Abstract
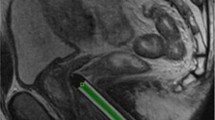
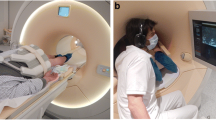
The purpose of this study was to examine the feasibility and safety of MR-guided biopsies with a transgluteal approach in patients with uncertain or suspicious prostate lesions. Twenty-five patients with uncertain or suspicious focal prostate lesions detected by high-field MR imaging of the prostate gland using endorectal coil imaging were biopsied with a transgluteal approach in a low-field MRI system (0.2 T, Concerto, Siemens). The procedures were guided using T1-weighted FLASH sequences. The prostate gland was biopsied repeatedly with a coaxial technique through a 15-gauge pencil tip with a 16-gauge biopsy handy (median 3.8 samples per patient). Complications and biopsy findings were documented retrospectively. Using T1-weighted sequences biopsy procedures were performed successfully with MR guidance in all cases without any side effects or complications. The median intervention time was 11.3 min. Pathological findings revealed ten cases of hyperplasia or atrophy, three cases of prostatitis, ten cases of carcinoma and two cases of normal tissue. The clinical follow-up showed that in two patients prostate cancer was missed at MR-guided biopsy. Transgluteal MR-guided biopsy of the prostate gland is a safe and promising approach for histological clarification of uncertain or suspicious lesions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mettlin CJ, Murphy GP, Rosenthal DS, Menck HR (1998) The National Cancer Data Base report on prostate carcinoma after the peak in incidence rates in the U.S. The American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer and the American Cancer Society. Cancer 83:1679–1684
Beyersdorff D, Taupitz M, Winkelmann B, Fischer T, Lenk S, Loening SA, Hamm B (2002) Patients with a history of elevated prostate-specific antigen levels and negative transrectal US-guided quadrant or sextant biopsy results: value of MR imaging. Radiology 224:701–706
Colombo T, Schips L, Augustin H, Gruber H, Hebel P, Petritsch PH, Hubmer G (1999) Value of transrectal ultrasound in preoperative staging of prostate cancer. Minerva Urol Nefrol 51:1–4
Perrotti M, Han KR, Epstein RE, Kennedy EC, Rabbani F, Badani K, Pantuck AJ, Weiss RE, Cummings KB (1999) Prospective evaluation of endorectal magnetic resonance imaging to detect tumor foci in men with prior negative prostastic biopsy: a pilot study. J Urol 162:1314–1317
Schiebler ML, Schnall MD, Pollack HM, Lenkinski RE, Tomaszewski JE, Wein AJ, Whittington R, Rauschning W, Kressel HY (1993) Current role of MR imaging in the staging of adenocarcinoma of the prostate. Radiology 189:339–352
Jager GJ, Ruijter ET, van de Kaa CA, de la Rosette JJ, Oosterhof GO, Thornbury JR, Barentsz JO (1996) Local staging of prostate cancer with endorectal MR imaging: correlation with histopathology. Am J Roentgenol 166:845–852
Scheidler J, Hricak H, Vigneron D et al (1999) Prostate cancer: localization with three-dimensional proton MR spectroscopic imaging—clinicopathologic study. Radiology 213:473–480
Coakley FV, Kurhanewicz J, Lu Y, Jones KD, Swanson MG, Chang SD, Carroll PR, Hricak H (2002) Prostate cancer tumor volume: measurement with endorectal MR and MR spectroscopic imaging. Radiology 223:91–97
Wefer AE, Hricak H, Vigneron DB, Coakley FV, Lu Y, Wefer J, Mueller-Lisse U, Carroll PR, Kurhanewicz J (2000) Sextant localization of prostate cancer: comparison of sextant biopsy, magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging with step section histology. J Urol 164:400–404
Dhingsa R, Qayyum A, Coakley F, Lu Y, Jones K, Swanson M, Carroll P, Hricak H, Kurhanewicz J (2004) Prostate cancer localization with endorectal MR imaging and MR spectroscopic imaging: effect of clinical data on reader accuracy. Radiology 230:215–220
