Abstract
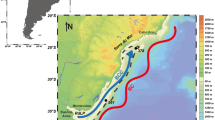
Eulerian time-series were completed at three sites on the south eastern shelf of the Sub-Antarctic Prince Edward Islands (PEI), from 9 to 27 April 2000, to investigate the spatial and temporal variability of mesozooplankton communities in relation to on-shelf hydrodynamics. Surface temperature and phytoplankton biomass were recorded daily at all three sites, while two Bongo net tows and vertical temperature profiles were collected daily at two sites. Contrary to predictions of on-shelf water retention at low ambient current velocities, cross-correlation analysis identified a northward advection of ∼8.23 cm s−1 over the study area. Day to day changes in both physical and biological parameters were associated with cross-shelf advection. However, sea temperature had a narrow range of 6.2–7.4°C, while average between sample Bray–Curtis similarity in zooplankton communities was high, exceeding 75%. The relatively consistent average sample biomass amounted to ∼494 tonnes dry weight of mesozooplankton per day being advected onto the south eastern sector of the PEI shelf. We hypothesise that the observed stability of both physical and biological parameters was due to the Sub-Antarctic Front, with its high volume transport and steep physical gradients, being far to the north of the islands. Spatial and temporal variability of hydrodynamics on the PEI shelf, and particularly its relationship to shifting frontal positions, is highlighted as a future research area necessary to quantify the gross delivery of allochthonous biomass to the PEI ecosystem.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansorge IJ, Lutjeharms JRE (2000) Twenty-five years of physical oceanographic research at the Prince Edward Islands. S Afr J Sci 96:557–566
Ansorge IJ, Lutjeharms JRE (2002) The hydrography and dynamics of the ocean environment of the Prince Edward Islands (Southern Ocean). J Mar Syst 37:107–127
Boden BP, Parker LD (1986) The plankton of the Prince Edward Islands. Polar Biol 5:81–93
Branch GM, Attwood CG, Gianakouras D, Branch ML (1993) Patterns in the benthic communities on the shelf of the sub-Antarctic Prince Edward Islands. Polar Biol 13:23–34
Brown CR (1989) Energy requirements and food consumption of Eudyptes penguins at the Prince Edward Islands. Antarct Sci 1:15–21
Brown CR, Klages NT, Adams NJ (1990) Short and medium-term variation in the diets of penguins at Marion Island. S Afr J Antarct Res 20:13–20
Clarke KR, Warwick RM (1994) Change in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation. Natural Environment Research Council, Cambridge
Condy PR (1981) Annual food consumption and seasonal fluctuations in biomass of seals at Marion Island. Mammalia 45:21–30
Deacon GER (1982) Physical and biological zonation in the Southern Ocean. Deep Sea Res A 29:14–15
Duncombe Rae CM (1989) Physical and chemical marine environment of the Prince Edward Islands (Southern Ocean) during April/May 1987. S Afr J Mar Sci 8:301–311
Hunt BPV (2000) Mesozooplankton community structure in the vicinity of the Prince Edward Islands (Southern Ocean) 37°50′E, 46°45′S. MSc thesis, Rhodes University, Grahamstown, 180pp
Hunt BPV, Pakhomov EA (2003) Mesozooplankton interactions with the shelf around the sub-Antarctic Prince Edward Island archipelago. J Plankton Res 25:885–904
Hunt BPV, Pakhomov EA, McQuaid CD (2001) Short-term variation and long-term changes in the oceanographic environment and zooplankton community in the vicinity of a sub-Antarctic archipelago. Mar Biol 138:369
Kaehler S, Pakhomov EA, Kalin RM, Davis S (2006) Trophic importance of kelp-derived suspended particulate matter in a through-flow sub-Antarctic system. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 316:17–22
Legendre P, Legendre L (1998) Numerical ecology: developments in ecological modelling. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 853 pp
