Abstract
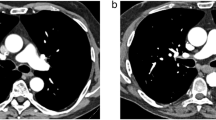
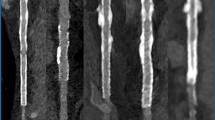
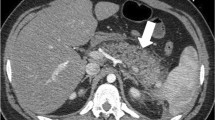
The aim of our study was to evaluate the use of a 1-molar gadolinium chelate (gadobutrol) as an alternative contrast medium for computed tomography angiography (CTA) exams of the aorta. CTA exams of the thoracic and/or abdominal aorta were performed on 15 patients with contraindications for the use of iodine who were not suitable for magnetic resonance examinations. The exams were performed with a 16-detector row scanner, injecting a mean dose of 0.37 mmol Gd/kg of body weight at a flow rate of 4 ml/s. Creatinine levels were obtained prior to the exam in patients with impaired renal function, and 24 and 48 h afterwards. The mean attenuation values obtained in the middle ascending and middle descending thoracic aorta were 202.3 and 216.8, respectively. The mean HU values of the abdominal aorta were 210.4 at the level of the renal arteries and 186.8 in the aortic bifurcation. All the exams were considered diagnostically adequate. No significant increase in serum creatinine was observed 24 and 48 h after the exam. We believe that gadobutrol could be an alternative contrast medium for CTA exams with 16-detector row scanners in patients with contraindications for iodinated contrast medium.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Janon EA (1989) Gadolinium-DTPA: a radiographic contrast agent. Am J Roentgenol 152:1348
Bloem JL, Wondergem J (1989) Gd-DTPA as a contrast agent in CT. Radiology 171:578–579
Luboldt W, De Santis M, Von Smekal A, Reiser M (1997) Attenuation characteristics and application of gadolinium-DTPA in fast helical computed tomography. Invest Radiol 35:690–695
Gierada DS, Bae KT (1999) Gadolinium as a CT contrast agent: assessment in a porcine model. Radiology 210:829–834
Niendorf H, Dinger J, Haustein J, Cornelius I, Alhassan A, Clauss W (1991) Tolerance of Gd-DTPA: a review. Eur J Radiolo 13:15–20
Prince MR, Arnoldus C, Frisoli JK (1996) Nephrotoxicity of high-dose gadolinium compared with iodinated contrast. JMRI 6:162–166
Kuhtz-Buschbeck JP, Ehrhardt K, Köhnlein S, Radtke W, Heintzen P (1997) Gadopentate dimeglumine and iodinated contrast media: hemodynamic side effects after bolus injection in pigs. Invest Radiol 32:111–119
Rieger J, Sitter T, Toepfer M, Lisenmaier U, Pfeifer KJ, Schiff H (2002) Gadolinium as an alternative contrast agent for diagnostic and interventional procedures in patients with impaired renal function. Nephrol Dial Trasplant 17:824–828
Kinno Y, Odagiri K, Andoh K, Itoh I, Tarao K (1993) Gadopentate dimeglumine as an alternative contrast agent for the use in angiography. AJR AM J Roentgenol 16:1293–1294
Spinosa D, Matsumoto A, Angle J, Hagspiel KD (1998) Use of gadopentate dimeglumine as a contrast agent for percutaneous transluminal renal angioplasty and stent placement. Kidney Int 53:503–507
Spinosa DJ, Kaufmann JA, Hartwell GD (2002) Gadolinium chelates in angiography and interventional radiology: a useful alternative to iodinated contrast media for angiography. Radiology 223:319–325
Hammer FD, Malaise J, Goffette PP, Mathurin P (2000) Gadolinium dimeglumine : an alternative contrast agent for digital subtraction angiography in patients with renal failure. Trasplant Proc 32:432–433
Wagner HJ, Kalinowski M, Klose KJ, Alfke H (2001) The use of gadolinium-chelates for X-ray digital subtraction angiography. Invest Radiol 36:257–265
Albrecht T, Dawson P (2000) Gadolinium-DTPA as X-ray contrast medium in clinical studies. Br J Radiol 73:878–882
Priebe M, Mohr A, Brossmann J, Heller M, Frahm C (2002) Gadobutrol: an altetrnative contrast agent for digital subtraction dacryosystography. Eur Radiol 12:2083–2086
Pena CS, Kaufman JA, Geller SC, Waltman AC (1999) Gadopentetate dimeglumine: a possible alternative contrast for CT angiography of the aorta. J Comput Assist Tomogr 23:23–24
Coche EE, Hammer FD, Goffette PP (2001) Demonstration of pulmonary embolism with gadolinium-enhanced spiral CT. Eur Radiol 11:2306–2309
Gupta AK, Alberico A, Litwin A, Kanter P, Grossman ZD (2002) Gadopentetate dimeglumine is potentially an alternative contrast agent for three-dimensional computed tomography angiography with multidetector-row helical scanning. J Comput Assist Tomogr 26:869–874
