Abstract
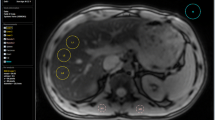
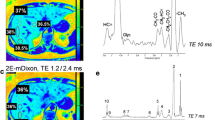
Phosphorus-31 NMR spectroscopy using slice selection (DRESS) was used to investigate the absolute concentrations of metabolites in the human liver. Absolute concentrations provide more specific biochemical information compared to spectrum integral ratios. Nine patients with histopathologically proven diffuse liver disease and 12 healthy individuals were examined in a 1.5-T MR scanner (GE Signa LX Echospeed plus). The metabolite concentration quantification procedures included: (1) determination of optimal depth for the in vivo measurements, (2) mapping the detection coil characteristics, (3) calculation of selected slice and liver volume ratios using simple segmentation procedures and (4) spectral analysis in the time domain. The patients had significantly lower concentrations of phosphodiesters (PDE), 6.3±3.9 mM, and ATP-β, 3.6±1.1 mM, (P<0.05) compared with the control group (10.0±4.2 mM and 4.2±0.3 mM, respectively). The concentrations of phosphomonoesters (PME) were higher in the patient group, although this was not significant. Constructing an anabolic charge (AC) based on absolute concentrations, [PME]/([PME] + [PDE]), the patients had a significantly larger AC than the control subjects, 0.29 vs. 0.16 (P<0.005). Absolute concentration measurements of phosphorus metabolites in the liver are feasible using a slice selective sequence, and the technique demonstrates significant differences between patients and healthy subjects.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Graham RA, Taylor AH, Brown TR (1994) A method for calculating the distribution of pH in tissues and a new source of pH error from the 31P-NMR spectrum. Am J Physiol 266:R638–R645
Lundberg P, Harmsen E, Ho C, Vogel HJ (1990) Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of cellular metabolism. Anal Biochem 191:193–222
Buchli R, Duc CO, Martin E, Boesiger P (1994) Assessment of absolute metabolite concentrations in human tissue by 31P MRS in vivo. Part I. Cerebrum, cerebellum, cerebral gray and white matter. Magn Reson Med 32:447–452
Meyerhoff DJ, Boska MD, Thomas AM, Weiner MW (1989) Alcoholic liver disease: quantitative image-guided P-31 MR spectroscopy. Radiology 173:393–400
Rajanayagam V, Lee RR, Ackerman Z, Bradley WG, Ross BD (1992) Quantitative P-31 MR spectroscopy of the liver in alcoholic cirrhosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 2:183–190
Oberhaensli R, Rajagopalan B, Galloway GJ, Taylor DJ, Radda GK (1990) Study of human liver disease with P-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Gut 31:463–467
Li CW, Negendank WG, Murphy-Boesch J, Padavic-Shaller K, Brown TR (1996) Molar quantitation of hepatic metabolites in vivo in proton-decoupled, nuclear Overhauser effect enhanced 31P NMR spectra localized by three-dimensional chemical shift imaging. NMR Biomed 9:141–155
Sijens PE, Dagnelie PC, Halfwerk S, van Dijk P, Wicklow K, Oudkerk M (1998) Understanding the discrepancies between 31P MR spectroscopy assessed liver metabolite concentrations from different institutions. Magn Reson Imaging 16:205–211
Tosner Z, Dezortova M, Tintera J, Hajek M (2001) Application of two-dimensional CSI for absolute quantification of phosphorus metabolites in the human liver. Magma 13:40–46
Bottomley PA, Foster TB, Darrow RD (1984) Depth-resolved surface-coil spectroscopy (DRESS) for in vivo 1H, 31P, and 13C NMR. J Magn Reson 59:338–342
van den Boogaart A, Van Hecke P, Van Huffel S, Graveron-Demilly D, van Ormondt D, de Beer R (1996) MRUI: a graphical user interface for accurate routine MRS data analysis. In: Proceedings of the ESMRMB 13th Annual Meeting, Prague 318
van den Boogaart (1997) A MRUI MANUAL V. 96.3. A user’s guide to the Magnetic Resonance User Interface Software Package. Delft Technical University, Delft
van der Veen JWC, de Beer R, Luyten PR, van Ormondt D (1988) Accurate quantification of in vivo 31-P NMR signals using the variable projection method and prior knowledge. Magn Reson Med 6:92–98
Robitaille P-M, Robitaille PA, Brown GG, Browns GG (1991) An analysis of the pH-dependent chemical shift behaviour of phosphorus-containing metabolites. J Magn Reson 92:73–84
Graham RA, Meyer RA, Szwergold BS, Brown TR (1987) Observation of myo-inositol 1,2-(cyclic) phosphate in a Morris hepatoma by 31P NMR. J Biol Chem 262:35–37
Bates TE, Williams SR, Gadian DG (1989) Phosphodiesters in the liver: the effect of field strength on the 31P signal. Magn Reson Med 12:145–150
de Kruijff B, van den Besselaar AMPH, Cullis PR, van den Bosch H, van Deenen LLM (1978) Evidence for isotropic motion of phospholipids in liver microsomal membranes. A 31P-NMR study. Biochim Biophys Acta 514:1–8
Murphy EJ, Rajagopalan B, Brindle KM, Radda GK (1989) Phospholipid bilayer contribution to 31P NMR spectra in vivo. Magn Reson Med 12:282–289
Buchli R, Meier D, Martin E, Boesiger P (1994) Assessment of absolute metabolite concentrations in human tissue by 31P MRS in vivo. Part II. Muscle, liver, kidney. Magn Reson Med 32:453–458
Hultman E, Nilsson LH, Sahlin K. (1975) Adenine nucleotide content in human liver; normal values and fructose induced deplation. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 35:245–251
