Abstract
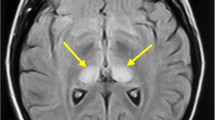
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease is a rare fatal neurodegenerative disorder, characterized by rapidly progressive dementia and neurological signs. There is a need for early and accurate clinical diagnosis in order to exclude any treatable disorder. Additionally, it is of public interest to differentiate the sporadic form of the disease from the variant CJD type (vCJD), which is probably transmitted from cattle infected with bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE). High signal in the striatum on T2-weighted, FLAIR and diffusion weighted (DW) MRI as well as cortical high signal in FLAIR and DW MRI are the classical findings in sCJD. The “pulvinar sign”, defined as high signal in the pulvinar thalami that is brighter than potential additional high signal in the basal ganglia, is considered pathognomonic for vCJD.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BSE:
-
bovine spongiform encephalopathy
- DW:
-
diffusion weighted
- EEG:
-
electroencephalogram
- FFI:
-
fatal familial insomnia
- FLAIR:
-
fluid attenuated inversion recovery
- PD:
-
proton density
- PSWCs:
-
periodic sharp wave complexes
- sCJD:
-
sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- SFI:
-
sporadic fatal insomnia
- TSE:
-
transmissible spongiform encephalopathy
- vCJD:
-
variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
References
Prusiner SB (1998) Prions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:13363–13383
Masters CL, Harris JO, Gajdusek DC, Gibbs CJ Jr, Bernoulli C, Asher DM (1979) Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: patterns of worldwide occurrence and the significance of familial and sporadic clustering. Ann Neurol 5:177–188
World Health Organization (1998) Human transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Weekly Epidemiological Record 73:361–365
Steinhoff BJ, Racker S, Herrendorf G, et al (1996) Accuracy and reliability of periodic sharp wave complexes in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch Neurol 53:162–166
Zerr I, Pocchiari M, Collins S et al (2000) Analysis of EEG and CSF 14-3-3 proteins as aids to the diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 55:811–815
Steinhoff BJ, Zerr I, Glatting M, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Poser S, Kretzschmar HA (2004) Diagnostic value of periodic complexes in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann Neurol 56:702–708
Poser S, Mollenhauer B, Kraubeta A et al (1999) How to improve the clinical diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Brain 122 (Pt 12):2345–2351
Parchi P, Giese A, Capellari S et al (1999) Classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease based on molecular and phenotypic analysis of 300 subjects. Ann Neurol 46:224–233
Tschampa HJ, Neumann M, Zerr I et al (2001) Patients with Alzheimer’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies mistaken for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 71:33–39
Boesenberg C, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ, Meissner B et al (2005) Clinical course in young patients with sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann Neurol 58(4):533–543
Windl O, Giese A, Schulz-Schaeffer W et al (1999) Molecular genetics of human prion diseases in Germany. Hum Genet 105:244–252
Kovacs GG, Puopolo M, Ladogana A et al (2005) Genetic prion disease: the EUROCJD experience. Hum Genet 1–9
Shimizu S, Hoshi K, Muramoto T et al (1999) Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with florid-type plaques after cadaveric dura mater grafting. Arch Neurol 56:357–362
Will RG, Ironside JW, Zeidler M et al (1996) A new variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in the UK. Lancet 347:921–925
From the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (1996) World Health Organization Consultation on public health issues related to bovine spongiform encephalopathy and the emergence of a new variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. JAMA 275:1305–1306
Hill AF, Desbruslais M, Joiner S et al (1997) The same prion strain causes vCJD and BSE. Nature 389:448–50
Will RG, Zeidler M, Stewart GE et al (2000) Diagnosis of new variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann Neurol 47:575–582
Kretzschmar HA, Ironside JW, DeArmond SJ, Tateishi J (1996) Diagnostic criteria for sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch Neurol 53:913–920
Kropp S, Finkenstaedt M, Zerr I, Schroter A, Poser S (2000) Diffusion-weighted MRI in patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Nervenarzt 71:91–95
Shiga Y, Miyazawa K, Sato S et al (2004) Diffusion-weighted MRI abnormalities as an early diagnostic marker for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 63:443–449
Young GS, Geschwind MD, Fischbein NJ et al (2005) Diffusion-weighted and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery imaging in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: high sensitivity and specificity for diagnosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1551–1562
Matoba M, Tonami H, Miyaji H, Yokota H, Yamamoto I (2001) Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: serial changes on diffusion-weighted MRI. J Comput Assist Tomogr 25:274–277
