Abstract
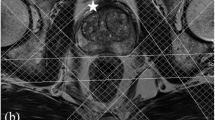
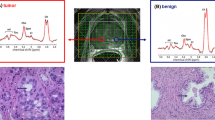
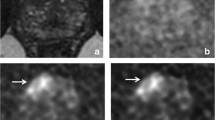
The objective of this study was to demonstrate the feasibility of 3D proton MR spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) of the prostate using a standard spine instead of a dedicated endorectal coil at 1.5 T. Twenty-eight patients (25 with biopsy proven prostate cancers and three patients with a benign prostate hyperplasia) were examined. MRI and MRSI were conducted with commercial array surface coils at 1.5 T. Ratios of choline (Cho), creatine (Cr) and citrate (Ci) were calculated for tumour, central and peripheral zone retrospectively, based on axial T2 weighed MR images and histology reports. Prostate cancer was characterized by significantly elevated (Cho+Cr)/Ci ratio compared with non-tumourous prostate tissue. The quality of all proton MR spectra was considered to be good or acceptable in 17/28 patients (61%) and poor in 11/28 (39%) examinations. In 20/25 patients with proven malignancy (80%), MRSI was considered to be helpful for the detection of prostate cancer. In 4/25 patients with proven malignancy (16%) who underwent seed implantation, radiotherapy or hormone deprivation before MR examination spectroscopy was of poor and non-diagnostic quality. MRSI of the prostate is feasible within clinical routine using the spine array surface coil at 1.5 T. It can consequently be applied to patients even with contraindications for endorectal coils. However, spectral quality and signal-to-noise ratio is clearly inferior to 3D MRSI examinations with endorectal coils.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greenlee RT, Hill-Harmon MB, Murray T, Thun M (2001) Cancer statistics CA. Cancer J Clin 51:15–36
Holmberg L, Bill-Axelson A, Helgesen F, Salo JO, Folmerz P, Haggman M, Andersson SO, Spangberg A, Busch C, Nordling S, Palmgren J, Adami HO, Johansson JE, Norlen BJ, Scandinavian Prostatic Cancer Group Study Number 4 (2002) A randomized trial comparing radical prostatectomy with watchful waiting in early prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 347:781–789
Ikonen S, Kivisaari L, Tervahartiala P, Vehmas T, Taari K, Rannikko S (2001) Prostate MR imaging: accuracy in differentiating cancer from other prostatic disorders. Acta Radiol 42:348–354
Hricak H, White S, Vigneron D, Kurhanewicz J, Kosco A, Levin D, Weiss J, Narayan P, Carroll PR (1994) Carcinoma of the prostate gland: MR imaging with pelvic phased-array coils versus integrated endorectal-pelvic phased-array coils. Radiology 193:703–709
Jager GJ, Severens JL, Thornbury JR, de la Rosette JJ, Ruijs SH, Barentsz JO (2000) Prostate cancer staging: should MR imaging be used? A decision analytic approach. Radiology 215:445–451
May F, Treumann T, Dettmar P, Hartung R, Breul J (2001) Limited value of endorectal magnetic resonance imaging and transrectal ultrasonography in the staging of clinically localized prostate cancer. BJU Int 87:66–69
Engelbrecht MR, Jager GJ, Laheij RJ, Verbeek AL, Van Lier HJ, Barentsz JO (2002) Local staging of prostate cancer using magnetic resonance imaging: a meta-analysis. Eur Radiol 12:2294–2302
Schlemmer HP, Merkle J, Grobholz R, Jaeger T, Michel MS, Werner A, Rabe J, Van Kaick G (2004) Can pre-operative contrast-enhanced dynamic MR imaging for prostate cancer predict microvessel density in prostatectomy specimens? Eur Radiol 14:309–317
Kiessling F, Lichy M, Grobholz R, Heilmann M, Farhan N, Michel MS, Trojan L, Ederle J, Abel U, Kauczor HU, Semmler W, Delorme S (2004) Simple models improve the discrimination of prostate cancers from the peripheral gland by T1-weighted dynamic MRI. Eur Radiol 14:1793–1801
Rouviere O, Raudrant A, Ecochard R, Colin-Pangaud C, Pasquiou C, Bouvier R, Marechal JM, Lyonnet D (2003) Characterization of time-enhancement curves of benign and malignant prostate tissue at dynamic MR imaging. Eur Radiol 13:931–942
Scheidler J, Hricak H, Vigneron DB, Yu KK, Sokolov DL, Huang LR, Zaloudek CJ, Nelson SJ, Carroll PR, Kurhanewicz J (1999) Prostate cancer: localization with three-dimensional proton MR spectroscopic imaging—clinicopathological study. Radiology 213:473–480
Yu KK, Schneidler J, Hricak H, Vigneron CJ, Zaloudek CJ, Males RG, Neslon SJ, Carroll PR, Kurhanewiccz J (1999) Prostate cancer: prediction of extracapsular extension with endorectal MR imaging and three-dimensional proton MR spectroscopic imaging. Radiology 213:481–488
