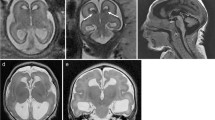
Abstract
The fetal cortical maturation is a long process with predefined steps. Abnormalities can occur at different stages of cortical maturation, resulting in various malformations. They can result from disturbance in cell proliferation, cell differentiation, cell migration and in organization of the cortex. Analysis of the different abnormalities of cortical maturation is given with illustrations of the principal malformations encountered in utero and accessible to MRI.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Girard N, Gambarelli D (2001) Normal fetal brain. Magnetic resonance imaging. An atlas with anatomic correlations. The Journal of Paediatric and Fetal Imaging, Rickmansworth
Girard N, Raybaud C, Gambarelli D (2001) Pediatric neuroimaging: fetal MR imaging. In: Demaerel P (ed) Recent advances in diagnostic neuroradiology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 373–398
Girard NJ, Raybaud CA (1992) In vivo MRI of fetal brain cellular migration. J Comput Assist Tomogr 16:265–267
Girard N, Raybaud C, Dercole C, Boubli L, Chau C, Cahen S, Potier A, Gamerre M (1993) In vivo MRI of the fetal brain. Neuroradiology 35:431–436
Girard N, Raybaud C, Poncet M (1995) In vivo MR study of brain maturation in normal fetuses. Am J Neuroradiol 16:407–413
Girard N (2002) Fetal MR imaging. Eur Radiol 12:1869–1871
Girard N, Gambarelli D (2004) Fetal brain abnormalities. Magnetic resonance imaging. An atlas with anatomic–pathologic correlations. Label Production, Marseilles
Raybaud C, Levrier O, Brunel H, Girard N, Farnarier P (2003) MR imaging of fetal brain malformations. Child’s Nerv Syst 19:455–470
Girard N, Gire C, Sigaudy S, Porcu G, d’Ercole C, Figarella-Branger D, Raybaud C, Confort-Gouny S (2003) MR imaging of acquired fetal brain disorders. Child’s Nerv Syst 19:490–500
Barkovich AJ, Girard N (2003) Fetal brain infections. Child’s Nerv Syst 19:501–507
Huisman TA, Wisser J, Martin E, Kubik-Huch R, Marincek B (2002) Fetal magnetic resonance imaging of the central nervous system: a pictorial essay. Eur Radiol 12:1952–1961
Sonigo PC, Rypens FF, Carteret M, Delezoide AL, Brunelle FO (1998) MR imaging of fetal cerebral anomalies. Pediatr Radiol 28:212–222
Brisse H, Sebag G, Fallet C, Elmaleh M, Garel C, Rossler L, Vuillard E, Oury JF, Hassan M (1998) Prenatal MRI of corpus callosum agenesis. Study of 20 cases with neuropathological correlations. J Radiol 79:659–666
Garel C, Brisse H, Sebag G, Elmaleh M, Oury JF, Hassan M (1998) Magnetic resonance imaging of the fetus. Pediatr Radiol 28:201–211
Merzoug V, Ferey S, Andre C, Gelot A, Adamsbaum C (2002) Magnetic resonance imaging of the fetal brain. J Neuroradiol 29:76–90
Simon EM, Goldstein RB, Coakley FV, Filly RA, Broderick KC, Musci TJ, Barkovich AJ (2000) Fast MR imaging of fetal CNS anomalies in utero. Am J Neuroradiol 21:1688–1698
Levine D (2002) MR imaging of fetal central nervous system abnormalities. Brain Cogn 50:432–448
Hubbard AM, Harty MP (2000) MRI for the assessment of the malformed fetus. Baillière’s Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 14:629–650
Golden JA (2001) Cell migration and cerebral cortical development. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 27:22–28
Kuzniecky RI, Barkovich AJ (2001) Malformations of cortical development and epilepsy. Brain Dev 23:2–11
Barkovich AJ, Kuzniecky RI, Jackson GD, Guerrini R, Dobyns WB (2001) Classification system for malformations of cortical development: update 2001. Neurology 57:2168–2178
Barkovich AJ (2002) Magnetic resonance imaging: role in the understanding of cerebral malformations. Brain Dev 24:2–12
Barkovich AJ (2000) Pediatric neuroimaging, 3rd edn. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia
Allen KM, Walsh CA (1999) Genes that regulate neuronal migration in the cerebral cortex. Epilepsy Res 36:143–154
Copp AJ, Harding BN (1999) Neuronal migration disorders in humans and in mouse models—an overview. Epilepsy Res 36:133–141
Walsh CA, Goffinet AM (2000) Potential mechanisms of mutations that affect neuronal migration in man and mouse. Curr Opin Genet Dev 10:270–274
Norman MG, McGillivray BC, Kalousek DK, Hill A, Poskitt KJ (1995) Congenital malformations of the brain. Pathological, embryological, clinical, radiological and genetic aspects. Oxford University, New York
Evrard P, De Saint-Georges P, Kadhim H (1989) Pathology of prenatal encephalopathies. In Brookes PH (ed) Child neurology and developmental disabilities, Baltimore, pp 153–176
Sonigo P, Elmaleh A, Fermont L, Delezoide AL, Mirlesse V, Brunelle F (1996) Prenatal MRI diagnosis of fetal cerebral tuberous sclerosis. Pediatr Radiol 26:1–4
Gamzu R, Achiron R, Hegesh J, Weiner E, Tepper R, Nir A, Rabinowitz R, Auslander R, Yagel S, Zalel Y, Zimmer E (2002) Evaluating the risk of tuberous sclerosis in cases with prenatal diagnosis of cardiac rhabdomyoma. Prenat Diagn 22:1044–1047