Zeidler M, Collie DA, Macleod MA, Sellar RJ, Knight R (2001) FLAIR MRI in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 56:282
Gertz HJ, Henkes H, Cervos-Navarro J (1988) Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: correlation of MRI and neuropathologic findings. Neurology 38:1481–1482
Finkenstaedt M, Szudra A, Zerr I et al (1996) MR imaging of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Radiology 199:793–798
Barboriak DP, Provenzale JM, Boyko OB (1994) MR diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: significance of high signal intensity of the basal ganglia. AJR Am J Roentgenol 162:137–140
Milton WJ, Atlas SW, Lavi E, Mollman JE (1991) Magnetic resonance imaging of Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease. Ann Neurol 29:438–440
Tartaro A, Fulgente T, Delli PC, Bonomo L, Bocola V, Onofrj M (1993) MRI alterations as an early finding in Creutzfeld-Jakob disease. Eur J Radiol 17:155–158
Rother J, Schwartz A, Harle M, Wentz KU, Berlit P, Hennerici M (1992) Magnetic resonance imaging follow-up in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Neurol 239:404–406
Pearl GS, Anderson RE (1989) Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: high caudate signal on magnetic resonance imaging. South Med J 82:1177–1180
Schroter A, Zerr I, Henkel K, Tschampa HJ, Finkenstaedt M, Poser S (2000) Magnetic resonance imaging in the clinical diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch Neurol 57:1751–1757
Tschampa HJ, Kallenberg K, Urbach H et al (2005) MRI in the diagnosis of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: a study on inter-observer agreement. Brain 128:2026–2033
de Priester JA, Jansen GH, de Kruijk JR, Wilmink JT (1999) New MRI findings in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: high signal in the globus pallidus on T1-weighted images. Neuroradiology 41:265–268
Kovanen J, Erkinjuntti T, Iivanainen M et al (1985) Cerebral MR and CT imaging in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Comput Assist Tomogr 9:125–128
Ukisu R, Kushihashi T, Kitanosono T et al (2005) Serial diffusion-weighted MRI of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol 184:560–566
Bahn MM, Kido DK, Lin W, Pearlman AL (1997) Brain magnetic resonance diffusion abnormalities in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch Neurol 54:1411–1415
Bahn MM, Parchi P (1999) Abnormal diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch Neurol 56:577–583
Yee AS, Simon JH, Anderson CA, Sze CI, Filley CM (1999) Diffusion-weighted MRI of right-hemisphere dysfunction in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 52:1514–1515
Demaerel P, Baert AL, Vanopdenbosch L, Robberecht W, Dom R (1997) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet 349:847–848
Demaerel P, Sciot R, Robberecht W et al (2003) Accuracy of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the diagnosis of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Neurol 250:222–225
Murata T, Shiga Y, Higano S, Takahashi S, Mugikura S (2002) Conspicuity and evolution of lesions in creutzfeldt-jakob disease at diffusion-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1164–1172
Tschampa HJ, Murtz P, Flacke S, Paus S, Schild HH, Urbach H (2003) Thalamic involvement in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: a diffusion-weighted MR imaging study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:908–915
Young GS, Lin Y, Chen N, Dillon WP, Wong S (2005) Abnormality of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) in Somatosensory Cortex in Jakob-Creutzfeldt disease (CJD): Is Rolandic Cortex Really Spared? RSNA Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting Program 517; SSQ12–08–517
Sellars RJ, Collie DA, Will RJ (2002) Progress in understanding Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1070–1072
Rowley HA, McCue J, Salamat MS, Fleming J (2004) Diffusion and Perfusion MRI in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Proc Intl Soc Magn Reson Med 11:1340
Burdette JH, Durden DD, Elster AD, Yen YF (2001) High b-value diffusion-weighted MRI of normal brain. J Comput Assist Tomogr 25:515–519
Tschampa HJ, Kallenberg K, Zerr I, Kretzschmar HA, Knauth M, Urbach H (2005) Pattern of cortical changes in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. RSNA Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting Program, 515
Poon MA, Stuckey S, Storey E (2001) MRI evidence of cerebellar and hippocampal involvement in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neuroradiology 43:746–749
Tribl GG, Strasser G, Zeitlhofer J et al (2002) Sequential MRI in a case of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neuroradiology 44:223–226
Matsusue E, Kinoshita T, Sugihara S, Fujii S, Ogawa T, Ohama E (2004) White matter lesions in panencephalopathic type of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: MR imaging and pathologic correlations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:910–918
Zeidler M, Will RG, Ironside JW, Sellar R, Wardlaw J (1996) Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and bovine spongiform encephalopathy. Magnetic resonance imaging is not a sensitive test for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. BMJ 312:844
