Abstract
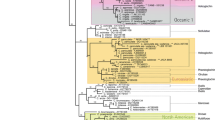
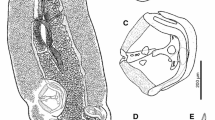
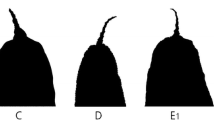
Isotoma klovstadi Carpenter, 1902 was one of the first Collembola described from the Antarctic continent. It was first collected in November 1899 during the British Antarctic Expedition on the north coast of Victoria Land in the Ross Sea region. It is now known to occur in an extensive area of northern Victoria Land, including the offshore Possession, Coulman, and Foyn Islands. More recently, I. klovstadi was moved to the genus Gnathisotoma Cassagnau, 1957 and has been included in this genus in an unpublished checklist (online) of all described Collembola. Here, we redescribe the species and use morphological and molecular (COI and 18S genes) evidence to investigate its affinities within the Isotominae. We show that it does not belong to Gnathisotoma, or Isotoma s. str. (the viridis group) as currently conceived, but is likely to be part of the species complex of Isotoma s. lat. We discuss reasons for placing it in the genus Desoria Nicolet, 1841. Our results reinforce the already high level of endemicity in the Antarctic fauna and emphasise the value of both morphological and molecular studies in examining relict Gondwanan taxa and their evolutionary relationships with those of other Southern Hemisphere continents.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ant.:
-
Antenna or antennal
- Abd.:
-
abdomen
- PAO:
-
postantennal organ
References
Avise JC (2004) Molecular markers, natural history and evolution, 2nd edn. Sinauer, Sunderland, pp 541
Bellinger PF, Christiansen KA, Janssens F (2004) Online checklist of the Collembola of the World (http://www.collembola.org)
Black WC, Klompen JSH, Kierans JE (1997) Phylogenetic relationships among tick subfamilies (Ixodida: Ixodidae: Argasidae) based on the 18S nuclear rDNA gene. Mol Phylogenet Evol 7:129–144
Carpenter G (1902) Aptera: Collembola, Insecta, chap 9. The report on the collections of natural history made in the Antarctic regions during the voyage of the Southern Cross. British Museum (Natural History), London, pp 221–223
Czarnetzki AB, Tebbe CC (2004) Diversity of bacteria associated with Collembola—a cultivation-independent survey based on PCR-amplified 16S rRNA genes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 49:217–227
Deharveng L (1981) Collemboles des Iles Subantarctiques de l’Ocean Indien. Comité National Français des Recherches Antartiques 48:33–109
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Fjellberg A (2003) Revision of six northern species of the Isotoma viridis Bourlet, 1839 complex (Collembola, Isotomidae). Nor J Entomol 50:91–98
Folmer O, Black M, Hoeh W, Lutz R, Vrijenhoek R (1994) DNA primers for the amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol 3:294–299
Frati F, Fanciulli PP, Carapelli A, Dallai R (1997a) The Collembola of northern Victoria Land Antarctica: distribution and ecological remarks. Pedobiologia 41:50–55
Frati F, Fanciulli PP, Carapelli A, DeCarlo L, Dallai R (1997b) Collembola of northern Victoria Land: distribution, population structure and preliminary molecular data to study origin and evolution of Antarctic Collembola. In: 3rd meeting on Antarctic biology, Santa Margherita Ligure, Italy, Camerino University Press, pp 321–330
Frati F, Carapelli A (1999) An assessment of the value of nuclear and mitochondrial genes in elucidating the origin and evolution of Isotoma klovstadi Carpenter (Insecta, Collembola). Antarct Sci 11:160–174
Frati F, Fanciulli PP, Carapelli A, Dell’ampio E, Nardi F, Spinsanti G, Dallai R (2000) DNA sequence analysis to study the evolution of Antarctic Collembola. Ital J Zool Suppl 1:133–139
Frati F, Spinsanti G, Dallai R (2001) Genetic variation of mtCOII gene sequences in the collembolan Isotoma klovstadi from Victoria Land, Antarctica: evidence for population differentiation. Polar Biol 24:934–940
Garrick RC, Sands CJ, Rowell DM, Tait NN, Greenslade P, Sunnucks P (2004) Phylogeography recapitulates topography: very fine-scale local endemism of a saproxylic ‘giant’ springtail at Tallaganda in the Great Dividing Range of south-east Australia. Mol Ecol 13:3329–3344
Giribet G, Ribera C (2000) A review of arthropod phylogeny: new data based on Ribosomal DNA sequences and direct character optimization. Cladistics 16:204–231
Greenslade P (1995) Collembola from the Scotia Arc and Antarctic Peninsula including descriptions of two new species and notes on biogeography. Pol Pismo Entomol 64:305–319
Hillis DM, Dixon MT (1991) Ribosomal DNA: molecular evolution and phylogenetic inference. Q Rev Biol 66:411–453
Hillis DM, Huelsenbeck JP (1992) Signal, noise, and reliability in molecular phylogenetic analyses. J Hered 83:189–195
Hogg ID, Hebert PDN (2004) Biological identification of springtails (Hexapoda: Collembola) from the Canadian Arctic, using mitochondrial DNA barcodes. Can J Zool 82:749–754
Hogg ID, Stevens MI (2002) Soil fauna of Antarctic coastal landscapes. In: Beyer L, Bölter M (eds) Geoecology of Antarctic ice-free coastal landscapes, vol 154. Ecological studies analysis and synthesis, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 265–278
