Abstract
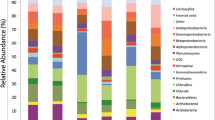
Bacterial community structures in soils collected from eight sites around Casey Station, Antarctica, were investigated using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) of amplified 16S rRNA gene fragments. Higher bacterial diversity was found in soils from protected or relatively low human-impacted sites in comparison to highly impacted sites. However, the highest diversity was detected in samples from Wilkes Tip, a former waste disposal site that has been undisturbed for the last 50 years. Comparison of community structure based on non-metric multidimensional scaling plots revealed that all sites, except the hydrocarbon-contaminated (oil spill) site, were clustered with a 45% similarity. A total of 23 partial 16S rRNA gene sequences were obtained from the excised DGGE bands, with the majority of the sequences closely related to those of the Cytophaga–Flexibacter–Bacteroides group. No significant correlation was established between environmental variables, including soil pH, electrical conductivity, carbon, nitrogen, water content and heavy metals, with bacterial diversity across the eight study sites.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aislabie JM, Chhour K, Saul DJ, Miyauchi S, Ayton J, Paetzold RF, Balks MR (2006) Dominant bacteria in soils of Marble Point and Wright Valley, Victoria Land, Antarctica. Soil Biol Biochem 38:3041–3056. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.02.018
Aislabie JM, Jordan S, Barker GM (2008) Relation between soil classification and bacterial diversity in soils of the Ross Sea region, Antarctica. Geoderma 144:9–20. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2007.10.006
Beyer L, Bolter M (2000) Chemical and biological properties, formation, occurrence and classification of Spodic Cryosols in a terrestrial ecosystem of East Antarctica (Wilkes Land). Catena 39:95–119. doi:10.1016/S0341-8162(99)00089-2
Bolter M (1992) Environmental conditions and microbiological properties from soils and lichens from Antarctica (Casey Station, Wilkes Land). Polar Biol 11:591–599. doi:10.1007/BF00237953
Claridge GGC, Campbell IB, Powell HKJ, Amin ZH, Balks MR (1995) Heavy metal contamination in some soils of the McMurdo Sound region, Antarctica. Ant Sci 7(1):9–14. doi:10.1017/S0954102095000034
Coenye T, Laevens S, Willems A, Ohlén M, Hannant W, Govan JRW, Gillis M, Falsen E, Vandamme P (2001) Burkholderia fungorum sp nov. and Burkholderia caledonica sp. nov., two new species isolated from the environment, animals and human clinical samples. J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1099–1107
Dorigo U, Volatier L, Humbert JF (2005) Molecular approaches to the assessment of biodiversity in aquatic microbial communities. Water Res 39:2207–2218. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2005.04.007
Gadd GM, Griffiths AJ (1978) Microorganisms and heavy metal toxicity. Microb Ecol 4:303–317. doi:10.1007/BF02013274
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackerbrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucliec acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, New York, pp 115–175
Hinojosa MB, Carreira JA, García-Ruíz R, Dick RP (2005) Microbial response to heavy metal-polluted soils: community analysis from phospholipid-linked fatty acids and ester-linked fatty acids extracts. J Environ Qual 34:1789–1800. doi:10.2134/jeq2004.0470
Konopka A, Zakharova T, Bischoff M, Oliver L, Nakatsu C, Turco RF (1999) Microbial biomass and activity in lead-contaminated soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(5):2256–2259
Li S, Xiao X, Yin X, Wang F (2006) Bacterial community along a historic lake sediment core of Ardley Island, West Antarctica. Extremophiles 10:461–467. doi:10.1007/s00792-006-0523-2
Muyzer G (1999) DGGE/TGGE a method for identifying genes from natural ecosystems. Curr Opin Microbiol 2:317–322. doi:10.1016/S1369-5274(99)80055-1
Newberry CJ, Webster G, Cragg BA, Parkes RJ, Weightman AJ, Fry JC (2004) Diversity of prokaryotes and methanogenesis in deep subsurface sediments from the Nankai Trough, Ocean Drilling Program Leg 190. Environ Microbiol 6(3):274–287. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2004.00568.x
Pearce DA (2003) Bacterioplankton community structure in a Maritime Antarctic oligotrophic lake during period of Holomixis, as determined by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) and fluorescence in situ hydridization (FISH). Microb Ecol 46:92–105. doi:10.1007/s00248-002-2039-3
Powell SM, Bowman JP, Snape I, Stark JS (2003) Microbial community in pristine and polluted nearshore Antarctic sediments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 45:135–145. doi:10.1016/S0168-6496(03)00135-1
Powell SM, Snape I, Bowman JP, Thompson BAW, Stark JS, McCammon SA, Riddle MJ (2004) A comparison of the short term effects of diesel fuel and lubricant oils on Antarctic benthic microbial communities. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 322:53–65. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2005.02.005