Matson GB, Meyerhoff DJ, Lawry TJ et al (1993) Use of computer simulations for quantitation of 31P ISIS MRS results. NMR Biomed 6:215–224
Ljungberg M, Starck G, Vikhoff-Baaz B, Alpsten M, Ekholm S, Forssell-Aronsson E (2002) The magnitude of signal errors introduced by ISIS in quantitative 31P MRS. Magma 14:30–38
Kuesel AC, Stoyanova R, Aiken NR et al (1996) Quantitation of resonances in biological 31P NMR spectra via principal component analysis: potential and limitations. NMR Biomed 9:93–104
Menon DK, Sargentoni J, Taylor-Robinson SD et al (1995) Effect of functional grade and etiology on in vivo hepatic phosphorus-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy in cirrhosis: biochemical basis of spectral appearances. Hepatology 21:417–427
Zakian KL, D’Angelica M, Matei C et al (2000) A quantitativce assessement of liver metabolites during jaundice using three dimensional phosphorus chemical shift imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 18:181–187
Dixon RM, Angus PW, Rajagopalan B, Radda GK (1991) Abnormal phosphomonoester signals in 31P MR spectra from patients with hepatic lymphoma. A possible marker of liver infiltration and response to chemotherapy. Br J Cancer 63:953–958
Cox IJ, Bell JD, Peden CJ et al (1992) In vivo and in vitro 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy of focal hepatic malignancies. NMR Biomed 5:114–120
Brinkmann G, Melchert UH (1992) A study of T1-weighted 31phosphorus MR-spectroscopy from patients with focal and diffuse liver disease. Magn Reson Imaging 10:949–956
Bell JD, Cox IJ, Sargentoni J et al (1993) A 31P and 1H-NMR investigation in vitro of normal and abnormal human liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 1225:71–77
Yamane Y, Umeda M, O’Uchi T, Mitsushima T, Nakata K, Nagataki S (1994) Phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance in vivo spectroscopy of human liver during hepatitis A virus infection. Dig Dis Sci 39:33–38
Bourdel-Marchasson I, Biran M, Thiaudiere E et al (1996) 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy of human liver in elderly patients: changes according to nutritional status and inflammatory state. Metabolism 45:1059–1061
Cox IJ (1996) Development and applications of in vivo clinical magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 65:45–81
Dagnelie PC, Sijens PE, Kraus DJ, Planting AS, van Dijk P (1999) Abnormal liver metabolism in cancer patients detected by (31)P MR spectroscopy. NMR Biomed 12:535–544
Mann DV, Lam WW, Magnus Hjelm N et al (2002) Biliary drainage for obstructive jaundice enhances hepatic energy status in humans: a 31-phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Gut 50:118–122
Angus PW, Dixon RM, Rajagopalan B et al (1990) A study of patients with alcoholic liver disease by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Clin Sci (Colch) 78:33–38
Munakata T, Griffiths RD, Martin PA, Jenkins SA, Shields R, Edwards RH (1993) An in vivo 31P MRS study of patients with liver cirrhosis: progress towards a non-invasive assessment of disease severity. NMR Biomed 6:168–172
Taylor-Robinson SD, Thomas EL, Sargentoni J, Marcus CD, Davidson BR, Bell JD (1995) Cirrhosis of the human liver: an in vitro 31P nuclear magnetic resonance study. Biochim Biophys Acta 1272:113–118
van Wassenaer-van Hall HN, van der Grond J, van Hattum J, Kooijman C, Hoogenraad TU, Mali WP (1995) standardized serum, clinical, and histological changes in diffuse liver disease. Hepatology 21:443–449
Menon DK, Harris M, Sargentoni J, Taylor-Robinson SD, Cox IJ, Morgan MY (1995) In vivo hepatic 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy in chronic alcohol abusers. Gastroenterology 108:776–788
Taylor-Robinson SD, Sargentoni J, Bell JD et al (1997) In vivo and in vitro hepatic 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy and electron microscopy of the cirrhotic liver. Liver 17:198–209
Jalan R, Sargentoni J, Coutts GA et al (1996) Hepatic phosphorus-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy in primary biliary cirrhosis and its relation to prognostic models. Gut 39:141–146
Lim AK, Patel N, Hamilton G, Hajnal JV, Goldin RD, Taylor-Robinson SD (2003) The relationship of in vivo 31P MR spectroscopy to histology in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 37:788–794
Kiyono K, Shibata A, Sone S et al (1998) Relationship of 31P MR spectroscopy to the histopathological grading of chronic hepatitis and response to therapy. Acta Radiol 39:309–314
Atkinson DE (1968) The energy charge of the adenylate pool as a regulatory parameter—interaction with feedback modifiers. Biochemistry 7:4030
Cortez-Pinto H, Chatham J, Chacko VP, Arnold C, Rashid A, Diehl AM (1999) Alterations in liver ATP homeostasis in human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a pilot study. J Am Med Assoc 282:1659–1664
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Norén, B., Lundberg, P., Ressner, M. et al. Absolute quantification of human liver metabolite concentrations by localized in vivo 31P NMR spectroscopy in diffuse liver disease. Eur Radiol 15, 148–157 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-004-2434-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-004-2434-x