Abstract
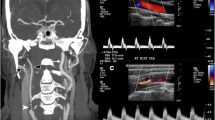
The purpose was to evaluate whether B-flow can improve the ultrasonographic diagnosis of preocclusive stenosis and occlusion of the internal carotid artery (ICA) compared with colour-coded Doppler and power Doppler. Ninety patients with occlusions or preocclusive stenoses of the ICA suspected by Doppler sonography were examined with B-flow in comparison with colour-coded Doppler sonography (CCDS), power Doppler (PD) and intra-arterial digital subtraction angiography (DSA). Intrastenotic flow detection and lengths of stenoses were the main criteria. Ulcerated plaques found by surgery in 42/90 patients were compared by ultrasonography (US). Diagnosis of ICA occlusion with CCDS, PD and B-flow was correct in all 42 cases. A preocclusive ICA stenosis in DSA was detected correctly in all 48/48 cases (100%) for B-flow, in 44/48 (92%) for PD and in 39/48 (81%) for CCDS. Surgical findings showed in 17/42 cases ulcerated plaques; 15/17 (89%) of these cases were detected with B-flow, 12/17 (71%) with PD, 10/17 (59%) with CCDS, and 8/17 (47%) with DSA. With B-flow the extent of stenosis was appraised more precisely than with PD and CCDS (P<0.0001). In conclusion, B-flow is a reliable method for preocclusive stenosis of the ICA with less intrastenotic flow artefacts. B-flow facilitates the characterization of plaque morphologies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators (1991) Beneficial effect of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high-grade stenosis. N Engl J Med 325:445–452
European Carotid Surgery Trialists Collaborative Group (1995) Risk of stroke in the distribution of an asymptomatic carotid artery. Lancet 345:445–453
Hetzel A, Eckenweber B, Trummer B, Wernz M, Schumacher M, von Reutern G (1998) Colour-coded duplex sonography of preocclusive carotid stenoses. Eur J Ultrasound 8:183–191
Mead GE, Lewis SC, Wardlaw JM (2000) Variability in Doppler ultrasound influences referral of patients for carotid surgery. Eur J Ultrasound 12:137–143
Schminke U, Motsch L, Hilker I, Kessler C (2000) Three-dimensional ultrasound observation of carotid artery plaque ulceration. Stroke 31:1651–1655
Fürst G, Saleh A, Wenserski F, Malms J, Cohnen M, Aulich A, Neumann-Haefelin T, Schroeter M, Steinmetz H, Sitzer M (1999) Reliability and validity of noninvasive imaging of internal carotid artery pseudo-occlusion. Stroke 30:1444–1449
Polak JF (2001) Carotid ultrasound. Radiol Clin North Am 39:569–589
Borisch I, Horn M, Butz B, Zorger N, Dragnanski B, Hoelscher T, Bogdahn U, Link J (2003) Preoperative evaluation of carotid artery stenosis: comparison of contrast-enhanced MR angiography and Duplex sonography with digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1117–1122
Polak JF, Shemnski I, O’Leary DH, Lefkowitz D, Price TR, Savage PJ, Brant WE, Reid C (1998) Hypoechoic plaque at US of the carotid artery: an independent risk factor for incident stroke in adults aged 65 years or older. Cardiovascular Health Study. Radiology 209:288–289
Lee VS, Hertzberg BS, Workman MJ, Smith TP, Kliewer MA, De Long DM, Carroll BA (2000) Variability of Doppler US measurements along the common carotid artery: effects on estimates of internal carotid arterial stenosis in patients with angiographically proved disease. Radiology 214:387–392
Bonig L, Weder B, Schott D, Keel A, Nguyen T, Zaunbauer W (2000) Prediction of angiographic carotid artery stenosis indexes by colour Doppler-assisted duplex imaging. A critical appraisal of the parameters used. Eur J Neurol 7:183–190
Eckstein HH, Winter R, Eichbaum M, Klemm K, Schumacher H, Dorfler A, Schulte K, Neuwith A, Grass W, Schnabel P, Allenberg JR (2001) Grading of internal carotid artery stenosis: validation of Doppler/duplex ultrasound criteria and angiography against endarterectomy specimen. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 21:301–310
Remonda L, Senn P, Barth A, Arnold M, Lövblad K-O, Schroth G (2002) Contrast-Enhanced 3 D MR Angiography of carotid artery: comparison with conventional digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:213–219
Yuan C, Mitsumori LM, Beach KW, Maravilla KR (2001) Carotid atherosclerotic plaque: noninvasive MR characterization and identification of vulnerable lesions. Radiology 221:285–299
Randoux B, Marro B, Koskas F, Duyme M, Sahel M, Zouaoui A, Marsault C (2001) Carotid artery stenosis: prospective comparison of CT, three-dimensional gadolinium-enhanced MR, and conventional angiography. Radiology 220:179–185
