Abstract
Objective
To investigate the feasibility of 7T MR imaging of the kidneys utilising a custom-built 8-channel transmit/receive radiofrequency body coil.
Methods
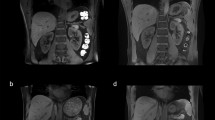
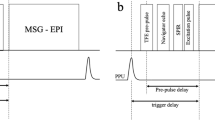
In vivo unenhanced MR was performed in 8 healthy volunteers on a 7T whole-body MR system. After B0 shimming the following sequences were obtained: 1) 2D and 3D spoiled gradient-echo sequences (FLASH, VIBE), 2) T1-weighted 2D in and opposed phase 3) True-FISP imaging and 4) a T2-weighted turbo spin echo (TSE) sequence. Visual evaluation of the overall image quality was performed by two radiologists.
Results
Renal MRI at 7T was feasible in all eight subjects. Best image quality was found using T1-weighted gradient echo MRI, providing high anatomical details and excellent conspicuity of the non-enhanced vasculature. With successful shimming, B1 signal voids could be effectively reduced and/or shifted out of the region of interest in most sequence types. However, T2-weighted TSE imaging remained challenging and strongly impaired because of signal heterogeneities in three volunteers.
Conclusion
The results demonstrate the feasibility and diagnostic potential of dedicated 7T renal imaging. Further optimisation of imaging sequences and dedicated RF coil concepts are expected to improve the acquisition quality and ultimately provide high clinical diagnostic value.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kinkel K, Lu Y, Both M et al (2002) Detection of hepatic metastases from cancers of the gastrointestinal tract by using noninvasive imaging methods (US, CT, MR imaging, PET): a meta-analysis 1. Radiology 224:748–756
Akisik FM, Sandrasegaran K, Aisen AM et al (2007) Abdominal MR imaging at 3.0 T. Radiographics 27:1433–1444
Barth MM, Smith MP, Pedrosa I et al (2007) Body MR imaging at 3.0 T: understanding the opportunities and challenges. Radiographics 27:1445–1462
Elmar MM, Brian MD, Erik KP (2006) Abdominal MR imaging at 3 T. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 14:17–26
Lauenstein TC, Salman K, Saar B et al (2007) MR colonography: 1.5T versus 3T. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 15:395–402
Ramalho M, Altun E, Heredia V et al (2007) Liver MR imaging: 1.5T versus 3T. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 15:321
Ramalho M, Herédia V, Tsurusaki M et al (2009) Quantitative and qualitative comparison of 1.5 and 3.0 tesla MRI in patients with chronic liver diseases. J Magn Reson Imaging 29:869–879
Schindera ST, Merkle EM (2007) MR cholangiopancreatography: 1.5T versus 3T. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 15:355–364
von Falkenhausen M, Meyer C, Lutterbey G et al (2007) Intra-individual comparison of image contrast in SPIO-enhanced liver MRI at 1.5T and 3.0T. Eur Radiol 17:1256–1261
Kollia K, Maderwald S, Putzki N et al (2009) First clinical study on ultra-high-field mr imaging in patients with multiple sclerosis: comparison of 1.5T and 7T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:699–702
Maderwald S, Ladd S, Gizewski E et al (2008) To TOF or not to TOF: strategies for non-contrast-enhanced intracranial MRA at 7 T. Magn Reson Mater Phys Biol Med 21:159–167
Mönninghoff C, Maderwald S, Theysohn JM et al (2009) Evaluation of intracranial aneurysms with 7 T versus 1.5 T time-of-flight MR Angiography“initial experience. Beurteilung von intrakraniellen Hirnarterienaneurysmen mit 7 Tesla versus 1, 5 Tesla-Time-of-Flight-MR-Angiografie“erste Erfahrungen. Rofo 181:16–23
Regatte RR, Schweitzer ME (2007) Ultra-high-field MRI of the musculoskeletal system at 7.0T. J Magn Reson Imaging 25:262–269
Bernstein MA, Huston J 3rd, Ward HA (2006) Imaging artifacts at 3.0T. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:735–746
Soher BJ, Dale BM, Merkle EM (2007) A review of MR physics: 3T versus 1.5T. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 15:277–290
Banerjee S, Krug R, Carballido-Gamio J et al (2008) Rapid in vivo musculoskeletal MR with parallel imaging at 7T. Magn Reson Med 59:655–660
Behr B, Stadler J, Michaely H et al (2009) MR imaging of the human hand and wrist at 7 T. Skeletal Radiol 38:911–917
Vaughan JT, Snyder CJ, DelaBarre LJ et al (2009) Whole-body imaging at 7T: preliminary results. Magn Reson Med 61:244–248
Orzada S, Quick HH, Ladd ME et al (2009) A flexible 8-channel transmit/receive body coil for 7 T human imaging. Proceedings of the 17th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, Honolulu, HI, USA 2009 (Abstract 2999)
Bitz A, Brote I, Orzada S et al (2009) Am 8-channel add-on RF shimming system for whole-body 7 Tesla MRI including real-time SAR monitoring. Proceedings of the 17th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, HI, USA 2009 (Abstract 4767)
Christ A, Kainz W, Hahn EG et al (2010) The Virtual Family – development of surface-based anatomical models of two adults and two children for dosimetric simulations. Phys Med Biol 55:23–38
Snyder CJ, DelaBarre L, Metzger GJ et al (2009) Initial results of cardiac imaging at 7 Tesla. Magn Reson Med 61:517–524
Maderwald S, Orzada S, Schäfer LC et al (2009) 7T Human in vivo Cardiac Imaging with an 8-Channel Transmit/Receive Array. Proceedings of the 17th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, Honolulu USA 2009
Vikram R, Sandler CM, Ng CS (2009) Imaging and staging of transitional cell carcinoma: part 2, upper urinary tract. AJR Am J Roentgenol 192:1488–1493
Lauenstein TC, Salman K, Morreira R et al (2007) Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: center case review. J Magn Reson Imaging 26:1198–1203
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), Grant No. 01EZ0716, which is administered by the German Aerospace Center (DLR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umutlu, L., Orzada, S., Kinner, S. et al. Renal imaging at 7 Tesla: preliminary results. Eur Radiol 21, 841–849 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-1962-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-1962-9