Laure-Kamionowska M, Maslinska D, Raczkowska B (2002) Discrete glioneuronal malformative lesions in the foetal and infantile cerebral cortex. Folia Neuropathol 40:183–191
Des Portes V, Francis F, Pinard JM, Desguerre I, Moutard ML, Snoeck I, Meiners LC, Capron F, Cusmai R, Ricci S, Motte J, Echenne B, Ponsot G, Dulac O, Chelly J, Beldjord C (1998) Doublecortin is the major gene causing X-linked subcortical laminar heterotopia (SCLH). Hum Mol Genet 7:1063–1070
Puche A, Rodriguez T, Domingo R, Casas C, Vicente T, Martinez-Lage JF (1998) X-linked subcortical laminar heterotopia and lissencephaly: a new family. Neuropediatrics 29:276–278
Sun XZ, Takahashi S, Cui C, Zhang R, Sakata-Haga H, Sawada K, Fukui Y (2002) Normal and abnormal neuronal migration in the developing cerebral cortex. J Med Investig 49:97–110
Larroche JC, Girard N, Narcy F, Fallet C (1994) Abnormal cortical plate (polymicrogyria), heterotopias and brain damage in monozygous twins. Biol Neonate 65:343–352
Chang BS, Piao X, Bodell A, Basel-Vanagaite L, Straussberg R, Dobyns WB, Qasrawi B, Winter RM, Innes AM, Voit T, Grant PE, Barkovich AJ, Walsh CA (2003) Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria: clinical and radiological features in 10 families with linkage to chromosome 16. Ann Neurol 53:596–606
Eriksson SH, Thom M, Heffernan J, Lin WR, Harding BN, Squier MV, Sisodiya SM (2001) Persistent reelin-expressing Cajal–Retzius cells in polymicrogyria. Brain 124:1350–1361
Ghariani S, Dahan K, Saint-Martin C, Kadhim H, Morsomme F, Moniotte S, Verellen-Dumoulin C, Sebire G (2002) Polymicrogyria in chromosome 22q11 deletion syndrome. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 6:73–77
Clark GD (2004) The classification of cortical dysplasias through molecular genetics. Brain Dev 26:351–362
Villard L, Nguyen K, Cardoso C, Martin CL, Weiss AM, Sifry-Platt M, Grix AW, Graham JM Jr, Winter RM, Leventer RJ, Dobyns WB (2002) A locus for bilateral perisylvian polymicrogyria maps to Xq28. Am J Hum Genet 70:1003–1008
Sztriha L, Nork M (2002) Bilateral symmetrical frontoparietal polymicrogyria. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 6:229–232
Raybaud C, Girard N, Canto-Moreira N, Poncet M (1996) High-definition magnetic resonance imaging identification of cortical dysplasias: micropolygyria versus lissencephaly. In: Guerrini R, Andermann F, Canapicchi R, Roger J, Zifkin BG, Pfanner P (eds) Dysplasia of cerebral cortex and epilepsy. Lippincot-Raven, Philadelphia, pp 131–143
Girard N, Raybaud C, Gambarelli D, Figarella-Branger D (2001) Fetal brain MR imaging. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 9:19–56
Righini A, Zirpoli S, Mrakic F, Parazzini C, Pogliani L, Triulzi F (2004) Early prenatal MR imaging diagnosis of polymicrogyria. Am J Neuroradiol 25:343–346
Yakovlev PI, Wadsworth RC (1946) Schizencephalies. A study of the congenital clefts in the cerebral mantle: II. Clefts with hydrocephalus and lips separated. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 169–176
Yakovlev PI, Wadsworth RC (1946) Schizencephalies. A study of the congenital clefts in the cerebral mantle: I. Clefts with fused lips. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 116–130
Raybaud C, Girard N, Levrier O, Peretti-Viton P, Manera L, Farnarier P (2001) Schizencephaly: correlation between the lobar topography of the cleft(s) and absence of the septum pellucidum. Child’s Nerv Syst 17:217–222
Adamsbaum C, Moutard ML, Andre C, Merzoug V, Ferey S, Quere MP, Lewin F, Fallet-Bianco C (2005) MRI of the fetal posterior fossa. Pediatr Radiol 35:124–140
Adamsbaum C, Moreau V, Bulteau C, Burstyn J, Lair Milan F, Kalifa G (1994) Vermian agenesis without posterior fossa cyst. Pediatr Radiol 24:543–546
Patel S, Barkovich AJ (2002) Analysis and classification of cerebellar malformations. Am J Neuroradiol 23:1074–1087
Philip N, Chabrol B, Lossi AM, Cardoso C, Guerrini R, Dobyns WB, Raybaud C, Villard L (2003) Mutations in the oligophrenin-1 gene (OPHN1) cause X linked congenital cerebellar hypoplasia. J Med Genet 40:441–446
Sarnat HB, Benjamin DR, Siebert JR, Kletter GB, Cheyette SR (2002) Agenesis of the mesencephalon and metencephalon with cerebellar hypoplasia: putative mutation in the EN2 gene—report of 2 cases in early infancy. Pediatr Dev Pathol 5:54–68
Brunel H, Girard N, Confort-Gouny S, Viola A, Chaumoitre K, D’Ercole C, Figarella-Branger D, Raybaud C, Cozzone P, Panuel M (2004) Fetal brain injury. J Neuroradiol 31:123–137
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fogliarini, C., Chaumoitre, K., Chapon, F. et al. Assessment of cortical maturation with prenatal MRI. Eur Radiol 15, 1781–1789 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-2779-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-2779-9