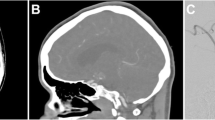
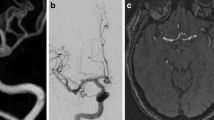
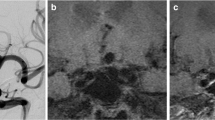
Abstract
Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is still considered the gold standard for most applications in neurovascular imaging. However, with the ongoing development of cross-sectional imaging modalities DSA is increasingly being replaced by less invasive methods. This contribution describes the diagnostic value and the increasing potential of computed tomography angiography (CTA) and magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) in the diagnosis and follow-up of intracranial aneurysms. The main role of CTA is in the diagnosis and therapy planning of ruptured aneurysms; in contrast, MRA plays an increasingly important role in the screening for asymptomatic aneurysms (especially in cases of familial subarachnoid hemorrhage) and in the follow-up after endovascular therapy with coils and/or intracranial stents. Technical issues concerning examination technique are covered here as well as an approach to advanced postprocessing of the image data. Furthermore, a brief outlook on the impact of new developments (MRA with parallel imaging and at 3.0 T) is given.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anzalone N, Scomazzoni F, Strada L, Patay Z, Scotti G (1998) Intracranial vascular malformations. Eur Radiol 8:685–690
Atkinson D, Brant-Zawadzki M, Gillan G, Purdy D, Laub G (1994) Improved MR angiography: magnetization transfer suppression with variable flip angle excitation and increased resolution. Radiology 190:890–894
Edelman RR, Ahn SS, Chien D, Li W, Goldmann A, Mantello M, Kramer J, Kleefield J (1992) Improved time-of-flight MR angiography of the brain with magnetization transfer contrast. Radiology 184:395–399
Pike GB, Hu BS, Glover GH, Enzmann DR (1992) Magnetization transfer time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography. Magn Reson Med 25:372–379
Mathews VP, Ulmer JL, White ML, Hamilton CA, Reboussen DM, Elster AD (1999) Depiction of intracranial vessels with MRA: utility of magnetization transfer saturation and gadolinium. J Comput Assist Tomogr 23:597–602
Özsarlak O, Van Goethem JW, Parizel PM (2004) 3D time-of-flight MR angiography of the intracranial vessels: optimization of the technique with water excitation, parallel acquisition, eight-channel phased-array head coil and low-dose contrast administration. Eur Radiol 14:2067–2071
Schick F (1996) Pulsed magnetization transfer contrast MRI by a sequence with water selective excitation. J Comput Assist Tomogr 20:73–79
Hatabu H, Gaa J, Stock KW, Li W, Thomasson D, Edelman RR (1999) Application of a spectral-spatial water excitation for MR angiography. Eur J Radiol 29:253–258
Gizewski ER, Ladd ME, Paul A, Wanke I, Goricke S, Forsting M (2005) Water excitation: a possible pitfall in cerebral time-of-flight angiography. Am J Neuroradiol 26:152–155
Özsarlak O, Van Goethem JW, Maes M, Parizel PM (2004) MR angiography of the intracranial vessels: technical aspects and clinical applications. Neuroradiology 46:955–972
Huston J III, Nichols DA, Luetmer PH, Goodwin JT, Meyer FB, Wiebers DO, Weaver AL (1994) Blinded prospective evaluation of sensitivity of MR angiography to known intracranial aneurysms: importance of aneurysm size. Am J Neuroradiol 15:1607–1614
Metens T, Rio F, Baleriaux D, Roger T, David P, Rodesch G (2000) Intracranial aneurysms: detection with gadolinium-enhanced dynamic three-dimensional MR angiography-initial results. Radiology 216:39–46
Bosmans H, Wilms G, Dymarkowski S, Marchal G (2001) Basic principles of MRA. Eur J Radiol 38:2–9
Gottschalk S, Gaebel C, Haendler G, Gellissen J, Missler U, Seidel G, Nowak G, Petersen D (2002) Contrast-enhanced intracranial 3 D MR angiography (CE-MRA) in assessing arterial stenoses and aneurysms (in German). Rofo Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Neuen Bildgeb Verfahr 174:704–713
