Abstract
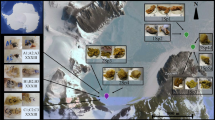
The fatty acid composition of marine cold-water sponges of genus Latrunculia, namely Latrunculia bocagei Ridley and Dendy, 1886, and Latrunculia biformis Kirkpatrick, 1907, for which no fatty acid data had been previously reported, has been examined. High levels of long-chain fatty acids (C24–30) with high unsaturation levels (mainly polyunsaturation), and high incidence of branched- and odd-chain fatty acids in sponges are suggested to be partially connected with their specific cell membrane requirements to surmount the negative effects of low temperatures and to enable growth in extreme environments. Furthermore, variations in the fatty acid profile at the species level may reflect variations in compositions or quantities of symbiotic microorganisms that commonly represent up to 60 % of the sponge wet weight. The fatty acid compositions of lipid-rich sponge extracts from five Latrunculia specimens dredged from the Bransfield Strait near the Antarctic Peninsula, were obtained using supercritical carbon dioxide and analyzed using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry–flame ionization detection. Furthermore, the antioxidant activities of these extracts were determined using the photochemiluminescent method. Along with common fatty acids, the chemical analyses revealed very long-chain fatty acids (C22, C24). Differences were seen for the fatty acid levels between both species and different specimens of the same species. The observed differences do not seem connected to the habitat depth of the specimen, but rather indicate the variations within the associated microbiome. Furthermore, these sponge extracts showed antioxidant activities, confirming that they contain lipidic compounds that strongly scavenge free radicals.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas S, Kelly M, Bowling J, Sims J, Waters A, Hamann M (2011) Advancement into the Arctic region for bioactive sponge secondary metabolites. Mar Drugs 9:2423–2437
Abele D, Puntarulo S (2004) Formation of reactive species and induction of antioxidant defence systems in polar and temperate marine invertebrates and fish. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 138:405–415
Antunes EM, Copp BR, Davies-Coleman MT, Samaai T (2005) Pyrroloiminoquinone and related metabolites from marine sponges. Nat Prod Rep 22:62–72
Bergquist PR, Lawson MP, Lavis A, Cambie RC (1984) Fatty acid composition and the classification of the Porifera. Biochem Syst Ecol 12:63–84
Botić T, Kunčić MK, Sepčić K, Knez Ž, Gunde-Cimerman N (2012) Salt induces biosynthesis of hemolytically active compounds in the xerotolerant food-borne fungus Wallemia sebi. FEMS Micro Lett 326:40–46
D’Amico S, Collins T, Marx JC, Feller G, Gerday C (2006) Psychrophilic microorganisms: challenges for life. EMBO Rep 7:385–389
Dorantes-Aranda JJ, Garcia-de la Parra LM, Alonso-Rodriguez R, Morquecho L (2009) Hemolytic activity and fatty acids composition in the ichthyotoxic dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides isolated from Bahia de La Paz, Gulf of California. Mar Pollut Bull 58:1401–1405
Ford J, Capon RJ (2000) Discorhabdin R: a new antibacterial pyrroloiminoquinone from two Latrunculiid marine sponges, Latrunculia sp. and Negombata sp. J Nat Prod 63:1527–1528
Gerasimenko NI, Chaykina EL, Busarova NG, Anisimov MM (2010) Antimicrobic and hemolytic activity of low-molecular metabolites of brown seaweed Laminaria cichorioides (Miyabe). Appl Biochem Microbiol 46:426–430
Göcke C, Janussen D (2013) Sponge assemblages of the deep Weddell Sea: ecological and zoogeographic results of ANDEEP I-III and SYSTCO I expeditions. Polar Biol 36:1059–1068
Grkovic T, Copp BR (2009) New natural products in the discorhabdin A- and B-series from New Zealand-sourced Latrunculia spp. sponges. Tetrahedron 65:6335–6340