Lutjeharms JRE (1985) Location of frontal systems between South Africa and Antarctica: some preliminary results. Deep Sea Res 32:1499–1509
Nowlin WD, Whitworth T, Pillsbury RB (1977) Structure and transport of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current at the Drake Passage from short-term measurements. J Phys Oceanogr 7:788–802
Pakhomov EA, Chown SL (2003) The Prince Edward Islands: Southern Ocean oasis. Ocean Yearb 17:348–379
Pakhomov EA, Froneman PW (1999) Macroplankton/micronekton dynamics in the vicinity of the Prince Edward Islands (Southern Ocean). Mar Biol 134:501–515
Pakhomov EA, Froneman PW, Kuun PJ, Balarin M (1999) Feeding dynamics and respiration of the bottom-dwelling caridean shrimp Nauticaris marionis Bate, 1888 (Crustacea: Decapoda) in the vicinity of Marion Island (Southern Ocean). Polar Biol 21:112–121
Pakhomov EA, Ansorge IJ, Froneman PW (2000a) Variability in the inter-island environment of the Prince Edward Islands (Southern Ocean). Polar Biol 23:593–603
Pakhomov EA, Hunt BPV, Gurney LJ (2000b) The fifth cruise of the Marion Island Oceanographic Survey (MIOS-V), April to May 2000. S Afr J Sci 96:541–543
Perissinotto R, Duncombe Rae CM (1990) Occurrence of anticyclonic eddies on the Prince Edward Plateau (Southern Ocean): effects on phytoplankton biomass and production. Deep Sea Res 37:777–793
Perissinotto R, McQuaid CD (1990) Role of the sub-Antarctic shrimp Nauticaris marionis in coupling benthic and pelagic food webs. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 64:81–87
Perissinotto R, McQuaid CD (1992) Land-based predator impact on vertically migrating zooplankton and micronekton advected to a Southern Ocean archipelago. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 80:15–27
Perissinotto R, Lutjeharms JRE, van Ballegooyen RC (2000) Biological–physical interactions determining the phytoplankton productivity in the vicinity of the Prince Edward Islands. J Mar Syst 24:327–341
Pyper BJ, Peterman RM (1997) Comparison of methods to account for autocorrelation in correlation analyses of fish data. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 55:2127–2140
Queiroga H, Almeida MJ, Alpuim T, Flores AAV, Francisco S, Gonzàlez-Gordillo I, Miranda AI, Silva I, Paula J (2006) Tide and wind control of megalopal supply to estuarine crab populations on the Portuguese west coast. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 307:21–36
Robertson AA, Alexander DGW, Miller DGM (1981) Modified collapsible opening and closing midwater trawls (RMT-8 and RMT-2). Fish Bull S Afr 14:103–113
Steele WK, Klages NT (1986) Diet of the blue petrel at sub-Antarctic Marion Island. S Afr J Zool 21:253–256
Wiebe PH (1970) Small-scale spatial distribution in oceanic zooplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 15:205
Williams AJ, Siegfried WR, Burger AI, Berruti A (1979) The Prince Edward Islands: a sanctuary for seabirds in the Southern Ocean. Biol Conserv 15:59–71
Zo Z (1978) Zooplankton spin splitter. Deep Sea Res 25:571–576
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the National Research Foundation (NRF) and the South African Department of Environmental Affairs and Tourism, through the South African National Antarctic Program (SANAP). We are grateful to Rhodes University, University of Fort Hare and the Department of Marine and Coastal Management for providing the equipment and facilities required for this study, the officers and crew of the MV “SA Agulhas”, and to all individuals who assisted in sample collection and Val Meaton for processing the zooplankton samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Table 5
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hunt, B.P.V., Gurney, L.J. & Pakhomov, E.A. Time-series analysis of hydrological and biological variability on the Prince Edward Island (Southern Ocean) shelf. Polar Biol 31, 893–904 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-008-0427-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-008-0427-y