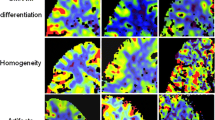
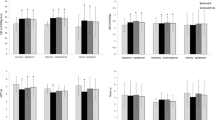
Abstract
Objectives
To compare a 256-slice CT with a simulated standard CT for brain CT perfusion (CTP).
Methods
CTP was obtained in 51 patients using a 256-slice CT (128 detector rows, flying z-focus, 8-cm detector width, 80 kV, 120mAs, 20 measurements, 1 CT image/2.5 s). Signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) were compared in grey and white matter. Perfusion maps were evaluated for cerebral blood flow (CBF), cerebral blood volume (CBV) and mean transit time (MTT) in hypoperfused areas and corresponding contralateral regions. Two reconstructed 10-mm slices for simulation of a standard CT (SDCT) were compared with the complete data sets (large-volume CT, LVCT).
Results
Adequate image quality was achieved in 50/51 cases. SNR were significantly different in grey and white matter. A perfusion deficit was present in 27 data sets. Differences between the hypoperfusions and the control regions were significant for MTT and CBF, but not for CBV. Three lesions were missed by SDCT but detected by LVCT; 24 lesions were covered incompletely by SDCT, and 6 by LVCT. 21 lesions were detected completely by LVCT, but none by SDCT.
Conclusions
CTP imaging of the brain using an increased detector width can detect additional ischaemic lesions and cover most ischaemic lesions completely.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klingebiel R, Busch M, Bohner G, Zimmer C, Hoffmann O, Masuhr F (2002) Multi-slice CT angiography in the evaluation of patients with acute cerebrovascular disease—a promising new diagnostic tool. J Neurol 249:43–49
Wintermark M (2005) Brain perfusion-CT in acute stroke patients. Eur Radiol 15(Suppl 4):D28–D31
Mayer TE, Hamann GF, Baranczyk J, Rosengarten B, Klotz E, Wiesmann M, Missler U, Schulte-Altedorneburg G, Brueckmann HJ (2000) Dynamic CT perfusion imaging of acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1441–1449
Lövblad KO, Baird AE (2010) Computed tomography in acute ischemic stroke. Neuroradiology 52:175–187
Silvernnoinen HM, Hamberg LM, Lindberg PJ et al (2008) CT Perfusion identifies increased salvage of tissue in patients receiving intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator within 3 hours of stroke onset. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:1118–1123
Konstas AA, Goldmakher GV, Lee TY, Lev MH (2009) Theoretic basis and technical implementations of CT perfusion in acute ischemic stroke, part 2: technical implementations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:885–892
Soares BP, Dankbaar JW, Bredno J, Cheng S, Bhogal S, Dillon WP, Wintermark M (2009) Automated versus manual post-processing of perfusion-CT data in patients with acute cerebral ischemia: influence on interobserver variability. Neuroradiology 51:445–451
Murayama K, Katada K, Nakane M, Toyama H, Anno H, Hayakawa M, Ruiz DS, Murphy KJ (2009) Whole-brain perfusion CT performed with a prototype 256-detector row CT system: initial experience. Radiology 250:202–211
Siebert E, Bohner G, Dewey M, Masuhr F, Hoffmann KT, Mews J, Engelken F, Bauknecht HC, Diekmann S, Klingebiel R (2009) 320-slice CT neuroimaging: initial clinical experience and image quality evaluation. Br J Radiol 82:561–570
Mori S, Obata T, Nakajima N, Ichihara N, Endo M (2005) Volumetric perfusion CT using prototype 256-detector row CT scanner: preliminary study with healthy porcine model. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2536–2541
Page M, Nandurkar D, Crossett MP, Stuckey SL, Lau KP, Kenning N, Troupis JM (2010) Comparison of 4 cm Z-axis and 16 cm Z-axis multidetector CT perfusion. Eur Radiol 20:1508–1514
Mullins ME, Lev MH, Bove P, O’Reilly CE, Saini S, Rhea JT et al (2004) Comparison of image quality between conventional and low-dose nonenhanced head CT. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:533–8.22
Wintermark M, Maeder P, Thiran JP et al (2001) Quantitative assessment of regional cerebral blood flows by perfusion CT studies at low injection rates: a critical review of the underlying theoretical models. Eur Radiol 11:1220–1230
Axel L (1983) Tissue mean transit time from dynamic computed tomography by a simple deconvolution technique. Invest Radiol 18:94–99
Axel L (1980) Cerebral blood flow determination by rapid-sequence computed tomography: theoretical analysis. Radiology 137:679–686
Meier P, Zierler KL (1954) On the theory of the indicator-dilution method for measurement of cerebral blood flow and volume. J Appl Physiol 6:731–744
Lee IH, You JH, Lee JY, Whang K, Kim MS, Kim YJ, Lee MS (2010) Brain Research Group. Accuracy of the detection of infratentorial stroke lesions using perfusion CT: an experimenter-blinded study. Neuroradiology 52:1095–1100
Wintermark M, Fischbein NJ, Smith WS et al (2005) Accuracy of dynamic perfusion CT with deconvolution in detecting acute hemispheric stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:104–112
Eastwood JD, Lev MH, Wintermark M et al (2003) Correlation of early dynamic CT perfusion imaging with whole-brain MR diffusion and perfusion imaging in acute hemispheric stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1869–1875
Roberts HC, Roberts TP, Smith WS, Lee TJ, Fischbein NJ, Dillon WP (2001) Multisection dynamic CT perfusion for acute cerebral ischemia: the “toggling-table” technique. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1077–1080
Furtado AD, Lau BC, Vittinghoff E, Dillon WP, Smith WS, Rigby T, Boussel L, Wintermark M (2010) Optimal brain perfusion CT coverage in patients with acute middle cerebral artery stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:691–695
Diekmann S, Siebert E, Juran R, Roll M, Deeg W, Bauknecht HC, Diekmann F, Klingebiel R, Bohner G (2010) Dose exposure of patients undergoing comprehensive stroke imaging by multidetector-row CT: comparison of 320-detector row and 64-detector row CT scanners. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:1003–1009
Wintermark M, Reichhart M, Thiran JP, Maeder P, Chalaron M, Schnyder P, Bogousslavsky J, Meuli R (2002) Prognostic accuracy of cerebral blood flow measurement by perfusion computed tomography, at the time of emergency room admission, in acute stroke patients. Ann Neurol 51:417–432
Wintermark M, Smith WS, Ko NU, Quist M, Schnyder P, Dillon WP (2004) Dynamic perfusion CT: optimizing the temporal resolution and contrast volume for calculation of perfusion CT parameters in stroke patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:720–729
Wiesmann M, Berg S, Bohner G, Klingebiel R, Schöpf V, Stoeckelhuber BM, Yousry I, Linn J, Missler U (2008) Dose reduction in dynamic perfusion CT of the brain: effects of the scan frequency on measurements of cerebral blood flow, cerebral blood volume, and mean transit time. Eur Radiol 18:2967–2974
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dorn, F., Muenzel, D., Meier, R. et al. Brain perfusion CT for acute stroke using a 256-slice CT: improvement of diagnostic information by large volume coverage. Eur Radiol 21, 1803–1810 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2128-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2128-0