Lee VS, Flyer MA, Weinreb JC, Krinsky GA, Rofsky NM (1996) Image subtraction in gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging. Am J Roentgenol 167:1427–1432
Pruessmann KP, Weiger M, Scheidegger MB, Boesiger P (1999) SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magn Reson Med 42:952–962
Sodickson DK, McKenzie CA, Ohliger MA, Yeh EN, Price MD (2002) Recent advances in image reconstruction, coil sensitivity calibration, and coil array design for SMASH and generalized parallel MRI. MAGMA 13:158–163
Griswold MA, Jakob PM, Heidemann RM, Nittka M, Jellus V, Wang J, Kiefer B, Haase A (2002) Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magn Reson Med 47:1202–1210
Heidemann RM, Ozsarlak O, Parizel PM, Michiels J, Kiefer B, Jellus V, Muller M, Breuer F, Blaimer M, Griswold MA, Jakob PM (2003) A brief review of parallel magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Radiol 13:2323–2337
Al-Kwifi O, Emery DJ, Wilman AH (2002) Vessel contrast at three tesla in time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography of the intracranial and carotid arteries. Magn Reson Imaging 20:181–187
Willinek WA, Born M, Simon B, Tschampa HJ, Krautmacher C, Gieseke J, Urbach H, Textor HJ, Schild HH (2003) Time-of-flight MR angiography: comparison of 3.0-T imaging and 1.5-T imaging-initial experience. Radiology 229:913–920
Ohkawa M, Tanabe M, Toyama Y, Kimura N, Mino S, Takayama K, Satoh G (1998) CT angiography with helical CT in the assessment of acute stage of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Radiat Med 16:91–97
Chappell ET, Moure FC, Good MC (2003) Comparison of computed tomographic angiography with digital subtraction angiography in the diagnosis of cerebral aneurysms: a meta-analysis. Neurosurgery 52:624–631
Wilms G, Demaerel P, Bosmans H, Marchal G (1999) MRI of non-ischemic vascular disease: aneurysms and vascular malformations. Eur Radiol 9:1055–1060
Wiebers DO, Whisnant JP, Huston J III, Meissner I, Brown RD Jr, Piepgras DG, Forbes GS, Thielen K, Nichols D, O’Fallon WM, Peacock J, Jaeger L, Kassell NF, Kongable-Beckman GL, Torner JC (2003) Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment. Lancet 362:103–110
Brilstra EH, Rinkel GJ, van der Graaf Y, van Rooij WJ, Algra A (1999) Treatment of intracranial aneurysms by embolization with coils: a systematic review. Stroke 30:470–476
Raaymakers TW, Rinkel GJ, Limburg M, Algra A (1998) Mortality and morbidity of surgery for unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a meta-analysis. Stroke 29:1531–1538
Schievink WI (1997) Genetics of intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 40:651–662
van Gijn J, Rinkel GJ (2001) Subarachnoid haemorrhage: diagnosis, causes and management. Brain 124:249–278
Ronkainen A, Hernesniemi J, Tromp G (1995) Special features of familial intracranial aneurysms: report of 215 familial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 37:43–46
Raaymakers TW, Rinkel GJ, Ramos LM (1998) Initial and follow-up screening for aneurysms in families with familial subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurology 51:1125–1130
Bederson JB, Awad IA, Wiebers DO, Piepgras D, Haley EC Jr, Brott T, Hademenos G, Chyatte D, Rosenwasser R, Caroselli C (2000) Recommendations for the management of patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Stroke Council of the American Heart Association. Stroke 31:2742–2750
Brown BM, Soldevilla F (1999) MR angiography and surgery for unruptured familial intracranial aneurysms in persons with a family history of cerebral aneurysms. Am J Roentgenol 173:133–138
Wermer MJ, Rinkel GJ, van Gijn J (2003) Repeated screening for intracranial aneurysms in familial subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 34:2788–2791
White PM, Teasdale EM, Wardlaw JM, Easton V (2001) Intracranial aneurysms: CT angiography and MR angiography for detection prospective blinded comparison in a large patient cohort. Radiology 219:739–749
Bosmans H, Wilms G, Marchal G, Demaerel P, Baert AL (1995) Characterisation of intracranial aneurysms with MR angiography. Neuroradiology 37:262–266