Karcaaltincaba M, Foley D (2002) Gadolinium.enhanced multidetector CT angiography of the thoracoabdominal aorta. J Comput Assist Tomogr 26:875–878
Henson JW, Nogueira DJ, Covarrubias R, Gonzalez RG, Lev MH (2004) Gadolinium-enhanced CT angiography of the circle of Willis and neck. M J Neuroradiol 25:969–972
Bae KT, McDermott R, Gierada DS, Heiken JP, Nolte MA, Takahashi N, Hong C (2004) Gadolinium-enhanced computed tomography angiography in multi-detector row computed tomography: initial observations. Acad Radiol 11:61–68
Wicky S, Greenfield A, Fan CM, Geller SC, Hamberg LM, Hoffmann U, Waltman AC (2004) Aortoiliac gadolinium-enhanced CT angiography: improved results with a 16-detector row scanner compared with a four-detector row scanner. J Vasc Interv Radiol 15:947–954
Remy-Jardin M, Dequiedt P, Ertzbischoff O, Tillie-Leblond I, Bruzzi J, Duhamel A, Remy J (2005) Safety and effectiveness of gadolinium-enhanced multidetector row spiral CT angiography of the chest: results in 37 patients with contraindications to iodinated contrast agents. Radiology 235:819–826
Tombach B, Bremer C, Reimer P, Schaefer RM, Ebert W, Geens V, Heindel W (2000) Pharmacokinetics of 1 M gadobutrol in patients with chronic renal failure. Invest Radiol 35:35–40
Nyman U, Elmståhl B, Leander P, Nilsson P, Golman K, Almén T (2002) Are gadolinium-based contrast media really safer than iodinated media for digital subtraction angiography in patients with azotemia? Radiology 223:311–318
Spinosa DJ, Kaufman JA, Hartwell GD (2002) Commentary on the viewpoint of Nyman et al. Radiology 223:328–329
Thomsen HS (2003) Guidelines for contrast media from the European Society of Urogenital Radiology. AJR 181:1463–1471
Thomsen HS, Morcos SK (2003) Contrast media and the kidney: European Society of Urogenital Radiology (ESUR) guidelines. Br J Radiol 76:513–518
Elmståhl B, Nyman U, Leander P, Chai CM, Frennby B, Almén T (2004) Gadolinium contrast media are more nephrotoxic than a low osmolar iodine medium employing doses with equal x-ray attenuation in renal arteriography: an experimental stugy in pigs. Acad Radiol 11:1219–1228
Thomsen HS (2004) Gadolinium-based contrast media may be neprhotoxic even at approved doses. Eur Radiol 14:1654–1656
Sam AD, Morasch MD, Collins J, Song G, Chen R, Pereles S (2003) Safety of gadolinium contrast angiography in patients with chronic renal insufficiency. J Vasc Surg 38:313–318
Staks T, Schumann-Giampieri G, Frenzel T, Weinmann HJ, Platzek J (1994) Pharmacokinetics, dose proportionality and tolerability of gadobutrol after single intravenous injection in healthy volunteers. Invest Radiol 29:709–715
Tombach B, Bremer C, Reimer P, Kisters K, Schaefer RM, Geens V, Heindel W (2001) Renal tolerance of a neutral gadolinium chelate (gadobutrol) in patients with chronic renal failure: results of a randomized study. Radiology 218:651–657
Tombach B, Heindel W (2002) Value of 1.0-M gadolinium chelates: review of preclinical and clinical data on gadobutrol. Eur Radiol 12:1550–1556
Kalinowski M, Kress O, Wels T, Alfke H, Klose KJ, Wagner HJ (2003) 1-molar gadobutrol as a contrast agent for computed tomography: results from a comparative porcine study. Invest Radiol 38:193–199
Schenker MP, Solomon JA, Roberts DA (2001) Gadolinium arteriography complicated by acute pancreatitis and acute renal failure. J Vasc Intervent Radiol 12:393
Gemery J, Idelson B, Reid, Yucel EK, Pagan-Marin, Ali S, Casserly L (1998) Acute renal failure after arteriography with a gadolinium-based contrast agent. AJR 171:1277–1278
Strunk HM, Schild H (2004) Actual clinical use of gadolinium-chelates for non-MRI applications. Eur Radiol 14:1055–1062
Thomsen HS (2006) Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: a serious late adverse reaction to gadodiamine. Eur Radiol 16:2619–2621
Chicoskie C, Tello C (2005) Gadolinium-enhanced MDCT angiography of the abdomen: Feasibility and limitations. AJR 184:1821–1828
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esteban, J.M., Alonso, A., Cervera, V. et al. One-molar gadolinium chelate (gadobutrol) as a contrast agent for CT angiography of the thoracic and abdominal aorta. Eur Radiol 17, 2394–2400 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0590-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0590-5