Revill AT, Snape I, Lucieer A, Guille D (2007) Constraints on transport and weathering of petroleum contamination at Casey Station, Antarctica. Cold Regions Sci Technol 48:154–167
Roser DJ, Seppelt RD, Ashbolt N (1993) Microbiology of ornithogenic soils from the windmill islands, budd coast, continental Antarctica: Microbial biomass distribution. Soil Biol Biochem 25(2):165–175. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(93)90023-5
Santos IR, Silva-Filho EV, Schaefer CEGR, Albuquerque-Filho MR, Campos LS (2005) Heavy metal contamination in coastal sediments and soils near the Brazilian Antarctic Station, King George Island. Mar Pollut Bull 50:185–194. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.10.009
Saul DJ, Aislabie JM, Brown CE, Harris L, Foght JM (2005) Hydrocarbon contamination changes the bacterial diversity of soil from around Scott Base, Antarctica. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 53:141–155. doi:10.1016/j.femsec.2004.11.007
Scouller RC, Snape I, Stark JS, Gore DB (2006) Evaluation of geochemical methods for discrimination of metal contamination in Antarctic marine sediments: a case study from Casey Station. Chemosphere 65:294–309. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.02.062
Shigematsu T, Yumihara K, Ueda Y, Numaguchi M, Morimura S, Kida K (2003) Delftia tsuruhatensis sp. nov., a terephthalate-assimilating bacterium isolated from activated sludge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1479–1483. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.02285-0
Snape I, Scouller RC, Stark SC, Stark J, Riddle MJ, Gore JB (2004) Characterisation of the dilute HCl extraction method for the identification of metal contamination in Antarctic marine sediments. Chemosphere 57:491–504. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.05.042
Snape I, Ferguson SH, Harvey PM, Riddle MJ (2006) Investigation of evaporation and biodegradation of fuel spills in Antarctica: II—Extent of natural attenuation at Casey Station. Chemosphere 63:89–98. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.07.040
Stark JS (2000) The distribution and abundance of soft-sediment macrobenthos around Casey Station, East Antarctica. Polar Biol 23:840–850. doi:10.1007/s003000000162
Stark JS, Riddle MJ, Snape I, Scouller RC (2003) Human impacts in Antartic marine soft-sediment assemblages: correlations between multivariate biological patterns and environmental variables at Casey Station. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 56:717–734. doi:10.1016/S0272-7714(02)00291-3
Stark JS, Snape I, Riddle MJ, Stark SC (2005) Constraints on spatial variability in soft-sediment communities affected by contamination from an Antarctic waste disposal site. Mar Pollut Bull 50:276–290. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.10.015
Thangaraj K, Kapley A, Purohit HJ (2008) Characterization of diverse Acinetobacter isolates for utilization of multiple aromatic compounds. Bioresour Technol 99:2488–2494. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2007.04.053
Townsend AT, Snape I (2008) Multiple Pb sources in marine sediments near the Australian Antarctic Station, Casey. Sci Total Environ 389:466–474. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.09.022
Wasley J (2004) The effect of climate change on Antarctic terrestrial flora. Ph.D. thesis, University of Wollongong
Webster G, Embley M, Prosser JI (2002) Grassland management regimens reduce small-scale heterogeneity and species diversity of proteobacterial ammonia oxidizer Populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:20–30. doi:10.1128/AEM.68.1.20-30.2002
Webster G, Newberry GJ, Fry JC, Weightman AJ (2003) Assessment of bacterial community structure in the deep sub-seafloor biosphere by 16S rDNA-based techniques: a cautionary tale. J Microbiol Methods 55:155–164. doi:10.1016/S0167-7012(03)00140-4
Xiao X, Li M, You Z, Wang F (2007) Bacterial communities inside and in the vicinity of the Chinese Great Wall Station, King George Island, Antarctica. Antarct Sci 19:11–16. doi:10.1017/S095410200700003X
Yergeau E, Bokhorst S, Huiskes AHL, Boschker HTS, Aerts R, Kowalchuk GA (2007) Size and structure of bacterial, fungal and nematode communities along an Antarctic environmental gradient. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 59:436–451. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2006.00200.x
Acknowledgments
This study was conducted under the auspices of the Malaysian Antarctic Research Programme, which is governed by the Academy of Sciences Malaysia. It was funded by the Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation and the University of Malaya (PPP: PS063-2007B). The Australian Antarctic Division supported the expedition to Casey Station where field guidance and laboratory facilities were provided for collection and storage of soil samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chong, C.W., Annie Tan, G.Y., Wong, R.C.S. et al. DGGE fingerprinting of bacteria in soils from eight ecologically different sites around Casey Station, Antarctica. Polar Biol 32, 853–860 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-009-0585-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-009-0585-6