Chung TS, Joo JY, Lee SK, Chien D, Laub G (1999) Evaluation of cerebral aneurysms with high-resolution MR angiography using a section-interpolation technique: correlation with digital subtraction angiography. Am J Neuroradiol 20:229–235
White PM, Wardlaw JM, Lindsay KW, Sloss S, Patel DK, Teasdale EM (2003) The non-invasive detection of intracranial aneurysms: are neuroradiologists any better than other observers? Eur Radiol 13:389–396
Russell SM, Lin K, Hahn SA, Jafar JJ (2003) Smaller cerebral aneurysms producing more extensive subarachnoid hemorrhage following rupture: a radiological investigation and discussion of theoretical determinants. J Neurosurg 99:248–253
Gibbs GF, Huston J III, Bernstein MA, Riederer SJ, Brown RD Jr (2004) Improved image quality of intracranial aneurysms: 3.0-T versus 1.5-T time-of-flight MR angiography. Am J Neuroradiol 25:84–87
Gibbs GF, Huston J III, Bernstein MA, Riederer SJ, Brown RD Jr (2005) 3.0-Tesla MR angiography of intracranial aneurysms: comparison of time-of-flight and contrast-enhanced techniques. J Magn Reson Imaging 21:97–102
Adams WM, Laitt RD, Jackson A (2000) The role of MR angiography in the pretreatment assessment of intracranial aneurysms: a comparative study. Am J Neuroradiol 21:1618–1628
Atlas SW, Sheppard L, Goldberg HI, Hurst RW, Listerud J, Flamm E (1997) Intracranial aneurysms: detection and characterization with MR angiography with use of an advanced postprocessing technique in a blinded-reader study. Radiology 203:807–814
Prokop M, Shin HO, Schanz A, Schaefer-Prokop CM (1997) Use of maximum intensity projections in CT angiography: a basic review. Radiographics 17:433–451
Tomandl BF, Kostner NC, Schempershofe M, Huk WJ, Strauss C, Anker L, Hastreiter P (2004) CT angiography of intracranial aneurysms: a focus on postprocessing. Radiographics 24:637–655
Mallouhi A, Felber S, Chemelli A, Dessl A, Auer A, Schocke M, Jaschke WR, Waldenberger P (2003) Detection and characterization of intracranial aneurysms with MR angiography: comparison of volume-rendering and maximum-intensity-projection algorithms. Am J Roentgenol 180:55–64
Velthuis BK, van Leeuwen MS, Witkamp TD, Boomstra S, Ramos LM, Rinkel GJ (1997) CT angiography: source images and postprocessing techniques in the detection of cerebral aneurysms. Am J Roentgenol 169:1411–1417
U-King-Im JM, Koo B, Trivedi RA, Higgins NJ, Tay KY, Cross JJ, Antoun NM, Gillard JH (2005) Current diagnostic approaches to subarachnoid haemorrhage. Eur Radiol 15:1135–1147
Wanke I, Egelhof T, Dorfler A, Forsting M (2003) Intracranial aneurysms: pathogenesis, rupture risk, treatment options (in German). Rofo Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Neuen Bildgeb Verfahr 175:1064–1070
Gasparotti R, Liserre R (2005) Intracranial aneurysms. Eur Radiol 15:441–447
Sankhla SK, Gunawardena WJ, Coutinho CM, Jones AP, Keogh AJ (1996) Magnetic resonance angiography in the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage: a study of 51 cases. Neuroradiology 38:724–729
Cloft HJ, Joseph GJ, Dion JE (1999) Risk of cerebral angiography in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage, cerebral aneurysm, and arteriovenous malformation: a meta-analysis. Stroke 30:317–320
Heiserman JE, Dean BL, Hodak JA, Flom RA, Bird CR, Drayer BP, Fram EK (1994) Neurologic complications of cerebral angiography. Am J Neuroradiol 15:1401–1407
Aoki S, Sasaki Y, Machida T, Ohkubo T, Minami M (1992) Cerebral aneurysms: detection and delineation using 3-D-CT angiography. Am J Neuroradiol 13:1115–1120
Alberico RA, Ozsvath R, Casey S, Patel M (1996) Helical CT angiography for the detection of intracranial aneurysms. Am J Neuroradiol 17:1002–1003
Alberico RA, Patel M, Casey S, Jacobs B, Maguire W, Decker R (1995) Evaluation of the circle of Willis with three-dimensional CT angiography in patients with suspected intracranial aneurysms. Am J Neuroradiol 16:1571–1578
