ROIs) were placed in the tumour centre (TU) and in the contralateral hemisphere (NWM). Informed consent was obtained. The study was approved by the local ethic comity.
Results
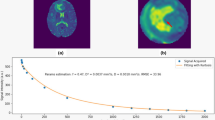
Mean values evaluated in the NWM / TU were (± standard deviation); ADC: 0.78 (±0.08) × 10-3 mm2/s / 1.32 (±0.27) × 10-3 mm2/s, T2: 101.66 (±12.00) ms / 252.11 (±104.53) ms, MTR: 0.52 (±0.01) / 0.40 (±0.04). The mean value of each parameter correlated highly significant with the others (p < 0.01).
Conclusion
Our results suggest that macromolecules binding protons in their vicinity are a major determinant of proton diffusivity in brain tumours in addition to other factors such as mechanical barriers like membranes or the size of the extra-cellular space.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Le Bihan D (2003) Looking into the functional architecture of the brain with diffusion MRI. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:469–480
Field AS, Alexander AL (2004) The role of diffusion tensor imaging in cerebral tumor diagnosis and therapy. Presented at NER Foundation Symposium 2004: Integration of Imaging Strategies in Neuroradiology, and ASNR 42nd Annual Meeting; June 5–11, 2004; Seattle, Wash.:19–24
Fiehler J (2003) Editorial comment–ADC and metabolites in stroke: even more confusion about diffusion? Stroke 34:e87–e88
Gass A, Niendorf T, Hirsch JG (2001) Acute and chronic changes of the apparent diffusion coefficient in neurological disorders–biophysical mechanisms and possible underlying histopathology. J Neurol Sci 186(Suppl 1):S15–S23
Staudt M, Schropp C, Staudt F, Obletter N, Bise K, Breit A (1993) Myelination of the brain in MRI: a staging system. Pediatr Radiol 23:169–176
Lobel U, Sedlacik J, Gullmar D, Kaiser WA, Reichenbach JR, Mentzel HJ (2009) Diffusion tensor imaging: the normal evolution of ADC, RA, FA, and eigenvalues studied in multiple anatomical regions of the brain. Neuroradiology 51:253–263
Engelbrecht V, Scherer A, Rassek M, Witsack HJ, Modder U (2002) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the brain in children: findings in the normal brain and in the brain with white matter diseases. Radiology 222:410–418
Sener RN (2004) Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging patterns in metabolic and toxic brain disorders. Acta Radiol 45:561–570
Grossman RI, Gomori JM, Ramer KN, Lexa FJ, Schnall MD (1994) Magnetization transfer: theory and clinical applications in neuroradiology. Radiographics 14:279–290
Ding XQ, Kucinski T, Wittkugel O et al (2004) Normal brain maturation characterized with age-related T2 relaxation times: an attempt to develop a quantitative imaging measure for clinical use. Invest Radiol 39:740–746
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD et al (2007) The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 114(2):97–109. doi:10.1007/s00401-007-0243-4
Lemaire L, Franconi F, Saint-Andre JP, Roullin VG, Jallet P, Le Jeune JJ (2000) High-field quantitative transverse relaxation time, magnetization transfer and apparent water diffusion in experimental rat brain tumour. NMR Biomed 13:116–123
Matsuoka Y, Hossmann KA (1982) Cortical impedance and extracellular volume changes following middle cerebral artery occlusion in cats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2:466–474
Silva MD, Omae T, Helmer KG, Li F, Fisher M, Sotak CH (2002) Separating changes in the intra- and extracellular water apparent diffusion coefficient following focal cerebral ischemia in the rat brain. Magn Reson Med 48:826–837. doi:10.1002/mrm.10296
Gupta RK, Rao AM, Mishra AM, Chawla S, Sekar DR, Venkatesan R (2005) Diffusion-weighted EPI with magnetization transfer contrast. Magn Reson Imaging 23:35–39
Guo AC, Cummings TJ, Dash RC, Provenzale JM (2002) Lymphomas and high-grade astrocytomas: comparison of water diffusibility and histologic characteristics. Radiology 224:177–183
Gupta RK, Cloughesy TF, Sinha U et al (2000) Relationships between choline magnetic resonance spectroscopy, apparent diffusion coefficient and quantitative histopathology in human glioma. J Neurooncol 50:215–226
Gupta RK, Sinha U, Cloughesy TF, Alger JR (1999) Inverse correlation between choline magnetic resonance spectroscopy signal intensity and the apparent diffusion coefficient in human glioma. Magn Reson Med 41:2–7
Castillo M (2001) Neuroimaging and cartography: mapping brain tumors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:597–598
Kono K, Inoue Y, Nakayama K et al (2001) The role of diffusion-weighted imaging in patients with brain tumors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1081–1088
Stadnik TW, Chaskis C, Michotte A et al (2001) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of intracerebral masses: comparison with conventional MR imaging and histologic findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:969–976
Sugahara T, Korogi Y, Kochi M et al (1998) Correlation of MR imaging-determined cerebral blood volume maps with histologic and angiographic determination of vascularity of gliomas. AJR Am J Roentgenol 171:1479–1486
Tien RD, Lai PH, Smith JS, Lazeyras F (1996) Single-voxel proton brain spectroscopy exam (Probe/SV) in patients with primary brain tumours. Am J Roentgenol 167:201–209
Vargova L, Homola A, Zamecnik J, Tichy M, Benes V, Sykova E (2003) Diffusion parameters of the extracellular space in human gliomas. Glia 42:77–88. doi:10.1002/glia.10204
Zamecnik J, Vargova L, Homola A, Kodet R, Sykova E (2004) Extracellular matrix glycoproteins and diffusion barriers in human astrocytic tumours. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 30:338–350. doi:10.1046/j.0305-1846.2003.00541.x
Vorisek I, Sykova E (2009) Measuring diffusion parameters in the brain: comparing the real-time iontophoretic method and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 195:101–110. doi:10.1111/j.1748-1716.2008.01924.x
Tanner JE (1983) Intracellular diffusion of water. Arch Biochem Biophys 224:416–428
Karampekios S, Papanikolaou N, Papadaki E et al (2005) Quantification of magnetization transfer rate and native T1 relaxation time of the brain: correlation with magnetization transfer ratio measurements in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neuroradiology 47:189–196. doi:10.1007/s00234-005-1344-1
Papanikolaou N, Maniatis V, Pappas J, Roussakis A, Efthimiadou R, Andreou J (2002) Biexponential T2 relaxation time analysis of the brain: correlation with magnetization transfer ratio. Invest Radiol 37:363–367
Barkovich AJ (2000) Concepts of myelin and myelination in neuroradiology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1099–1109
Holland BA, Haas DK, Norman D, Brant-Zawadzki M, Newton TH (1986) MRI of normal brain maturation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 7:201–208
Otaduy MC, Callegaro D, Bacheschi LA, Leite CC (2006) Correlation of magnetization transfer and diffusion magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 12:754–759
Sadeghi N, Camby I, Goldman S et al (2003) Effect of hydrophilic components of the extracellular matrix on quantifiable diffusion-weighted imaging of human gliomas: preliminary results of correlating apparent diffusion coefficient values and hyaluronan expression level. AJR Am J Roentgenol 181:235–241
Acknowledgements
J. Fiehler has received speakers’ fees from BRACCO, XQ, Ding has been financially supported by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) under the grant number 01GM0309. Funding sources had no influence on the acquisition, analysis or interpretation of the data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goebell, E., Fiehler, J., Siemonsen, S. et al. Macromolecule content influences proton diffusibility in gliomas. Eur Radiol 21, 2626–2632 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2206-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2206-3