Grkovic T, Ding Y, Li XC, Webb VL, Ferreira D, Copp BR (2008) Enantiomeric discorhabdin alkaloids and establishment of their absolute configurations using theoretical calculations of electronic circular dichroism spectra. J Org Chem 73:9133–9136
Grkovic T, Pearce AN, Munro MHG, Blunt JW, Davies-Coleman MT, Copp BR (2010) Isolation and characterization of diastereomers of Discorhabdins H and K and assignment of absolute configuration to Discorhabdins D, N, Q, S, T, and U. J Nat Prod 73:1686–1693
Harwood JL, Russell NJ (1984) Lipids in plants and microbes Allen and Unwin, London
Hentschel U, Hopke J, Horn M, Friedrich AB, Wagner M, Hacker J, Moore BS (2002) Molecular evidence for a uniform microbial community in sponges from different oceans. Appl Environ Micro 68:4431–4440
Hentschel U, Fieseler L, Wehrl M, Gernert C, Steinert M, Hacker J, Horn M (2003) Microbial diversity of marine sponges. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 37(59–88):83
Hentschel U, Usher KM, Taylor MW (2006) Marine sponges as microbial fermenters. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 55:167–177
Ikawa M (2004) Algal polyunsaturated fatty acids and effects on plankton ecology and other organisms. UNH Center Freshwat Biol Res 6:17–44
Janussen D, Downey RV (2014) Porifera. In: De Broyer C, Koubbi P, Griffiths HJ, Raymond B, Udekem d’Acoz C et al (eds) Biogeographic atlas of the Southern Ocean, 1st edn. The Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research, Cambridge, pp 94–102
Janussen D, Tendal OS (2007) Diversity and distribution of Porifera in the bathyal and abyssal Weddell Sea and adjacent areas. Deep Sea Res Pt II 54:1864–1875
Kersken D, Göcke C, Brandt A, Lejzerowicz F, Schwabe E, Seefeldt MA, Veit-Köhler G, Janussen D (2014) The infauna of three widely distributed sponge species (Hexactinellida and Demospongiae) from the deep Ekström Shelf in the Weddell Sea, Antarctica. Deep Sea Res Pt II 108:101–112
Klitgaard AB, Tendal OS (2004) Distribution and species composition of mass occurrences of large-sized sponges in the northeast Atlantic. Prog Oceanogr 61:57–98
Makar’eva TN, Krasokhin VB, Guzii AG, Stonik VA (2010) Strong ethanol solvate of discorhabdin A isolated from the far-east sponge Latruculia oparinae. Chem Nat Compd 46:152–153
Mancini I, Defant A, Mesaric T, Potocnik F, Batista U, Guella G, Turk T, Sepčić K (2011) Fatty acid composition of common barbel (Barbus barbus) roe and evaluation of its haemolytic and cytotoxic activities. Toxicon 57:1017–1022
Manconi R, Murgia S, Pronzato R (2008) Sponges from African inland waters: the genus Eunapius (Haplosclerida, Spongillina, Spongillidae). Fundam Appl Limnol 170:333–350
Miller K, Alvarez B, Battershill C, Northcote P, Parthasarathy H (2001) Genetic, morphological, and chemical divergence in the sponge genus Latrunculia (Porifera: Demospongiae) from New Zealand. Mar Biol 139:235–250
Na M, Ding Y, Wang B, Tekwani BL, Schinazi RF, Franzblau S, Kelly M, Stone R, Li XC, Ferreira D, Hamann MT (2010) Anti-infective discorhabdins from a deep-water Alaskan sponge of the genus Latrunculia. J Nat Prod 73:383–387
Nèeman I, Fishelson L, Kashman Y (1975) Isolation of a new toxin from the sponge Latrunculia magnifica in the Gulf of Aquaba (Red Sea). Mar Biol 30:293–296
Núñez-Pons L, Avila C (2014) Deterrent activities in the crude lipophilic fractions of Antarctic benthic organisms: chemical defences against keystone predators. Polar Res 33:216–224
Perry NB, Blunt JW, McCombs JD, Munro MHG (1986) Discorhabdin C, a highly cytotoxic pigment from a sponge of the genus Latrunculia. J Org Chem 51:5476–5478
Perry NB, Blunt JW, Munro MHG (1988a) Cytotoxic pigments from New Zealand sponges of the genus Latrunculia: discorhabdins A, B and C. Tetrahedron 44:1727–1734
Perry NB, Blunt JW, Munro MHG, Higa T, Sakai R (1988b) Discorhabdin D, an antitumor alkaloid from the sponges Latrunculia brevis and Prianos sp. J Org Chem 53:4127–4128