Harbaugh RE, Schlusselberg DS, Jeffery R, Hayden S, Cromwell LD, Pluta D (1992) Three-dimensional computerized tomography angiography in the diagnosis of cerebrovascular disease. J Neurosurg 76:408–414
Dorsch NW, Young N, Kingston RJ, Compton JS (1995) Early experience with spiral CT in the diagnosis of intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 36:230–236
Brown JH, Lustrin ES, Lev MH, Ogilvy CS, Taveras JM (1997) Characterization of intracranial aneurysms using CT angiography. Am J Roentgenol 169:889–893
Anderson GB, Findlay JM, Steinke DE, Ashforth R (1997) Experience with computed tomographic angiography for the detection of intracranial aneurysms in the setting of acute subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 41:522–527
White PM, Wardlaw JM, Easton V (2000) Can noninvasive imaging accurately depict intracranial aneurysms? A systematic review. Radiology 217:361–370
van Gelder JM (2003) Computed tomographic angiography for detecting cerebral aneurysms: implications of aneurysm size distribution for the sensitivity, specificity, and likelihood ratios. Neurosurgery 53:597–605
Jayaraman MV, Mayo-Smith WW, Tung GA, Haas RA, Rogg JM, Mehta NR, Doberstein CE (2004) Detection of intracranial aneurysms: multi-detector row CT angiography compared with DSA. Radiology 230:510–518
Anderson GB, Steinke DE, Petruk KC, Ashforth R, Findlay JM (1999) Computed tomographic angiography versus digital subtraction angiography for the diagnosis and early treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 45:1315–1320
Boet R, Poon WS, Lam JM, Yu SC (2003) The surgical treatment of intracranial aneurysms based on computer tomographic angiography alone-streamlining the acute mananagement of symptomatic aneurysms. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 145:101–105
Dehdashti AR, Rufenacht DA, Delavelle J, Reverdin A, de Tribolet N (2003) Therapeutic decision and management of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage based on computed tomographic angiography. Br J Neurosurg 17:46–53
Zouaoui A, Sahel M, Marro B, Clemenceau S, Dargent N, Bitar A, Faillot T, Capelle L, Marsault C (1997) Three-dimensional computed tomographic angiography in detection of cerebral aneurysms in acute subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 41:125–130
Jansen O, Braks E, Hahnel S, Schramm T, Sartor K (1998) [CT angiography to determine the size of intracranial aneurysms before GDC therapy]. Rofo Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Neuen Bildgeb Verfahr 169:175–181
Thornton J, Bashir Q, Aletich VA, Debrun GM, Ausman JI, Charbel FT (2000) What percentage of surgically clipped intracranial aneurysms have residual necks? Neurosurgery 46:1294–1298
Tsutsumi K, Ueki K, Morita A, Usui M, Kirino T (2001) Risk of aneurysm recurrence in patients with clipped cerebral aneurysms: results of long-term follow-up angiography. Stroke 32:1191–1194
Thornton J, Debrun GM, Aletich VA, Bashir Q, Charbel FT, Ausman J (2002) Follow-up angiography of intracranial aneurysms treated with endovascular placement of Guglielmi detachable coils. Neurosurgery 50:239–249
Matheus MG, Castillo M (2003) Development of de novo intracranial aneurysm in three months: case report and literature review. Am J Neuroradiol 24:709–710
Akyuz M, Tuncer R, Yilmaz S, Sindel T (2004) Angiographic follow-up after surgical treatment of intracranial aneurysms. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 146:245–250
Sindou M, Acevedo JC, Turjman F (1998) Aneurysmal remnants after microsurgical clipping: classification and results from a prospective angiographic study (in a consecutive series of 305 operated intracranial aneurysms). Acta Neurochir (Wien) 140:1153–1159
Shellock FG, Tkach JA, Ruggieri PM, Masaryk TJ, Rasmussen PA (2003) Aneurysm clips: evaluation of magnetic field interactions and translational attraction by use of "long-bore" and "short-bore" 3.0-T MR imaging systems. Am J Neuroradiol 24:463–471