Spencer E, Sheafor D, Hertzberg B, Bowie JD, Nelson R, Caroll B, Kliewer M (2001) Nonstenotic internal carotid arteries: Effects of age and blood pressure at the time of scanning on Doppler US velocity measurements. Radiology 220:174–178
Horrow MM, Stassi J, Shurman A, Brody J, Kirby CL, Rosenberg HL (2000) The limitations of carotid sonography: interpretive and technology-related errors. AJR Am J Roentgenol 174:189–194
Arbeille P, Bouin-Pineau MH, Herault S (1999) Accuracy of the main Doppler methods for evaluating the degree of carotid stenoses (continuous wave, pulsed wave and color Doppler). Ultrasound Med Biol 25:65–73
Weskott H-P (2000) B-flow - a new method for detecting blood flow. Ultraschall in Med 21:59–65
Claudon M, Winninger D, Briancon S, Pesque P (2001) Power Doppler US: evaluation of the morphology of stenoses with a flow phantom. Radiology 218:109–117
Connors JJ, Sacks D, Becker GJ, Barr JD (2003) Carotid artery angioplasty and stent placement: quality improvement guidelines to ensure stroke risk reduction. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14:1095–1097
Müller M, Cicotti R, Reiche W, Hagen T (2001) Comparison of color-flow Doppler scanning, power Doppler scanning, and frequency shift for assessment of carotid artery stenosis. J Vasc Surg 34:1090–1095
Schmidt P, Sliwka U, Simon SG, Noth J (1998) High-grade stenosis of the internal carotid artery assessed by color and power Doppler imaging. J Clin Ultrasound 26:85–89
Steinke W, Ries S, Artemis N, Schwartz A, Hennerici M (1997) Power Doppler imaging of carotid artery stenosis. Comparison with color Doppler flow imaging and angiography. Stroke 28:1981–1987
Droste DW, Jürgens R, Nabavi DG, Schuierer G, Weber S, Ringelstein E (1999) Echocontrast-enhanced ultrasound of extracranial internal carotid artery high-grade stenosis and occlusion. Stroke 30:2302–2306
Clevert D-A, Rupp N, Reiser M, Jung EM (2005) Improved diagnosis of vascular dissection by ultrasound B-flow: a comparison with color-coded Doppler and power Doppler sonography. Eur Radiol 15:342–347
Weskott H-P (1997) Amplitude Doppler US: slow blood flow detection level tested with a flow phantom. Radiology 202:125–130
Bucek RA, Reiter M, Koppensteiner I, Ahmadi R, Minar E, Lammer J (2002) B-flow evaluation of carotid arterial stenosis: initial experience. Radiology 225:295–299
Sabeti S, Schillinger M, Mlekusch W, Nachtmann T, Lang W, Ahmadi R, Minear E (2004) Contralateral high-grade carotid artery stenosis or occlusion is not associated with increased risk for poor neurologic outcome after elective carotid stent placement. Radiology 2:70–76
Jung EM, Kubale R, Clevert D-A, Lutz R, Rupp N (2002) [B-flow and contrast medium-enhanced power Doppler (Optison(R)) - preoperative diagnoisis of high-grade stenosis of the internal carotid artery]. RoFo 174:62–69
Grant EG, Benson CB, Moneta GL, Alexandrov AV, Baker JD, Bluth EI, Carroll BA, Eliasziw M, Gocke J, Hertzberg BS, Katanik S, Needleman L, Pellerito J, Pollak JF, Rholl KS, Wooster DL, Zierler E (2003) Carotis artery stenosis : grey-scale and Doppler US diagnosis—Society of Radiologists in ultrasound consensus conference. Radiology 229:340–346
Schminke U, Motsch L, Hilker L, Kessler C (2000) Three-dimensional ultrasound observation of carotid artery plaque ulceration. Stroke 31:1651–1655
Yadav JS (2004) Carotid stenting in high-risk patients: design and rationale of the SAPPHIRE trial. Cleve Clin J Med 71(Suppl 1):S45–S46
Arning C, Hammer E, Kortmann H, Hahm H, Müller-Jensen A, Lachenmayer L (2003) Quantifying stenosis of the internal carotid artery: which ultrasound criteria are relevant. Ultraschall Med 24:233–238
Long A, Lepoutre A, Corbillon E, Branchereau A (2002) Critical review of non- or minimally invasive methods (duplex ultrasonography, MR- and CT-angiography) for evaluating stenosis of the proximal internal carotid artery. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 24:43–52
Yurdakul M, Tola M, Cumhur T (2004) B-flow imaging of internal carotid artery stenosis: comparison with power Doppler imaging and digital subtraction angiography. J Clin ultrasound 32:243–248
Umemura A, Yamada K (2001) B-mode flow imaging of the carotid artery. Stroke 32:2055–2057
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, E.M., Kubale, R., Ritter, G. et al. Diagnostics and characterisation of preocclusive stenoses and occlusions of the internal carotid artery with B-flow. Eur Radiol 17, 439–447 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0285-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0285-3