Coakley FV, Kurhanewicz J, Lu Y, Jones KD, Swanson MG, Chang SD, Carroll PR, Hricak H (2002) Prostate cancer tumor volume: measurement with endorectal MR and MR spectroscopic imaging. Radiology 223:91–97
Heerschap A, Jager G, Van der Graaf M, Barentsz J, Ruijs S (1997) Proton MR spectroscopy of the normal human prostate with an endorectal coil and a double spin-echo pulse sequence. Magn Reson Med 37:204–213
Schick F, Bongers H, Kurz S, Jung WI, Pfeffer M, Lutz O (1993) Localized proton MR spectroscopy of citrate in vitro and of the human prostate in vivo at 1.5 T. Magn Reson Med 29:38–43
Kim JK, Kim DY, Lee YH, Sung NK, Chung DS, Kim OD, Kim KB (1998) In vivo differential diagnosis of prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia: localized proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy using external-body surface coil. Magn Reson Imaging 16:1281–1288
Kaji Y, Wada A, Imaoka I, Matsuo M, Terachi T, Kobashi Y, Sugimura K, Fujii M, Maruyama K, Takizawa O (2002) Proton two-dimensional chemical shift imaging for evaluation of prostate cancer: external surface coil vs. endorectal surface coil. J Magn Reson Imaging 16:697–706
Scheenen TW, Klomp DW, Roll SA, Futterer JJ, Barentsz JO, Heerschap A (2004) Fast acquisition-weighted three-dimensional proton MR spectroscopic imaging of the human prostate. Magn Reson Med 52:80–88
Pohmann R, von Kienlin M (2001) Accurate phosphorus metabolite images of the human heart by 3D acquisition-weighted CSI. Magn Reson Med 45:817–826
Mescher M, Merkle H, Kirsch J, Garwood M, Gruetter R (1998) Simultaneous in vivo spectral editing and water suppression. NMR Biomed 11:266–272
Garcia-Segura J, Sanchez-Chapado M, Ibarburen C, Viano J, Angulo J, Gonzales J, Rodriguez-Vallejo J (1999) In vivo 1H MRS of diseased prostate: spectroscopic features of malignant versus benign pathology. Magn Reson Imaging 17:755–765
Males R, Vigneron D, Star-Lack J, Falbo S, Nelson S, Hricak H, Kurhanewicz J (2000) Clinical application of BASING and spectral/spatial water and lipid suppression pulses for prostate cancer staging and localization by in vivo 3D 1H MR spectroscopic imaging. Magn Reson Med 43:17–22
Star-Lack J, Nelson SJ, Kurhanewicz J, Huang LR, Vigneron DB (1997) Improved water and lipid suppression for 3D PRESS CSI using RF band selective inversion with gradient dephasing (BASING). Magn Reson Med 38:311–321
Wefer A-E, Hricak H, Vigneron D-B, Coakley F-V, Lu Y, Wefer J, Mueller-Lisse U, Carroll P-R, Kurhanewicz J (2000) Sextant localization of prostate cancer: comparison of sextant biopsy, magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging with step section histology. J Urol 164:400–404
Pirtskhalaishvili G, Hrebinko RL, Nelson JB (2001) The treatment of prostate cancer: an overview of current options. Cancer Pract 9:295–306
Beerlage HP, Thuroff S, Madersbacher S, Zlotta AR, Aus G, de Reijke TM, de la Rosette JJ (2000) Current status of minimally invasive treatment options for localized prostate carcinoma. Eur Urol 37:2–13
Schlemmer HP, Corvin S (2004) Methods for volume assessment of prostate cancer. Eur Radiol 14:597–606
Heerschap A, Jager GJ, Van der Graaf M, Barentsz JO, de la Rosette JJ, Oosterhof GO, Ruijter ET, Ruijs SH (1997) In vivo proton MR spectroscopy reveals altered metabolite content in malignant prostate tissue. Anticancer Res 17:1455–1460
Kurhanewicz J, Vigneron DB, Hricak H, Narayan P, Carroll P, Nelson SJ (1996) Three-dimensional H-1 MR spectroscopic imaging of the in situ human prostate with high (0.24–0.7 cm3) spatial resolution. Radiology 198:795–805
Mueller-Lisse UG, Vigneron DB, Hricak H, Swanson MG, Carroll PR, Bessette A, Scheidler J, Srivastava A, Males RG, Cha I, Kurhanewicz (2001) Localized prostate cancer: effect of hormone deprivation therapy measured by using combined three-dimensional 1H MR spectroscopy and MR imaging: clinicopathologic case-controlled study. Radiology 221:380–390
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lichy, M.P., Pintaske, J., Kottke, R. et al. 3D proton MR spectroscopic imaging of prostate cancer using a standard spine coil at 1.5 T in clinical routine: a feasibility study. Eur Radiol 15, 653–660 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-004-2547-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-004-2547-2