Abstract
Objective:
To investigate the feasibility and handling of abdominal MRI-guided biopsies in a 3-T MRI system.
Methods:
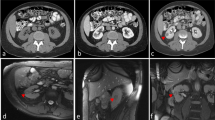
Over a 1-year period, 50 biopsies were obtained in 47 patients with tumours of the upper abdominal organs guided by 3-T MRI with a large-bore diameter of 70 cm. Lesions in liver (47), spleen (1) and kidney (2) were biopsied with a coaxial technique using a 16-G biopsy needle guided by a T1-weighted three-dimensional gradient recalled echo volumetric interpolated breath-hold examination (T1w-3D-GRE-VIBE) sequence. Sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, complication rate, interventional complexity, room/intervention time and needle artefacts were determined.
Results:
A sensitivity of 0.93, specificity of 1.0 and accuracy of 0.94 were observed. Three patients required a rebiopsy. There was a minor complications rate of 13.6%, and no major complications were observed. Histopathology revealed 38 malignant lesions, and 3-month follow-up confirmed 9 benign lesions. Mean lesion diameter was 3.4 ± 3.1 cm (50% being smaller than 2 cm). Mean needle tract length was 10.8 ± 3.3 cm. Median room time was 42.0 ± 19.8 min and intervention time 9.3 ± 8.1 min. Needle artefact size was about 9-fold greater for perpendicular access versus access parallel to the main magnetic field.
Conclusion:
Biopsies of the upper abdomen can be performed with great technical success and easy handling because of the large-bore diameter. The MRI-guided biopsy needle had an acceptable susceptibility artefact at 3 T. However future research must aim to reduce the susceptibility effects of the biopsy systems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chojniak R, Isberner RK, Viana LM, Yu LS, Aita AA, Soares FA (2006) Computed tomography guided needle biopsy: experience from 1, 300 procedures. Sao Paulo Med J 124:10–14
Welch TJ, Sheedy PF, Johnson CD, Johnson CM, Stephens DH (1989) CT-guided biopsy: prospective analysis of 1, 000 procedures. Radiology 171:493–496
Adam G, Bücker A, Nolte-Ernsting C, Tacke J, Günther RW (1999) Interventional MR imaging: percutaneous abdominal and skeletal biopsies and drainages of the abdomen. Eur Radiol 9:1471–1478
Zangos S, Kiefl D, Eichler K, Engelmann K, Heller M, Herzog C, Mack MG, Jacobi V, Vogl TJ (2003) MR-guided biopsies of undetermined liver lesions: technique and results. Rofo 175:688–694
Hammerstingl R, Huppertz A, Breuer J, Balzer T, Blakeborough A, Carter R, Fusté LC, Heinz-Peer G, Judmaier W, Laniado M, Manfredi RM, Mathieu DG, Müller D, Mortelè K, Reimer P, Reiser MF, Robinson PJ, Shamsi K, Strotzer M, Taupitz M, Tombach B, Valeri G, van Beers BE, Vogl TJ (2008) Diagnostic efficacy of gadoxetic acid (Primovist)-enhanced MRI and spiral CT for a therapeutic strategy: comparison with intraoperative and histopathologic findings in focal liver lesions. Eur Radiol 18:457–467
Langen HJ, Kugel H, Grewe S, Gindele A, Landwehr P, Fischbach R (2000) MR-guided biopsy using respiratory-triggered high-resolution T2-weighted sequences. AJR Am J Roentgenol 174:834–836
Schmidt AJ, Kee ST, Sze DY, Daniel BL, Razavi MK, Semba CP, Dake MD (1999) Diagnostic yield of MR-guided liver biopsies compared with CT- and US-guided liver biopsies. J Vasc Interv Radiol 10:1323–1329
Silverman SG, Collick BD, Figueira MR, Khorasani R, Adams DF, Newman RW, Topulos GP, Jolesz FA (1995) Interactive MR-guided biopsy in an open-configuration MR imaging system. Radiology 197:175–181
König CW, Trübenbach J, Fritz J, Lauer UM, Claussen CD, Pereira PL (2004) Contrast enhanced MR-guided biopsy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Abdom Imaging 29:71–76
Mueller PR, Stark DD, Simeone JF, Saini S, Butch RJ, Edelman RR, Wittenberg J, Ferrucci JT (1986) MR-guided aspiration biopsy: needle design and clinical trials. Radiology 161:605–609
Mahfouz AE, Rahmouni A, Zylbersztejn C, Mathieu D (1996) MR-guided biopsy using ultrafast T1- and T2-weighted reordered turbo fast low-angle shot sequences: feasibility and preliminary clinical applications. AJR Am J Roentgenol 167:167–169
Mueller PR, Silverman SG, Tung G, Brink JA, Cardenosa G, Saini S, Forman BH, Hahn PF (1989) New universal precaution aspiration tray. Radiology 173:278–279
