Abstract
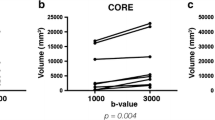
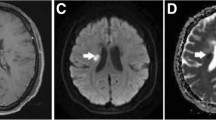
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) is a severe demyelinating disease of the central nervous system due to JC polyoma virus infection of oligodendrocytes. PML develops in patients with impaired T-cell function as occurs in HIV, malignancy or immunosuppressive drugs users. Until now no imaging methods have been reported to correlate with clinical status. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is a robust MRI tool in investigating white matter architecture and diseases. The aim of our work was to assess diffusion abnormalities in focal white matter lesions in patients with PML and to correlate the lesion load measured with conventional MRI and DWI to clinical variables. We evaluated eight patients with a biopsy or laboratory-supported diagnosis of PML. All patients underwent MRI including conventional sequences (fluid attenuated inversion recovery-FLAIR) and DWI. Mean diffusivity (MD) maps were used to quantify diffusion on white matter lesions. Global lesion load was calculated by manually tracing lesions on FLAIR images, while total, central core and peripheral lesion loads were calculated by manually tracing lesions on DWI images. Lesion load obtained with the conventional or DWI-based methods were correlated with clinical variables such as disease duration, disease severity and survival. White matter focal lesions are characterized by a central core with low signal on DWI images and high MD (1.853 × 10−3 mm2/s), surrounded by a rim of high signal intensity on DWI and lower MD (1.1 × 10−3 mm2/s). The MD value of normal-appearing white matter is higher although not statistically significant (0.783 × 10−3 mm2/s) with respect to control subjects (0.750 × 10−3 mm2/s). Inter-rater correlations of global lesion load between FLAIR (3.96%) and DWI (3.43%) was excellent (ICC =0.87). Global lesion load on FLAIR and DWI correlates with disease duration and severity (respectively, p = 0.037, p = 0.0272 with Karnofsky scale and p = 0.0338 with EDSS on FLAIR images; p = 0.043, p = 0.0296 with Karnofsky scale and p = 0.0365 with EDSS on DW images). Central core lesion load on DWI correlates with disease duration and severity (respectively p = 0.043, p = 0.0103 with Karnofsky scale and p = 0.0112 with EDSS), while peripheral lesion load does not correlate with any clinical variable. The global lesion load in PML correlates with disease duration and severity. DWI images, which can distinguish within lesions a central core from a peripheral rim, reveal that a larger central core component correlates to a worsened clinical status and longer disease duration. On the other hand the peripheral rim lesion load visualized on DWI images does not correlate with clinical variables and does not achieve obtaining further prognostic information with respect to conventional imaging.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger JR, Concha M (1995) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: the evolution of a disease once considered rare. Neurovirol (1) 5–18
Padgett BL, Walker DL (1973) Prevalence of antibodies in human sera against JC virus, an isolate from a case of multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Infect Dis 127:467–470
Holman RC, Torok TJ, Belay ED, Janssen RS, Schonberger LB (1998) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in the United States, 1979–1994: increased mortality associated with HIV infection. Neuroepidemiology 17(6):303–309
Major EO, Amemiya K, Tornatore CS, Houff SA, Berger JR (1992) Pathogenesis and molecular biology of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, the JC virus-induced demyelinating disease of the human brain. Clin Microbiol Rev 5(1):49–73
Brooks BR, Walker DL (1984) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurol Clin 2(2):299–313
Lima MA, Drislane FW, Koralnik IJ (2006) Seizures and their outcome in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurology 66(2):262–264
Berger JR, Mucke L (1988) Prolonged survival and partial recovery in AIDS-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurology 38(7):1060–1065
Nicoli F, Chave B, Peragut JC, Gastaut JL (1992) Efficacy of cytarabine in progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy in AIDS. Lancet 339(8788):306
Marra ChM, Rajicic N, Barker DE et al (2002) A pilot study of cidofovir for progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in AIDS. AIDS 16(13):1791–1797
Altschuler EL, Kast RE (2005) The atypical antipsychotic agents ziprasidone [correction of zisprasidone], risperdone and olanzapine as treatment for and prophylaxis against progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Med Hypotheses 65(3):585–586
