Abstract
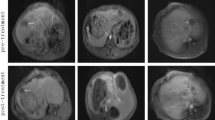
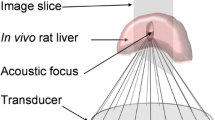
In order to find out whether high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) might be useful against hepatocellular carcinoma, we analyzed the effect of a microbubble agent (Levovist) on the temperature rise and tissue necrosis induced by HIFU. Rabbits were given 7 ml Levovist (300 mg/ml) or saline intravenously. Up to six areas per rabbit liver were exposed to HIFU for 60 s (2.18 MHz, ISPTA=400 W/cm2). The volume of the tissue coagulated by HIFU was measured 10 min after the start of HIFU. HIFU-induced lesions were larger in the animals given Levovist: (mm3, Levovist versus saline) 371±104 versus 166±71 (P<0.001). Temperatures in the animals given Levovist were also higher 60 s after the start of exposure: (°C, Levovist versus saline) 20.3±3.5 versus 13.2±3.8 (P<0.001). The amount of damage differed greatly, but the pathological changes caused by HIFU with Levovist were the same as those caused by HIFU with saline. Hemorrhagic areas and implosion cysts were seen, and many cells had been disrupted or destroyed. Microbubble agents developed for diagnostic uses could also be used in anticancer therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frizzell LA (1988) Threshold dosages for damage to mammalian liver by high-intensity focused ultrasound. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelect Freq Control 35:578–581
Linke CA, Carstensen EL, Frizzell LA, Elbodawi A, Fridd CW (1973) Localised tissue destruction by high-intensity focused ultrasound. Arch Surg 107:887–891
Moore WE, Lopez RM, Matthews DE, Sheets PW, Etchison MR, Hurwitz AS, Chalian AA, Fry FJ, Vane DW, Grosfeld JL (1989) Evaluation of high-intensity therapeutic ultrasound in the treatment of experimental hepatoma. J Pediatr Surg 24:30–33
Yang R, Reilly CR, Rescorla FJ, Faught PR, Sanghvi NT, Fry FJ, Franklin TD Jr, Lumeng L, Grosfeld JL (1991) High-intensity focused ultrasound in the treatment of experimental liver tumours. Arch Surg 126:1002–1010
Sibille A, Prat F, Chapelon JY, abou el Fadil F, Henry L, Theilliere Y, Ponchon T, Cathignol D (1993) Characterisation of extracorporeal ablation of normal and tumour-bearing liver tissue by high-intensity focused ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol 19:803–813
Vallancien G, Chartier-Kastler E, Bataille N, Chopin D, Haroumi M, Bougaran J (1993) Focused extracorporeal pyrotherapy. Eur Urol 23:48–52
Madersbacher S, Pedevilla M, Vingers L, Susani M, Marberger M (1995) Effect of high-intensity focused ultrasound on human prostate cancer in vivo. Cancer Res 55:3346–3351
Vallancien G, Harouni M, Guillonneau B, Veillon B, Bougaran J (1998) Ablation of superficial bladder tumours with pyrotherapy. Urology 47:204–207
Wu F, Wang ZB, Chen WZ, Zou JZ, Bai J, Zhu H, Li KQ, Xie FL, Jin CB, Su HB, Gao GW (2004) Extracorporeal focused ultrasound surgery for treatment of human solid carcinomas: early Chinese clinical experience. Ultrasound Med Biol 30:245–260
Gelczer RK, Charboneau JW, Hussain S, Brown DL (1998) Complications of percutaneous ethanol ablation. J Ultrasound Med 17:531–533
Solbiati L, Ierace T, Goldberg SN, Sironi S, Livraghi T, Fiocca R, Servadio G, Rizzatto G, Mueller PR, Del Maschio A, Gazelle GS (1997) Percutaneous US-guided radiofrequency tissue ablation of liver metastases: treatment and follow-up in 16 patients. Radiology 202:195–203
Yamada R, Sato M, Kawabata M, Nakatsuka H, Nakamura K, Takashima S (1983) Hepatic artery embolization in 120 patients with unresectable hepatoma. Radiology 148:397–401
