Abstract
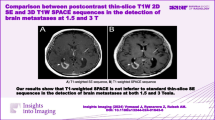
The objective of this study is to compare the detectability of brain metastases at 3T among three contrast-enhanced sequences, spin-echo (SE) sequence, inversion recovery fast SE (IR-FSE) sequence (both with section thickness of 6 mm), and three-dimensional fast spoiled gradient-echo (3D fast SPGR) sequence with 1.4 mm isotropic voxel. First, phantom studies were performed to quantify the contrast-enhancement ratio (CER) with three sequences. In 21 consecutive patients with brain metastases, axial images of three sequences at 3T were obtained after administration of gadoteridol. Two neuroradiologists assessed the detectability of brain metastases for the three sequences. In the phantom study, no evident difference in the CER was demonstrated among three sequences. Significantly more brain metastases were detected with 3D fast SPGR than with SE and IR-FSE (a total of 97 lesions with 3D fast SPGR vs. 64 with SE and 63 with IR-FSE). In particular, 3D fast SPGR was superior to the other two sequences in detection of the small lesions (<3 mm). At 3T, the contrast-enhanced 3D fast SPGR with 1.4 mm isotropic voxel is clinically more valuable for detecting small brain metastases than the SE and IR-FSE with section thickness of 6 mm.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SE:
-
Spin-echo
- IR-FSE:
-
Inversion recovery fast spin-echo
- 3D fast SPGR:
-
Three-dimensional fast spoiled gradient-echo
- CNR:
-
Contrast-to-noise ratio
- CER:
-
Contrast enhancement ratio
References
Mugler JP 3rd, Brookeman JR (1990) Three-dimensional magnetization-prepared rapid gradient-echo imaging (3D MP RAGE). Magn Reson Med 15:152–157
Mugler JP 3d, Brookeman JR (1993) Theoretical analysis of gadopentetate dimeglumine enhancement in T1-weighted imaging of the brain: comparison of two-dimensional spin-echo and three-dimensional gradient-echo sequences. J Magn Reson Imaging 3:761–769
Brant-Zawadzki M, Gillan GD, Nitz WR (1992) MP RAGE: a three-dimensional, T1-weighted, gradient-echo sequence initial experience in the brain. Radiology 182:769–775
Bluml S, Schad LR, Scharf J, Wenz F, Knopp MV, Lorenz WJ (1996) A comparison of magnetization prepared 3D gradient-echo (MPRAGE) sequences for imaging of intracranial lesions. Magn Reson Imaging 14:329–335
Krautmacher C, Willinek WA, Tschampa HJ et al (2005) Brain tumors: full- and half-dose contrast-enhanced MR imaging at 3.0 T compared with 1.5 T - initial experience. Radiology 237:1014–1019
Barth M, Nobauer-Huhmann IM, Reichenbach JR et al (2003) High-resolution three-dimensional contrast-enhanced blood oxygenation level-dependent magnetic resonance venography of brain tumors at 3 Tesla: first clinical experience and comparison with 1.5 Tesla. Invest Radiol 38:409–414
Trattnig S, Pinker K, Ba-Ssalamah A, Nobauer-Huhmann IM (2006) The optimal use of contrast agents at high field MRI. Eur Radiol 16:1280–1287
Trattnig S, Ba-Ssalamah A, Noebauer-Huhmann IM et al (2003) MR contrast agent at high-field MRI (3 Tesla). Top Magn Reson Imaging 14:365–375
Ross JS (2004) The high-field-strength curmudgeon. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:168–169
Nobauer-Huhmann IM, Ba-Ssalamah A, Mlynarik V et al (2002) Magnetic resonance imaging contrast enhancement of brain tumors at 3 tesla versus 1.5 tesla. Invest Radiol 37:114–119
White ML, Zhang Y, Kirby P, Ryken TC (2005) Can tumor contrast enhancement be used as a criterion for differentiating tumor grades of Oligodendrogliomas? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:784–790
Finelli DA (1997) Magnetization transfer effects on T1-weighted three-dimensional gradient-echo MR images of a phantom simulating enhancing brain lesions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:147–159
Yamada N, Imakita S, Sakuma T (1999) Value of diffusion-weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient in recent cerebral infarctions: a correlative study with contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193–198
Schwindt W, Kugel H, Bachmann R et al (2003) Magnetic resonance imaging protocols for examination of the neurocranium at 3T. Eur Radiol 13:2170–2179
Morakkabati-Spitz N, Gieseke J, Kuhl C et al (2006) MRI of the pelvis at 3 T: very high spatial resolution with sensitivity encoding and flip-angle sweep technique in clinically acceptable scan time. Eur Radiol 16:634–641
Lemke AJ, Alai-Omid M, Hengst SA, Kazi I, Felix R (2006) Eye imaging with a 3.0-T MRI using a surface coil - a study on volunteers and initial patients with uveal melanoma. Eur Radiol 16:1084–1086
Bachmann R, Reilmann R, Schwindt W, Kugel H, Heindel W, Kramer S (2006) FLAIR imaging for multiple sclerosis: a comparative MR study at 1.5 and 3.0 Tesla. Eur Radiol 16:915–921
Fischbach F, Bruhn H, Pech M et al (2005) Efficacy of contrast medium use for neuroimaging at 3.0 T: utility of IR-FSE compared to other T1-weighted pulse sequences. J Comput Assist Tomogr 29:499–505
Welker KM, Tsuruda JS, Hadley JR, Hayes CE (2001) Radio-frequency coil selection for MR imaging of the brain and skull base. Radiology 221:11–25
Schorner W, Laniado M, Niendorf HP, Schubert C, Felix R (1986) Time dependent changes in image contrast in brain tumors after gadolinium-DTPA. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 7:1013–1020
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kakeda, S., Korogi, Y., Hiai, Y. et al. Detection of brain metastasis at 3T: comparison among SE, IR-FSE and 3D-GRE sequences. Eur Radiol 17, 2345–2351 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0599-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0599-9