van Loon JJ, Yousry TA, Fink U, Seelos KC, Reulen HJ, Steiger HJ (1997) Postoperative spiral computed tomography and magnetic resonance angiography after aneurysm clipping with titanium clips. Neurosurgery 41:851–856
Steiger HJ, van Loon JJ (1999) Virtues and drawbacks of titanium alloy aneurysm clips. Acta Neurochir Suppl 72:81–88
Kato Y, Nair S, Sano H, Sanjaykumar MS, Katada K, Hayakawa M, Kanno T (2002) Multi-slice 3D-CTA-an improvement over single slice helical CTA for cerebral aneurysms. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 144:715–722
Brown JH, Lustrin ES, Lev MH, Ogilvy CS, Taveras JM (1999) Reduction of aneurysm clip artifacts on CT angiograms: a technical note. Am J Neuroradiol 20:694–696
Guglielmi G, Vinuela F, Sepetka I, Macellari V (1991) Electrothrombosis of saccular aneurysms via endovascular approach. I. Electrochemical basis, technique, and experimental results. J Neurosurg 75:1–7
Guglielmi G, Vinuela F, Dion J, Duckwiler G (1991) Electrothrombosis of saccular aneurysms via endovascular approach. II. Preliminary clinical experience. J Neurosurg 75:8–14
Molyneux A, Kerr R, Stratton I, Sandercock P, Clarke M, Shrimpton J, Holman R (2002) International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised trial. Lancet 360:1267–1274
Murayama Y, Nien YL, Duckwiler G, Gobin YP, Jahan R, Frazee J, Martin N, Vinuela F (2003) Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of cerebral aneurysms: 11 years’ experience. J Neurosurg 98:959–966
Cognard C, Weill A, Spelle L, Piotin M, Castaings L, Rey A, Moret J (1999) Long-term angiographic follow-up of 169 intracranial berry aneurysms occluded with detachable coils. Radiology 212:348–356
Shellock FG, Detrick MS, Brant-Zawadski MN (1997) MR compatibility of Guglielmi detachable coils. Radiology 203:568–570
Shellock FG, Gounis M, Wakhloo A (2005) Detachable coil for cerebral aneurysms: in vitro evaluation of magnetic field interactions, heating, and artifacts at 3T. Am J Neuroradiol 26:363–366
Derdeyn CP, Graves VB, Turski PA, Masaryk AM, Strother CM (1997) MR angiography of saccular aneurysms after treatment with Guglielmi detachable coils: preliminary experience. Am J Neuroradiol 18:279–286
Brunereau L, Cottier JP, Sonier CB, Medioni B, Bertrand P, Rouleau P, Sirinelli D, Herbreteau D (1999) Prospective evaluation of time-of-flight MR angiography in the follow-up of intracranial saccular aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils. J Comput Assist Tomogr 23:216–223
Kähärä VJ, Seppanen SK, Ryymin PS, Mattila P, Kuurne T, Laasonen EM (1999) MR angiography with three-dimensional time-of-flight and targeted maximum-intensity-projection reconstructions in the follow-up of intracranial aneurysms embolized with Guglielmi detachable coils. Am J Neuroradiol 20:1470–1475
Anzalone N, Righi C, Simionato F, Scomazzoni F, Pagani G, Calori G, Santino P, Scotti G (2000) Three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography in the evaluation of intracranial aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils. Am J Neuroradiol 21:746–752
Boulin A, Pierot L (2001) Follow-up of intracranial aneurysms treated with detachable coils: comparison of gadolinium-enhanced 3D time-of-flight MR angiography and digital subtraction angiography. Radiology 219:108–113
Cottier JP, Bleuzen-Couthon A, Gallas S, Vinikoff-Sonier CB, Bertrand P, Domengie F, Barantin L, Herbreteau D (2003) Intracranial aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils: is contrast material necessary in the follow-up with 3D time-of-flight MR angiography? Am J Neuroradiol 24:1797–1803
Okahara M, Kiyosue H, Hori Y, Yamashita M, Nagatomi H, Mori H (2004) Three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography for evaluation of intracranial aneurysms after endosaccular packing with Guglielmi detachable coils: comparison with 3D digital subtraction angiography. Eur Radiol 14:1162–1168
Yamada N, Hayashi K, Murao K, Higashi M, Iihara K (2004) Time-of-flight MR angiography targeted to coiled intracranial aneurysms is more sensitive to residual flow than is digital subtraction angiography. Am J Neuroradiol 25:1154–1157