Moran CM, Watson RJ, Fox KAA , McDicken WN (2002) In vitro acoustic characterisation of four intravenous ultrasonic contrast agents at 30 MHz. Ultrasound Med Biol 28:785–791
Blomley MJ, Cooke JC, Unger EC, Monaghan MJ, Cosgrove DO (2001) Microbubble contrast agents: a new era in ultrasound. BMJ 322:1222–1225
Yu T, Wang G, Hu K, Ma P, Bai J, Wang Z (2004) A microbubble agent improves the therapeutic efficiency of high intensity focused ultrasound: a rabbit kidney study. Urol Res 32:14–19
Umemura S, Kawabata K, Hashiba K (2001) Enhancement of ultrasound absorption by microbubbles for therapeutic application. In: Proceedings of 2001 IEEE ultrasonic symposium, vol 2, pp 1311–1314
Holt RG, Roy RA (2001) Measurement of bubble-enhanced heating from focused, MHz-frequency ultrasound in a tissue-mimicking material. Ultrasound Med Biol 27:1399–1412
Kaneko Y, Higaki T, Maruyama T, Matsumoto Y (2003) The effect of microbubbles as a heat transducer. In: Proceedings of 3rd international symposium on therapeutic ultrasound, June 22–25 Lyon, France, pp 55–60
Matsumoto Y, Allen JS, Yoshizawa S, Ikeda T, Kaneko Y (2005) Medical ultrasound with microbubbles. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 29:255–265
Prokop AF, Vaezy S, Noble ML, Kaczkowski PJ, Martin RW, Crum LA (2003) Polyacrylamide gel as an acoustic coupling medium for focused ultrasound therapy. Ultrasound Med Biol 29:1351–1358
ter Haar G, Rivens I, Chen L, Riddler S (1991) High intensity focused ultrasound for treatment of rat tumor. Phys Med Biol 36:1495–1501
Zeng J-Q, Wang G-M, Yao B, Wang G-X, He S-X (2004) Short-term results of 89 cases of rectal carcinoma treated with high-intensity focused ultrasound and low-dose radiotherapy. Ultrasound Med Biol 30:57–60
Umemura S, Kawabata K, Sanghvi N, Sasaki K (2002) Enhancement of ultrasonic absorption by microbubble agent for HIFU treatment. In: Proceedings of 2nd International Symposium on Therapeutic Ultrasound, July 29–August 1, Seattle, America, pp 527–532
Chen L, ter Haar G, Hill CR, Eccles SA, Box G (1998) Treatment of implanted liver tumors with focused ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol 24:1475–1488
Chen L, ter Haar G, Robertson D, Bensted JP, Hill CR (1999) Histological study of normal and tumor-bearing liver treated with focused ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol 25:847–856
Miller MW, Miller DL, Brayman AA (1996) A review of in vitro bioeffects of inertial ultrasonic cavitation from a mechanistic perspective. Ultrasound Med Biol 22:1131–1154
Baker KG, Robertson VJ, Duck FA (2001) A review of therapeutic ultrasound: biophysical effects. Phys Ther 81:1351–1358
Kennedy JE, Ter Haar GR, Cranston D (2003) High intensity focused ultrasound: surgery of the future? Br J Radiol 76:590–599
Tran BC, Seo J, Hall TL, Fowlkes JB, Cain CA (2003) Microbubble-enhanced cavitation for noninvasive ultrasound surgery. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 50:1296–1304
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, Culture, and Technology of Japan. Y.K. thanks JSPS Research Fellowships for Young Scientists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaneko, Y., Maruyama, T., Takegami, K. et al. Use of a microbubble agent to increase the effects of high intensity focused ultrasound on liver tissue. Eur Radiol 15, 1415–1420 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-2663-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-2663-7