Ikonen S, Karkkainen P, Kivisaari L, Salo JO, Taari K, Vehmas T, Tervahartiala P, Rannikko S (1998) Magnetic resonance imaging of clinically localized prostatic cancer. J Urol 159:915–919
Schiebler M, Tomaszewski J, Bezzi M et al (1989) Prostatic carcinoma and benign prostatic hyperplasia: correlation of high-resolution MR and histopathologic findings. Radiology 172:131–137
Hodge KK, McNeal JE, Stamey TA (1989) Ultrasound guided transrectal core biopsies of the palpably abnormal prostate. J Urol 142:66–70
Djavan B, Ravery V, Zlotta A et al (2001) Prospective evaluation of prostate cancer detected on biopsies 1, 2, 3 and 4: when should we stop? J Urol 166:1679–1683
Papanicolaou N, Eisenberg PJ, Silverman SG, McNicholas MM, Althausen AF (1996) Prostatic biopsy after proctocolectomy: a transgluteal, CT-guided approach. Am J Roentgenol 166:1332–1334
D’Amico AV, Tempany CM, Cormack R, Hata N, Jinzaki M, Tuncali K, Weinstein M, Richie JP (2000) Transperineal magnetic resonance image guided prostate biopsy. J Urol 164:385–387
Hata N, Jinzaki M, Kacher D et al (2001) MR imaging-guided prostate biopsy with surgical navigation software: device validation and feasibility. Radiology 220:263–268
Rodriguez LV, Terris MK (1998) Risks and complications of transrectal ultrasound guided prostate needle biopsy: a prospective study and review of the literature. J Urol 160:2115–2120
Cruz M, Tsuda K, Narumi Y et al (2002) Characterization of low-intensity lesions in the peripheral zone of prostate on pre-biopsy endorectal coil MR imaging. Eur Radiol 12:357–365
Chelsky MJ, Schnall MD, Seidmon EJ, Pollack HM (1993) Use of endorectal surface coil magnetic resonance imaging for local staging of prostate cancer. J Urol 150:391–395
Yu KK, Hricak H, Alagappan R, Chernoff DM, Bacchetti P, Zaloudek CJ (1997) Detection of extracapsular extension of prostate carcinoma with endorectal and phased-array coil MR imaging: multivariate feature analysis. Radiology 202:697–702
Quint LE, Van Erp JS, Bland PH, Del Buono EA, Mandell SH, Grossman HB, Gikas PW (1991) Prostate cancer: correlation of MR images with tissue optical density at pathologic examination. Radiology 179:837–842
Sommer FG, Nghiem HV, Herfkens R, McNeal J, Low RN (1993) Determining the volume of prostatic carcinoma: value of MR imaging with an external-array coil. Am J Roentgenol 161:81–86
Jager GJ, Ruijter ET, de la Rosette JJ, van de Kaa CA (1997) Amyloidosis of the seminal vesicles simulating tumor invasion of prostatic carcinoma on endorectal MR images. Eur Radiol 7:552–554
Tamada T, Sone T, Nagai K, Jo Y, Gyoten M, Imai S, Kajihara Y, Fukunaga M (2004) T2-weighted MR imaging of prostate cancer: multishot echo-planar imaging vs fast spin-echo imaging. Eur Radiol 14:318–325
Rouviere O, Raudrant A, Ecochard R, Colin-Pangaud C, Pasquiou C, Bouvier R, Marechal J, Lyonnet D (2003) Characterization of time-enhancement curves of benign and malignant prostate tissue at dynamic MR imaging. Eur Radiol 13:931–942
Engelbrecht M, Huisman H, Laheij R, Jager G, van Leenders G, Hulsbergen-Van DKC, de la Rosette J, Blickman J, Barentsz J (2003) Discrimination of prostate cancer from normal peripheral zone and central gland tissue by using dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 229:248–254
Yu KK, Scheidler J, Hricak H, Vigneron DB, Zaloudek CJ, Males RG, Nelson SJ, Carroll PR, Kurhanewicz J (1999) Prostate cancer: prediction of extracapsular extension with endorectal MR imaging and three-dimensional proton MR spectroscopic imaging. Radiology 213:481–488
Scheidler J, Hricak H, Vigneron DB et al (1999) Prostate cancer: localization with three-dimensional proton MR spectroscopic imaging—clinicopathologic study. Radiology 213:473–480