Reyes F, Martin R, Rueda A, Fernandez R, Montalvo D, Gomez C, Sánchez-Puelles JM (2004) Discorhabdins I and L, cytotoxic alkaloids from the sponge Latrunculia brevis. J Nat Prod 67:463–465
Rezanka T, Sigler K (2009) Odd-numbered very-long-chain fatty acids from the microbial, animal and plant kingdoms. Prog Lipid Res 48:206–238
Richard D, Kefi K, Barbe U, Bausero P, Visioli F (2008) Polyunsaturated fatty acids as antioxidants. Pharmacol Res 57:451–455
Rod’kina SA, Latyshev NA, Imbs AB (2003) Fatty acids from the sponge Halichondria panicea from the Sea of Japan. Bioorg Khim 29:419–424
Sahena F, Zaidul ISM, Jinap S, Karim AA, Abbas KA, Norulaini NAN, Omar AKM (2009) Application of supercritical CO2 in lipid extraction—a review. J Food Eng 95:240–253
Samaai T, Kelly M (2002) Family Latrunculiidae Topsent. Systema Porifera: guide to the classification of sponges. Kluwer, New York
Samaai T, Gibbons MJ, Kelly M (2006) Revision of the genus Latrunculia du Bocage, 1869 (Porifera: Demospongiae: Latrunculiidae) with descriptions of new species from New Caledonia and the Northeastern Pacific. Zootaxa 1127:1–71
Schlitzer R (2015) Ocean data view. http://odv.awi.de. Accessed 13 May 2015
Schöttner S, Hoffmann F, Cardenas P, Rapp HT, Boetius A, Ramette A (2013) Relationships between host phylogeny, host type and bacterial community diversity in cold-water coral reef sponges. PLoS ONE 8:e55505
Sepe V, D’Orsi R, Borbone N, Valeria D’Auria M, Bifulco G, Monti MC, Cataniac A, Zampella A (2006) Callipeltins F-I: new antifungal peptides from the marine sponge Latrunculia sp. Tetrahedron 62:833–840
Shaaban M, Abd-Alla H, Hassan A, Aly H, Ghani M (2012) Chemical characterization, antioxidant and inhibitory effects of some marine sponges against carbohydrate metabolizing enzymes. Org Med Chem Lett 2:30
Shimazawa M, Nakajima Y, Mashima Y, Hara H (2009) Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) has neuroprotective effects against oxidative stress in retinal ganglion cells. Brain Res 1251:269–275
Soest RWMV, Erpenbeck D, Alvarez B (2002) Family Dictyonellidae Van Soest, Diaz & Pomponi, 1990. In: Hooper JNA, Soest RWMV (eds) Systema porifera: a guide to the classification of sponges, 1st edn. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, pp 773–786
Storelli C, Acierno R, Maffia M (1998) Membrane lipid and protein adaptations in Antarctic fish. In: Pörtner HO, Playle RC (eds) Cold Ocean physiology, 1st edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 166–189
Turk T, Avguštin J, Batista U, Strugar G, Kosmina R, Čivović S, Janussen D, Kauferstein S, Mebs D, Sepčić K (2013) Biological activities of ethanolic extracts from deep-sea Antarctic marine sponges. Mar Drugs 11:1126–1139
Webster NS, Negri AP, Munro MMHG, Battershill N (2004) Diverse microbial communities inhabit Antarctic sponges. Environ Microbiol 6:288–300
Wu JT, Chiang YR, Huang WY, Jane WN (2006) Cytotoxic effects of free fatty acids on phytoplankton algae and cyanobacteria. Aquat Toxicol 80:338–345
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Slovenian Research Agency (Research Program P2-0046), the ERASMUS Staff Mobility—Staff training program for financial support to TB and Dr. Christopher Berrie for editing and appraisal of the manuscript. D. Janussen wishes to thank all of her colleagues who participated in Antarctic expedition, ANT XXIX/3 in 2003. Our thanks go to the captain and crew of the RV Polarstern. The Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) is acknowledged for financial support of her Antarctic Porifera Research Projects (JA 1063/17-1, JA-1063/14-1-3).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Botić, T., Cör, D., Anesi, A. et al. Fatty acid composition and antioxidant activity of Antarctic marine sponges of the genus Latrunculia . Polar Biol 38, 1605–1612 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-015-1722-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-015-1722-z