De Luca A, Giancola ML, Ammassari A et al (2001) Potent anti-retroviral therapy with or without cidofovir for AIDS-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: extended follow-up of an observational study. J Neurovirol 7(4):364–368
Cinque P, Scalpellini P, Vago L, Linde A, Lazzarin A (1997) Diagnosis of central nervous system complications in HIV-infected patients: cerebrospinal fluid analysis by the polymerase chain reaction. AIDS 11(1):1–17
Cinque P, Koralnik IJ, Clifford DB (2003) The evolving face of human immunodeficiency virus-related progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: defining a consensus terminology. J Neurovirol 9(Suppl 1):88–92
Whiteman ML, Post MJ, Berger JR et al (1993) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in 47 HIV-seropositive patients: neuroimaging with clinical and pathologic correlation. Radiology 187(1):233–240
Berger JR, Levy RM, Flomenhoft D, Dobbs M (1998) Predictive factors for prolonged survival in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Ann Neurol 44(3):341–349
Post MJ, Yiannoutsos C, Simpson D, Booss J et al (1999) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in AIDS: are there any MR findings useful to patient management and predictive of patient survival? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20(10):1896–1906
Thurnher MM, Post MJ, Rieger A et al (2001) Initial and follow-up MR imaging findings in AIDS-related progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22(5):977–984
Ernst T, Chang L, Witt M et al (1999) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and human immunodeficiency virus-associated white matter lesions in AIDS: magnetization transfer MR imaging. Radiology 210(2):539–543
Chang L, Ernst T, Tornatore C et al (1997) Metabolite abnormalities in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neurology 48(4):836–845
Bergui M, Bradac GB, Oguz KK et al (2004) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: diffusion-weighted imaging and pathological correlations. Neuroradiology 46(1):22–25
Kuker W, Mader I, Nagele T et al (2006) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: value of diffusion-weighted and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for diagnosis and treatment control. Eur J Neurol 13(8):819–826
Mader I, Herrlinger U, Klose U, Schimdt F, Kuker W (2003) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: analysis of lesion development with diffusion-weighted MRI. Neuroradiology 45(10):717–721
Karnofsky D, Abelmann W, Craver L, Burchenal J (1948) The use of nitrogen mustard in the palliative treatment of cancer. Cancer 1:634–656
Gasnault J, Kousignian P, Kahraman M, Rahoiljaon et al (2001) Cidofovir in AIDS-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: a monocenter observational study with clinical and JC virus load monitoring. J Neurovirol 7(4):375–381
De Luca A, Giancola ML, Cingolani A et al (1999) Clinical and virological monitoring during treatment with intrthecal cytarabine in patient with AIDS-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Clin Infect Dis 28(3):624–628
Rovaris M, Filippi M, Calori G, Rodegher M et al (1997) Intra-observer reproducibility in measuring new putative MR markers of demyelination and axonal loss in multiple sclerosis: a comparison with conventional T2-weighted images. J Neurol 244(4):266–270
Schaefer PW, Grant PE, Gonzalez RG (2000) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the brain. Radiology 217:331–345
Thomas DL, Lythgoe MF, Pell GS, Calamante F, Ordidge RJ (2000) The measurement of diffusion and perfusion in biological systems using magnetic resonance imaging. Phys Med Biol 45(8):R97–R138, Aug
Fleiss JL (ed) (1985) The design and analysis of clinical experiments. John Wiley, New York
Ohta K, Obara K, Sakauchi M, Obara K, Takane H, Yogo Y (2001) Lesion extension detected by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Neurol 248(9):809–811
da Pozzo S, Manara R, Tonello S, Carollo C (2006) Conventional and diffusion weighted MRI in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy; new elements for identification and follow-up. Radiol Med 111:971–977
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cosottini, M., Tavarelli, C., Del Bono, L. et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging in patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Eur Radiol 18, 1024–1030 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0845-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0845-1