Hirai T, Korogi Y, Yoshizumi K, Shigematsu Y, Sugahara T, Takahashi M (2000) Limbic lobe of the human brain: evaluation with turbo fluid-attenuated inversion-recovery MR imaging. Radiology 215:470–475
Collie DA, Summers DM, Sellar RJ et al (2003) Diagnosing variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with the pulvinar sign: MR imaging findings in 86 neuropathologically confirmed cases. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1560–1569
Zeidler M, Sellar RJ, Collie DA et al (2000) The pulvinar sign on magnetic resonance imaging in variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet 355:1412–1418
Martindale J, Geschwind MD, De Armond S et al (2003) Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease mimicking variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch Neurol 60:767–770
Rabinstein AA, Whiteman ML, Shebert RT (2002) Abnormal diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease following corneal transplantations. Arch Neurol 59:637–639
Meissner B, Kortner K, Bartl M et al (2004) Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: magnetic resonance imaging and clinical findings. Neurology 63:450–456
Kropp S, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ, Finkenstaedt M et al (1999) The Heidenhain variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch Neurol 56:55–61
Na DL, Suh CK, Choi SH et al (1999) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in probable Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: a clinical-anatomic correlation. Arch Neurol 56:951–957
Chung YL, Williams A, Ritchie D et al (1999) Conflicting MRI signals from gliosis and neuronal vacuolation in prion diseases. NeuroReport 10:3471–3477
Mittal S, Farmer P, Kalina P, Kingsley PB, Halperin J (2002) Correlation of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging with neuropathology in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch Neurol 59:128–134
Urbach H, Klisch J, Wolf HK, Brechtelsbauer D, Gass S, Solymosi L (1998) MRI in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: correlation with clinical and neuropathological data. Neuroradiology 40:65–70
Safar JG, Geschwind MD, Deering C et al (2005) Diagnosis of human prion disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:3501–3506
Haik S, Dormont D, Faucheux BA, Marsault C, Hauw JJ (2002) Prion protein deposits match magnetic resonance imaging signal abnormalities in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann Neurol 51:797–799
Russmann H, Vingerhoets F, Miklossy J et al (2005) Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: a comparison of pathological findings and diffusion weighted imaging. J Neurol 252:338–342
Henkel K, Zerr I, Hertel A et al (2002) Positron emission tomography with [(18)F]FDG in the diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD). J Neurol 249:699–705
de Silva R, Patterson J, Hadley D, Russell A, Turner M, Zeidler M (1998) Single photon emission computed tomography in the identification of new variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: case reports. BMJ 316:593–594
Collie DA, Sellar RJ, Zeidler M, Colchester AC, Knight R, Will RG (2001) MRI of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: imaging features and recommended MRI protocol. Clin Radiol 56:726–739
Zerr I, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ, Giese A et al (2000) Current clinical diagnosis in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: identification of uncommon variants. Ann Neurol 48:323–329
Castellani RJ, Colucci M, Xie Z et al (2004) Sensitivity of 14-3-3 protein test varies in subtypes of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 63:436–442
Hamaguchi T, Kitamoto T, Sato T et al (2005) Clinical diagnosis of MM2-type sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 64:643–648
Parchi P, Capellari S, Chin S et al (1999) A subtype of sporadic prion disease mimicking fatal familial insomnia. Neurology 52:1757–1763
Samman I, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ, Wohrle JC, Sommer A, Kretzschmar HA, Hennerici M (1999) Clinical range and MRI in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with heterozygosity at codon 129 and prion protein type 2. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 67:678–681
Fukushima R, Shiga Y, Nakamura M, Fujimori J, Kitamoto T, Yoshida Y (2004) MRI characteristics of sporadic CJD with valine homozygosity at codon 129 of the prion protein gene and PrPSc type 2 in Japan. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:485–487
Acknowledgements
We thank Hanno Schimikowski for his help with figure editing and Carsten Krautmacher for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article gives an overview on imaging features of sporadic and variant CJD. It discusses the clinical presentation and pathology of CJD, as well as the differential diagnoses on clinical and MR grounds.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tschampa, H.J., Zerr, I. & Urbach, H. Radiological assessment of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Eur Radiol 17, 1200–1211 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0456-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0456-2