Lockhart PJ, Steel MA, Hendy MD, Penny D (1994) Recovering evolutionary trees under a more realistic model of sequence evolution. Mol Biol Evol 11:605–612
Najt J (1981) Contribution a l’étude de la phylogenèse et de l’écomorphose chez les Isotoma: le sous-genera Gnathisotoma (Collembole, Isotomidae) et l’espéce-souche I. (Desoria) fjellbergi n. sp. Bulletin Museum Nationale d’Histoire Naturelle, Paris 4 Ser. 3:415–430
Otto JC, Wilson KJ (2001) Assessment of the usefulness of ribosomal 18S and mitochondrial COI sequences in Prostigmata phylogeny. In: Halliday RB, Walter DE, Proctor HC, Norton RA, Colloff MJ (eds) Acarology: proceedings of the 10th international congress, CSIRO publ., Melbourne, pp 100–109
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) Modeltest: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817–818
Potapov MB (1991) Species of the genus Isotoma subgenus Parisotoma Bagnall, 1940 and Sericeotoma subgen. nov. (Collembola, Isotomidae) of USSR fauna. Acta Zool Cracoviensia 34:267–301
Potapov M (2001) Synopses on Palaearctic Collembola: Isotomidae. Abhandlungen und Berichte des Naturkundemuseums Görlitz 73:1–603
Rounsevell DE (1978) Populations of introduced arthropods at Australian Antarctic stations. Pac Insects 18:199–202
Rusek J (2002) Do we have Cryptopygus—representatives (Collembola: Isotomidae) in Europe? Pedobiologia 46:302–310
Saiki RK, Gelfand DH, Stoffel S (1988) Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 239:487–491
Simon C, Frati F, Beckenback A, Crespi B, Liu H, Flook P (1994) Evolution, weighting, and phylogenetic utility of the mitochondrial gene sequences and a complilation of conserved polymerase chain reaction primers. Ann Entomol Soc Am 87:651–701
Simonsen V, Filser J, Krogh PH, Fjellberg A (1999) Three species of Isotoma (Collembola, Isotomidae) based on morphology, isozymes and ecology. Zool Scr 28:281–287
Soto-Adames FN (2002) Molecular phylogeny of the Puerto Rican Lepidocyrtus and Pseudosinella (Hexapoda: Collembola), a validation of Yoshii’s “color pattern species”. Mol Phylogenet Evol 25:27–42
Stevens MI, Hogg ID (2002) Expanded distributional records of Collembola and Acari in southern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Pedobiologia 46:485–496
Stevens MI, Hogg ID (2003) Long-term isolation and recent range expansion revealed for the endemic springtail Gomphiocephalus hodgsoni from southern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Mol Ecol 12:2357–2369
Stevens MI, Hogg ID (2006a) Molecular ecology of Antarctic terrestrial Invertebrates. In: Huiskes A, Convey P, Bergstrom D, (eds) Trends in Antarctic terrestrial and limnetic ecosystems. Kluwer (in press)
Stevens MI, Hogg ID (2006b) Contrasting levels of mitochondrial DNA variability between mites (Penthalodidae) and springtails (Hypogastruridae) from the Trans-Antarctic Mountains suggest long-term effects of glaciation and life history on substitution rates, and speciation processes. Soil Biol Biochem 38 (in press)
Stevens MI, Greenslade P, Hogg ID, Sunnucks P (2006) Southern Hemisphere springtails: could any have survived glaciation of Antarctica? Mol Biol Evol 23 (in press)
Sunnucks P, Hales DF (1996) Numerous transposed sequences of mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase I–II in aphids of the genus Sitobion (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Mol Biol Evol 13:510–524
Swofford DL (2002) PAUP* Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods), ver. 4.0b10. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
Yoshii R (1990) Report on the cryophilous Collembola , collected by Dr. S. Kohshima. Contributions from te Biological Laboraory, Kyotoa University 27:523–533
Wise KAJ (1967) Collembola (Springtails). Antarct Res Ser 10:123–148
Wise KAJ (1971) The Collembola of Antarctica. Pac Insects Monogr 25:57–74
Wise KAJ, Shoup J (1967) Distribution of Collembola at Cape Hallett. Antarct Res Ser 10:325–330
Wise KAJ, Shoup J (1971) Entomological investigations in Antarctica, 1964–1965 season. Pac Insects Monogr 25:27–56
Acknowledgements
We thank Ken Christiansen, Frans Janssens, and Francesco Frati for discussions that initiated this work, and to three anonymous reviewers for helpful comments on the manuscript. We are also indebted to Rod Seppelt, Allan Green, Catherine Beard, and Brent Sinclair for recent collections from Cape Hallett (1999–2004). Arctic collections were supported by an NSERC (Canada) operating grant to P.D.N. Hebert. We are also extremely grateful for logistic and/or financial support from David Penny, Bryan Gould, (University of Waikato Vice-Chancellor’s fund), Antarctica New Zealand, and Australian Antarctic Division (ASAC grants 2355, 2397).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stevens, M.I., Fjellberg, A., Greenslade, P. et al. Redescription of the Antarctic springtail Desoria klovstadi using morphological and molecular evidence. Polar Biol 29, 820–830 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-006-0120-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-006-0120-y