Akimoto S, Mori H, Fujii T, Furuya K (2009) Optimal scan timing for Gd-EOB-DTPA enhanced liver dynamic MR imaging. Nippon Hoshasen Gijutsu Gakkai Zasshi 65:626–630
Cardella JF, Bakal CW, Bertino RE, Burke DR, Drooz A, Haskal Z, Lewis CA, Malloy PC, Meranze SG, Oglevie SB, Sacks D, Towbin RB (2003) Quality improvement guidelines for image-guided percutaneous biopsy in adults (Appendix A). J Vasc Interv Radiol 14:227–230
No authors listed. Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic (2000) Report of a WHO consultation. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser 894:1–253
Yao L, Nelson SD, Seeger LL, Eckardt JJ, Eilber FR (1999) Primary musculoskeletal neoplasms: effectiveness of core-needle biopsy. Radiology 212:682–686
Yu SC, Liew CT, Lau WY, Leung TW, Metreweli C (2001) US-guided percutaneous biopsy of small hepatic lesions. Radiology 218:195–199
Middleton WD, Hiskes SK, Teefey SA, Boucher LD (1997) Small (1.5 cm or less) liver metastases: US-guided biopsy. Radiology 205:729–732
Eberhardt SC, Choi PH, Bach AM, Funt SA, Felderman HE, Hann LE (2003) Utility of sonography for small hepatic lesions found on computed tomography in patients with cancer. J Ultrasound Med 22:335–343
Stattaus J, Kuehl H, Ladd S, Schroeder T, Antoch G, Baba HA, Barkhausen J, Forsting M (2007) CT-guided biopsy of small liver lesions: visibility, artifacts, and corresponding diagnostic accuracy. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 30:928–935
Haage P, Piroth W, Staatz G, Adam G, Günther RW (1999) CT-guided percutaneous biopsies for the classification of focal liver lesions: a comparison between 14 G and 18 G puncture biopsy needles. Rofo 171:44–48
Choi BI, Han JK, Cho JM, Choi DS, Han MC, Lee HS, Kim CY (1995) Characterization of focal hepatic tumors. Value of two-phase scanning with spiral computed tomography. Cancer 76:2434–2442
Honda H, Onitsuka H, Kanazawa Y, Matsumata T, Hayashi T, Kaneko K, Fukuya T, Tateshi Y, Adachi E, Masuda K (1995) MR imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma. Correlation of metal content and signal intensity. Acta Radiol 36:163–167
Zangos S, Müller C, Mayer F, Naguib NN, Nour-Eldin NE, Hansmann ML, Herzog C, Hammerstingl RM, Thalhammer A, Mack M, Vogl TJ, Eichler K (2010) Retrospective 5-year analysis of MR-guided biopsies in a low-field MR system. Rofo 181:658–663
Langen HJ, Kugel H, Landwehr P (2002) MR-guided core biopsies using a closed 1.0 T imager. First clinical results. Eur J Radiol 41:19–25
Salomonowitz E (2001) MR imaging-guided biopsy and therapeutic intervention in a closed-configuration magnet: single-center series of 361 punctures. AJR Am J Roentgenol 177:159–163
Stattaus J, Maderwald S, Baba HA, Gerken G, Barkhausen J, Forsting M, Ladd ME (2008) MR-guided liver biopsy within a short, wide-bore 1.5 Tesla MR system. Eur Radiol 18:2865–2873
Ladd ME, Erhart P, Debatin JF, Romanowski BJ, Boesiger P, McKinnon GC (1996) Biopsy needle susceptibility artifacts. Magn Reson Med 36:646–651
Butts K, Pauly JM, Daniel BL, Kee S, Norbash AM (1999) Management of biopsy needle artifacts: techniques for RF-refocused MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 9:586–595
Weiss CR, Nour SG, Lewin JS (2008) MR-guided biopsy: a review of current techniques and applications. J Magn Reson Imaging 27:311–325
Müller-Bierl BM, Martirosian P, Graf H, Boss A, König C, Pereira PL, Schick F (2008) Biopsy needle tips with markers-MR compatible needles for high-precision needle tip positioning. Med Phys 35:2273–2278
Liu H, Martin AJ, Truwit CL (1998) Interventional MRI at high-field (1.5 T): needle artifacts. J Magn Reson Imaging 8:214–219
Gehl HB, Frahm C (1998) MRI-controlled biopsies. Radiologe 38:194–199
Arbogast-Ravier S, Gangi A, Choquet P, Brunot B, Constantinesco A (1995) An in vitro study at low field for MR guidance of a biopsy needle. Magn Reson Imaging 13:321–324
Hall WA, Galicich W, Bergman T, Truwit CL (2006) 3-Tesla intraoperative MR imaging for neurosurgery. J Neurooncol 77:297–303
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kühn, JP., Langner, S., Hegenscheid, K. et al. Magnetic resonance-guided upper abdominal biopsies in a high-field wide-bore 3-T MRI system: feasibility, handling, and needle artefacts. Eur Radiol 20, 2414–2421 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-1809-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-1809-4