Abstract
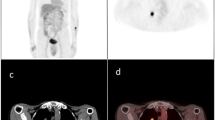
We present a case of bronchioloalveolar carcinoma manifesting as air-space consolidation with negative FDG uptake on integrated PET/CT in a 42-year-old woman. To know this pattern of uptake especially in the case of mucin-predominant lobar bronchioloalveolar carcinoma may help avoid misdiagnosis of this particular tumor.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miles KA (2003) Functional CT imaging in oncology. Eur Radiol 13:M134–M138
Juan R, Seifert B, Berthold T, Schulthess GK, Goerres GW (2004) Clinical evaluation of a breathing protocol for PET/CT. Eur Radiol 14:1118–1123
Hany TF, Heuberger J, Schulthess GK (2003) Iatrogenic FDG foci in the lungs: a pitfall of PET image interpretation. Eur Radiol 13:2122–2127
Schmid DT, Kneifel S, Stoeckli SJ, Padberg BC, Merrill G, Goerres GW (2003) Increased 18F-FDG uptake mimicking thyroid cancer in a patient with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Eur Radiol 13:2119–2121
Freudenberg LS, Antoch G, Gorges R et al (2003) Combined PET/CT with iodine-124 in diagnosis of spread metastatic thyroid carcinoma: a case report. Eur Radiol 13:L19–L23
Freudenberg LS, Antoch G, Jentzen W et al (2004) Value of 124I-PET/CT in staging of patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Eur Radiol 14:2092–2098
Berger KL, Nicholson SA, Dehdashti F, Siegel BA (2000) FDG PET evaluation of mucinous neoplasms: Correlation of FDG uptake with histopathologic features. Am J Roentgenol 174:1005–1008
Jadvar H, Segall GM (1997) False-negative fluorine-18-FDG PET in metastatic carcinoid. J Nucl Med 38:1382–1383
Kim BT, Kim Y, Lee KS et al (1998) Localized form of bronchioloalveolar carcinoma: FDG PET findings. Am J Roentgenol 170:935–939
Cook GJ, Wegner EA, Fogelman I (2004) Pitfalls and artifacts in 18F-FDG and PET/CT oncologic imaging. Semin Nucl Med 34:122–133
Higashi K, Nishikawa T, Seki H et al (1998) Comparison of fluorine-18-FDG PET and thallium-201 SPECT in evaluation of lung cancer. J Nucl Med 39:9–15
Heyneman LE, Patz EF (2002) PET imaging in patients with bronchioloalveolar cell carcinoma. Lung Cancer 38:261–266
Lee KS, Kim Y, Han J, Ko EJ, Park CK, Primack SL (1997) Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma: clinical, histopathologic, and radiologic findings. Radiographics 17:1345–1357
Higashi K, Clavo AC, Wahl RL (1993) Does FDG uptake measure proliferative activity of human cancer cells? In vitro comparison with DNA flow cytometry and tritiated thymidine uptake. J Nucl Med 34:414–419
Yap CS, Schiepers C, Fishbein MC, Phelps ME, Czernin J (2002) FDG-PET imaging in lung cancer: how sensitive is it for bronchioloalveolar carcinoma? Eur J Nucl Med 29:1166–1173
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sung, Y.M., Lee, K.S., Kim, BT. et al. Lobar mucinous bronchioloalveolar carcinoma of the lung showing negative FDG uptake on integrated PET/CT. Eur Radiol 15, 2075–2078 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-004-2604-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-004-2604-x