Hodge KK, McNeal JE, Terris MK, Stamey TA (1989) Random systematic versus directed ultrasound guided transrectal core biopsies of the prostate. J Urol 142:71–74 (discussion 74–75)
Peyromaure M, Ravery V, Messas A, Toublanc M, Boccon-Gibod L (2002) Pain and morbidity of an extensive prostate 10-biopsy protocol: a prospective study in 289 patients. J Urol 167:218–221
Naughton CK, Miller DC, Mager DE, Ornstein DK, Catalona WJ (2000) A prospective randomized trial comparing 6 versus 12 prostate biopsy cores: impact on cancer detection. J Urol 164:388–392
Halpern EJ, Frauscher F, Strup SE, Nazarian LN, O’Kane P, Gomella LG (2002) Prostate: high-frequency Doppler US imaging for cancer detection. Radiology 225:71–77
Halpern EJ, Frauscher F, Forsberg F, Strup SE, Nazarian LN, O’Kane P, Gomella LG (2002) High-frequency Doppler US of the prostate: effect of patient position. Radiology 222:634–639
Breslin JA, Turner BI, Faber RB, Rhamy RK (1978) Anaerobic infection as a consequence of transrectal prostatic biopsy. J Urol 120:502–503
Brewster SF, Rooney N, Kabala J, Feneley RC (1993) Fatal anaerobic infection following transrectal biopsy of a rare prostatic tumour. Br J Urol 72:977–978
Kaplan I, Oldenburg NE, Meskell P, Blake M, Church P, Holupka EJ (2002) Real time MRI-ultrasound image guided stereotactic prostate biopsy. Magn Reson Imaging 20:295–299
Vilanova J, Comet J, Capdevila A, Barcelo J, Dolz J, Huguet M, Barcelo C, Aldoma J, Delgado E (2001) The value of endorectal MR imaging to predict positive biopsies in clinically intermediate-risk prostate cancer patients. Eur Radiol 11:229–235
Lufkin R, Duckwiler G, Spickler E, Teresi L, Chang M, Onik G (1988) MR body stereotaxis: an aid for MR-guided biopsies. J Comput Assist Tomogr 12:1088–1089
Mueller PR, Stark DD, Simeone JF, Saini S, Hahn PF, Steiner E, Beaulieu P, Wittenberg J, Ferrucci JT Jr (1989) Clinical use of a nonferromagnetic needle for magnetic resonance-guided biopsy. Gastrointest Radiol 14:61–64
Duckwiler G, Lufkin RB, Hanafee WN (1989) MR-directed needle biopsies. Radiol Clin North Am 27:255–263
Kaufman L, Crooks L, Arakawa M, Hoenninger J, Watts J, Winkler M (1987) Prospects for increasing the accessibility of MRI. Adm Radiol 6:32–34 (see also pages 36–38)
Lufkin R, Teresi L, Hanafee W (1987) New needle for MR-guided aspiration cytology of the head and neck. Am J Roentgenol 149:380–382
Gupta S, Nguyen H, Morello F, Ahrar K, Wallace M, Madoff D, Murthy R, Hicks M (2004) Various approaches for CT-guided percutaneous biopsy of deep pelvic lesions: anatomic and technical considerations. Radiographics 24:175–189
Cormack RA, D’Amico AV, Hata N, Silverman S, Weinstein M, Tempany CM (2000) Feasibility of transperineal prostate biopsy under interventional magnetic resonance guidance. Urology 56:663–664
D’Amico A, Cormack R, Kumar S, Tempany CM (2000) Real-time magnetic resonance imaging-guided brachytherapy in the treatment of selected patients with clinically localized prostate cancer. J Endourol 14:367–370
Fichtinger G, DeWeese TL, Patriciu A, Tanacs A, Mazilu D, Anderson JH, Masamune K, Taylor RH, Stoianovici D (2002) System for robotically assisted prostate biopsy and therapy with intraoperative CT guidance. Acad Radiol 9:60–74
Halpern EJ, Frauscher F, Rosenberg M, Gomella LG (2002) Directed biopsy during contrast-enhanced sonography of the prostate. Am J Roentgenol 178:915–919
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zangos, S., Eichler, K., Engelmann, K. et al. MR-guided transgluteal biopsies with an open low-field system in patients with clinically suspected prostate cancer: technique and preliminary results. Eur Radiol 15, 174–182 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-004-2458-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-004-2458-2