Hartman J, Nguyen T, Larsen D, Teitelbaum GP (1997) MR artifacts, heat production, and ferromagnetism of Guglielmi detachable coils. Am J Neuroradiol 18:497–501
Gonner F, Heid O, Remonda L, Nicoli G, Baumgartner RW, Godoy N, Schroth G (1998) MR angiography with ultrashort echo time in cerebral aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils. Am J Neuroradiol 19:1324–1328
Farb RI, Nag S, Scott JN, Willinsky RA, Marotta TR, Montanera WJ, Tomlinson G, Terbrugge KG (2005) Surveillance of intracranial aneurysms treated with detachable coils: a comparison of MRA techniques. Neuroradiology 47:507–515
Gauvrit JY, Leclerc X, Pernodet M, Lubicz B, Lejeune JP, Leys D, Pruvo JP (2005) Intracranial aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils: usefulness of 6-month imaging follow-up with contrast-enhanced MR angiography. Am J Neuroradiol 26:515–521
Lylyk P, Ceratto R, Hurvitz D, Basso A (1998) Treatment of a vertebral dissecting aneurysm with stents and coils: technical case report. Neurosurgery 43:385–388
Sekhon LH, Morgan MK, Sorby W, Grinnell V (1998) Combined endovascular stent implantation and endosaccular coil placement for the treatment of a wide-necked vertebral artery aneurysm: technical case report. Neurosurgery 43:380–383
Wakhloo AK, Lanzino G, Lieber BB, Hopkins LN (1998) Stents for intracranial aneurysms: the beginning of a new endovascular era? Neurosurgery 43:377–379
Phatouros CC, Sasaki TY, Higashida RT, Malek AM, Meyers PM, Dowd CF, Halbach VV (2000) Stent-supported coil embolization: the treatment of fusiform and wide-neck aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms. Neurosurgery 47:107–113
Brassel F, Rademaker J, Haupt C, Becker H (2001) Intravascular stent placement for a fusiform aneurysm of the posterior cerebral artery: case report. Eur Radiol 11:1250–1253
Fiorella D, Albuquerque FC, Han P, McDougall CG (2004) Preliminary experience using the Neuroform stent for the treatment of cerebral aneurysms. Neurosurgery 54:6–16
Wanke I, Doerfler A, Schoch B, Stolke D, Forsting M (2003) Treatment of wide-necked intracranial aneurysms with a self-expanding stent system: initial clinical experience. Am J Neuroradiol 24:1192–1199
Alfke K, Straube T, Dorner L, Mehdorn HM, Jansen O (2004) Treatment of intracranial broad-neck aneurysms with a new self-expanding stent and coil embolization. Am J Neuroradiol 25:584–591
Lubicz B, Piotin M, Mounayer C, Spelle L, Moret J (2005) Selective endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms with a liquid embolic: a single-center experience in 39 patients with 41 aneurysms. Am J Neuroradiol 26:885–893
Molyneux AJ, Cekirge S, Saatci I, Gal G (2004) Cerebral Aneurysm Multicenter European Onyx (CAMEO) trial: results of a prospective observational study in 20 European centers. Am J Neuroradiol 25:39–51
Lenhart M, Volk M, Manke C, Nitz WR, Strotzer M, Feuerbach S, Link J (2000) Stent appearance at contrast-enhanced MR angiography: in vitro examination with 14 stents. Radiology 217:173–178
Maintz D, Tombach B, Juergens KU, Weigel S, Heindel W, Fischbach R (2002) Revealing in-stent stenoses of the iliac arteries: comparison of multidetector CT with MR angiography and digital radiographic angiography in a Phantom model. Am J Roentgenol 179:1319–1322
Nehra A, Moran CJ, Cross DT, 3rd, Derdeyn CP (2004) MR safety and imaging of neuroform stents at 3T. Am J Neuroradiol 25:1476–1478
Saatci I, Cekirge HS, Ciceri EF, Mawad ME, Pamuk AG, Besim A (2003) CT and MR imaging findings and their implications in the follow-up of patients with intracranial aneurysms treated with endosaccular occlusion with onyx. Am J Neuroradiol 24:567–578
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papke, K., Brassel, F. Modern cross-sectional imaging in the diagnosis and follow-up of intracranial aneurysms. Eur Radiol 16, 2051–2066 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-0092-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-0092-2